|
Albrecht Gessler
Albrecht Gessler, also known as Hermann, was a legendary 14th-century Habsburg bailiff (german: Landvogt) at Altdorf, whose brutal rule led to the William Tell rebellion and the eventual independence of the Old Swiss Confederacy. Legend According to the ''Chronicon Helveticum'' by Aegidius Tschudi (1505–1572), in 1307 Gessler raised a pole in the market square of Altdorf, Uri, Switzerland placed his hat atop it, and ordered all the townsfolk to bow before it. Tell, whose marksmanship and pride were legendary, publicly refused. Gessler's cruel wrath was tempered by his curiosity to test Tell's skill, so he gave Tell the option of either being executed or shooting an apple off his son's head in one try. Tell succeeded in splitting the apple with his arrow, saving his own life. When Gessler asked why he had readied two arrows, he lied and replied that it was out of habit. After being assured that he wouldn't be killed, Tell finally admitted that the second was intended for the ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Tell LCCN2003689314 (cropped)
William is a male given name of Germanic languages, Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will (given name), Will, Wills (given name), Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill (given name), Bill, and Billy (name), Billy. A common Irish people, Irish form is Liam. Scottish people, Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play Douglas (play)#Theme and response, ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma (given name), Wilma and Wilhelmina (given name), Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty's most prominent rulers – Frederick I (1155), Henry VI (1191) and Frederick II (1220) – ascended the imperial throne and also reigned over Italy and Burgundy. The non-contemporary name of 'Hohenstaufen' is derived from the family's Hohenstaufen Castle on the Hohenstaufen mountain at the northern fringes of the Swabian Jura, near the town of Göppingen. Under Hohenstaufen rule, the Holy Roman Empire reached its greatest territorial extent from 1155 to 1268. Name The name Hohenstaufen was first used in the 14th century to distinguish the 'high' (''hohen'') conical hill named Staufen in the Swabian Jura (in the district of Göppingen) from the village of the same name in the valley below. The new name was only applied to the hill ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agilaz
Egil is a legendary hero of the ''Völundarkviða'' and the '' Thidreks saga''. The name is from Proto-Germanic *Agilaz,https://web.archive.org/web/20110225031159/http://www.sofi.se/servlet/GetDoc?meta_id=1472 (archived link, 25 February 2011) and the same legend is reflected in Old English Ægil of the Franks Casket and Alamannic Aigil of the Pforzen buckle. The Proto-Germanic form of the legend may only be guessed at, but it appears likely that Egil was a renowned archer who defended a keep together with his wife Aliruna, against numerous attackers. The