|
Albert IV, Count Of Habsburg
Albert IV (or Albert the Wise) (c. 1188 – December 13, 1239) was Count of Habsburg in the Aargau and a progenitor of the royal House of Habsburg. He was the son of Count Rudolph II of Habsburg and Agnes of Staufen. About 1217, Albert married Hedwig (Heilwig), daughter of Count Ulrich of Kyburg (died 1237) and Anna of Zähringen. He was present at the signing of the Golden Bull of Rimini in March 1226. Upon the death of his father in 1232, he divided his family's estates with his brother Rudolph III, whereby he retained the ancestral seat at Habsburg Castle. A follower of Emperor Frederick II of Hohenstaufen, he took part in the Barons' Crusade of 1239 with King Theobald I of Navarre and died near Ashkelon. Albert was the father of King Rudolf I of Germany Rudolf I (1 May 1218 – 15 July 1291) was the first King of Germany from the House of Habsburg. The first of the count-kings of Germany, he reigned from 1273 until his death. Rudolf's election marked the end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Habsburg, french: Maison des Habsbourg and also known as the House of Austriagerman: link=no, Haus Österreich, ; es, link=no, Casa de Austria; nl, Huis van Oostenrijk, pl, dom Austrii, la, Domus Austriæ, french: Maison d'Autriche; hu, Ausztria Háza; it, Casa d'Austria; pt, Casa da Áustria is one of the most prominent and important dynasties in European history. The house takes its name from Habsburg Castle, a fortress built in the 1020s in present-day Switzerland by Radbot of Klettgau, who named his fortress Habsburg. His grandson Otto II was the first to take the fortress name as his own, adding "Count of Habsburg" to his title. In 1273, Count Radbot's seventh-generation descendant Rudolph of Habsburg was elected King of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