testimony of the Pforzen buckle is uncertain beyond naming ''Aigil'' and ''Ailrun'', possibly adding that they fought a battle at the Ilz river. The Franks Casket shows the scene of Aegil and his wife enclosed in the keep, with Aegil shooting arrows against attacking troops. ''Völundarkviða'' In the ''Völundarkviða'', Egil is a son of a Finn king, his elder brother being Slagfiðr, his younger one Völund. The three broth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Zürich
The canton of Zürich (german: Kanton Zürich ; rm, Chantun Turitg; french: Canton de Zurich; it, Canton Zurigo) is a Swiss canton in the northeastern part of the country. With a population of (as of ), it is the most populous canton in the country. Zürich is the ''de facto'' capital of the canton, but is not specifically mentioned in the constitution. The official language is German. The local Swiss German dialect, called '' Züritüütsch'', is commonly spoken. History Early history The prehistoric pile dwellings around Zürichsee comprise 11 of total 56 prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps in Switzerland, that are located around Lake Zürich in the cantons of Schwyz, St. Gallen and Zürich. Located on the shore of Lake Zürich, there are Freienbach–Hurden Rosshorn, Freienbach–Hurden Seefeld, Rapperswil-Jona/Hombrechtikon–Feldbach, Rapperswil-Jona–Technikum, Erlenbach–Winkel, Meilen–Rorenhaab, Wädenswil–Vorder Au, Zürich–Enge Alpenquai, Gross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grüningen
Grüningen is a town and municipality in the district of Hinwil in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, notable for its well-preserved historic nucleus. History Grüningen is first mentioned in 1243 as ''apud Gruningin''. The village of Itzikon was first mentioned in 837 as ''in Izinheimo'' and Binzikon was mentioned in 854 as ''in willa Pinuzzinhovun''. In the Strangenholz area of the municipality, burial mounds from a Hallstatt era population have been found. The Alamannic settlement dates to c. the 8th century, based on 9th-century records of Itzikon and Binzikon. Grüningen castle was built from the early 13th century, most likely by the counts of Rapperswil, who acted as reeves for Einsiedeln Abbey. Grüningen is recorded as a possession of Einsiedeln during 1217–1222. Around 1230, Grüningen passed from Einsiedeln to the Abbey of Saint Gall and was at first given as a fief to the counts of Kyburg, and in 1253 to Lütold VI, head of the baronial Regensberg fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
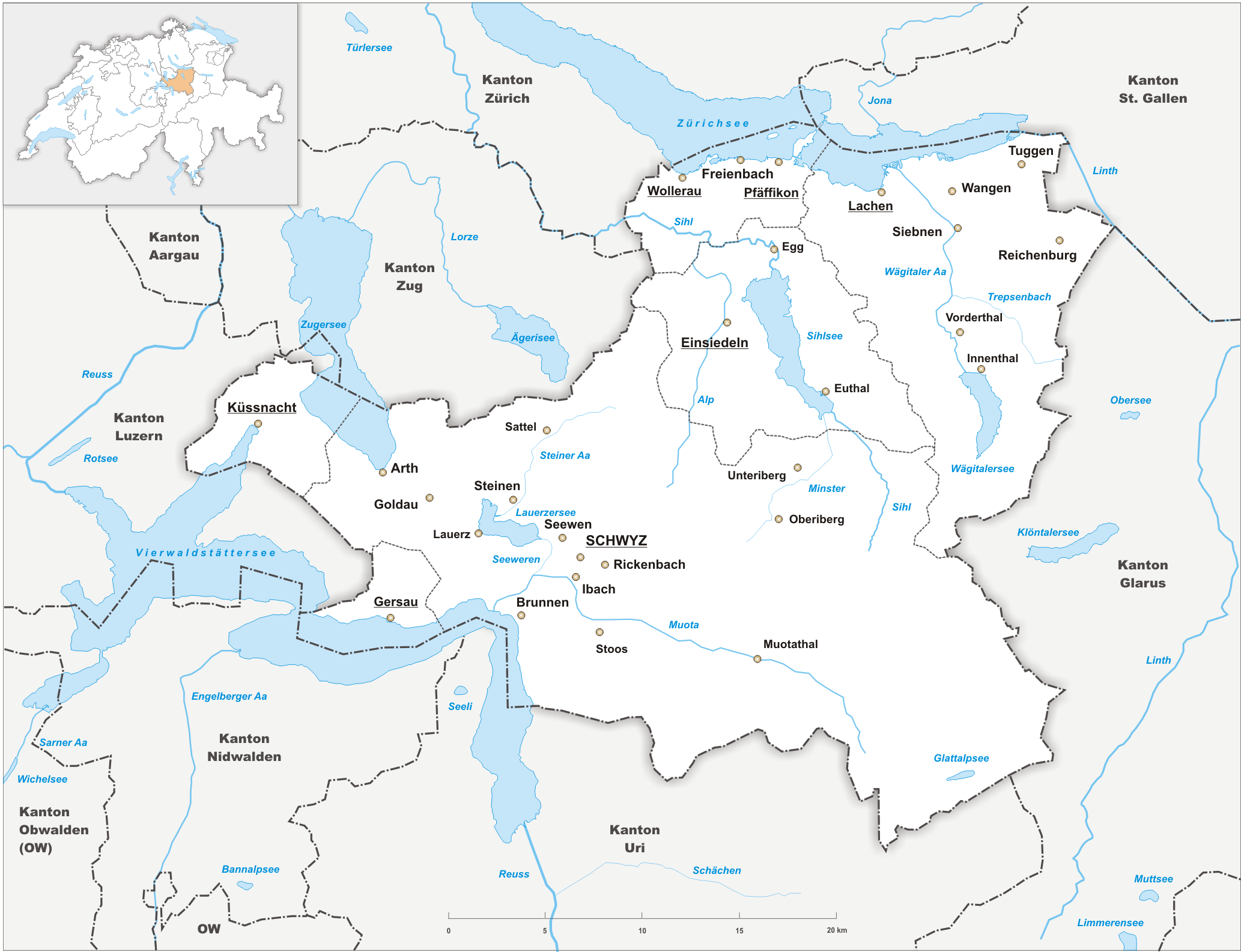
Canton Of Schwyz
The canton of Schwyz (german: Kanton Schwyz rm, Chantun Sviz; french: Canton de Schwytz; it, Canton Svitto) is a canton in central Switzerland between the Alps in the south, Lake Lucerne to the west and Lake Zürich in the north, centred on and named after the town of Schwyz. It is one of the founding cantons of Switzerland; Switzerland's name is derived from the name of the canton, and the flag of Switzerland from its coat of arms. For the history of the name, see Schwyz. The Swiss Federal Charter is on display in Schwyz. Northeast of the town of Schwyz is Einsiedeln Abbey. History Prehistory to the Roman era The earliest traces of humans in Schwyz are from the Upper Paleolithic and Early Mesolithic, or about 12,500 BC. An excavation of the karst caves in the valley of the Muota river (''Muotatal'') revealed numerous sites, some dating to the Younger Dryas period (c. 10,000 BC). The alpine meadows at Bödmeren, Twärenen and Silberen were Stone Age hunter-gatherer camps. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advocatus
During the Middle Ages, an (sometimes given as modern English: advocate; German: ; French: ) was an office-holder who was legally delegated to perform some of the secular responsibilities of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as an abbey. Many such positions developed, especially in the Holy Roman Empire. Typically, these evolved to include responsibility for aspects of the daily management of agricultural lands, villages and cities. In some regions, advocates were governors of large provinces, sometimes distinguished by terms such as (in German). While the term was eventually used to refer to many types of governorship and advocacy, one of the earliest and most important types of was the church advocate (). These were originally lay lords, who not only helped defend religious institutions in the secular world, but were also responsible for exercising lordly responsibilities within the church's lands, such as the handling of legal cases which might require the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Book Of Sarnen
The ''White Book of Sarnen'' (german: Weisses Buch von Sarnen) is a collection of medieval manuscripts compiled in the late 15th century by Hans Schriber, state secretary (''Landschreiber'') in the Swiss Confederation canton Obwalden. This volume, 258 pages in length, was given its name because of the white parchment in which it is bound. The White Book of Sarnen contains the earliest surviving reference to the Swiss national hero William Tell. Composition and structure The ''White Book of Sarnen'' was composed in 1474 by a country scribe called Hans Schriber.Bergier, p 63. Schriber’s book consists of two parts. The longer first part contains seventy-seven different documents that Schriber copied from original documents stored in the archives of Sarnen.Johnson, p 428. To this documentary section, Schriber added a brief report on the early history of the Old Swiss Confederacy.Bergier, p 63. This second part, 25 pages in length, makes mention of the Rütli oath ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
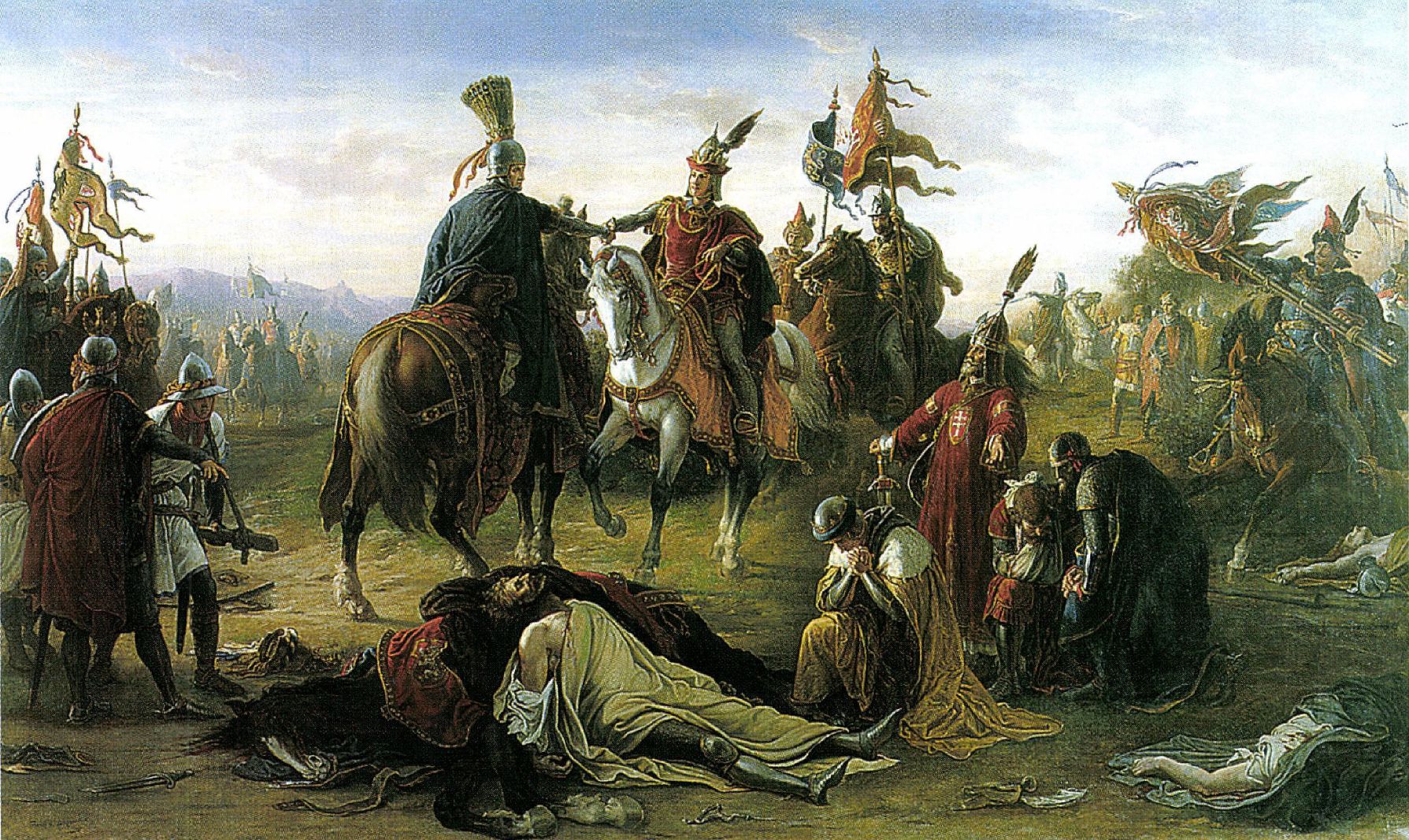
Battle On The Marchfeld
The Battle on the Marchfeld (''i.e. Morava Field''; german: Schlacht auf dem Marchfeld; cs, Bitva na Moravském poli; hu, Morvamezei csata) at Dürnkrut and Jedenspeigen took place on 26 August 1278 and was a decisive event for the history of Central Europe for the following centuries. The opponents were a Bohemian (Czech) army led by the Přemyslid king Ottokar II of Bohemia and the German army under the German king Rudolph I of Habsburg in alliance with King Ladislaus IV of Hungary. With 15,300 mounted troops, it was one of the largest cavalry battles in Central Europe during the Middle Ages. The Hungarian cavalry played a significant role in the outcome of the battle. King Ottokar II of Bohemia expanded his territories considerably from 1250 to 1273, but suffered a devastating defeat in November 1276, when the newly elected German king Rudolph I of Habsburg imposed the Imperial ban on Ottokar, declaring him an outlaw and took over Ottokar's holdings in Austria, Carinthia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottokar II Of Bohemia
Ottokar II ( cs, Přemysl Otakar II.; , in Městec Králové, Bohemia – 26 August 1278, in Dürnkrut, Lower Austria), the Iron and Golden King, was a member of the Přemyslid dynasty who reigned as King of Bohemia from 1253 until his death in 1278. He also held the titles of Margrave of Moravia from 1247, Duke of Austria from 1251, and Duke of Styria from 1260, as well as Duke of Carinthia and landgrave of Carniola from 1269. With Ottokar's rule, the Přemyslids reached the peak of their power in the Holy Roman Empire. His expectations of the imperial crown, however, were never fulfilled. Ottokar was the second son of King Wenceslaus I of Bohemia (reigned 1230–1253). Through his mother, Kunigunde, daughter of Philip of Swabia, he was related to the Holy Roman Emperors of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, which became extinct in the male line upon the execution of King Conradin of Sicily in 1268. Named after his grandfather King Přemysl Ottokar I, he was originally educate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Styria
The Duchy of Styria (german: Herzogtum Steiermark; sl, Vojvodina Štajerska; hu, Stájer Hercegség) was a duchy located in modern-day southern Austria and northern Slovenia. It was a part of the Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806 and a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary until its dissolution in 1918. History It was created by Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in 1180 when he raised the March of Styria to a duchy of equal rank with neighbouring Carinthia and Bavaria, after the fall of the Bavarian duke Henry the Lion earlier that year. Margrave Ottokar IV thereby became the first Duke of Styria and also the last of the ancient Otakar dynasty. As Ottokar had no issue, he in 1186 signed the Georgenberg Pact with the mighty House of Babenberg, rulers of Austria since 976, after which both duchies should in perpetuity be ruled in personal union. Upon his death in 1192, Styria as stipulated fell to the Babenberg duke Leopold V of Austria. The Austrian Babenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)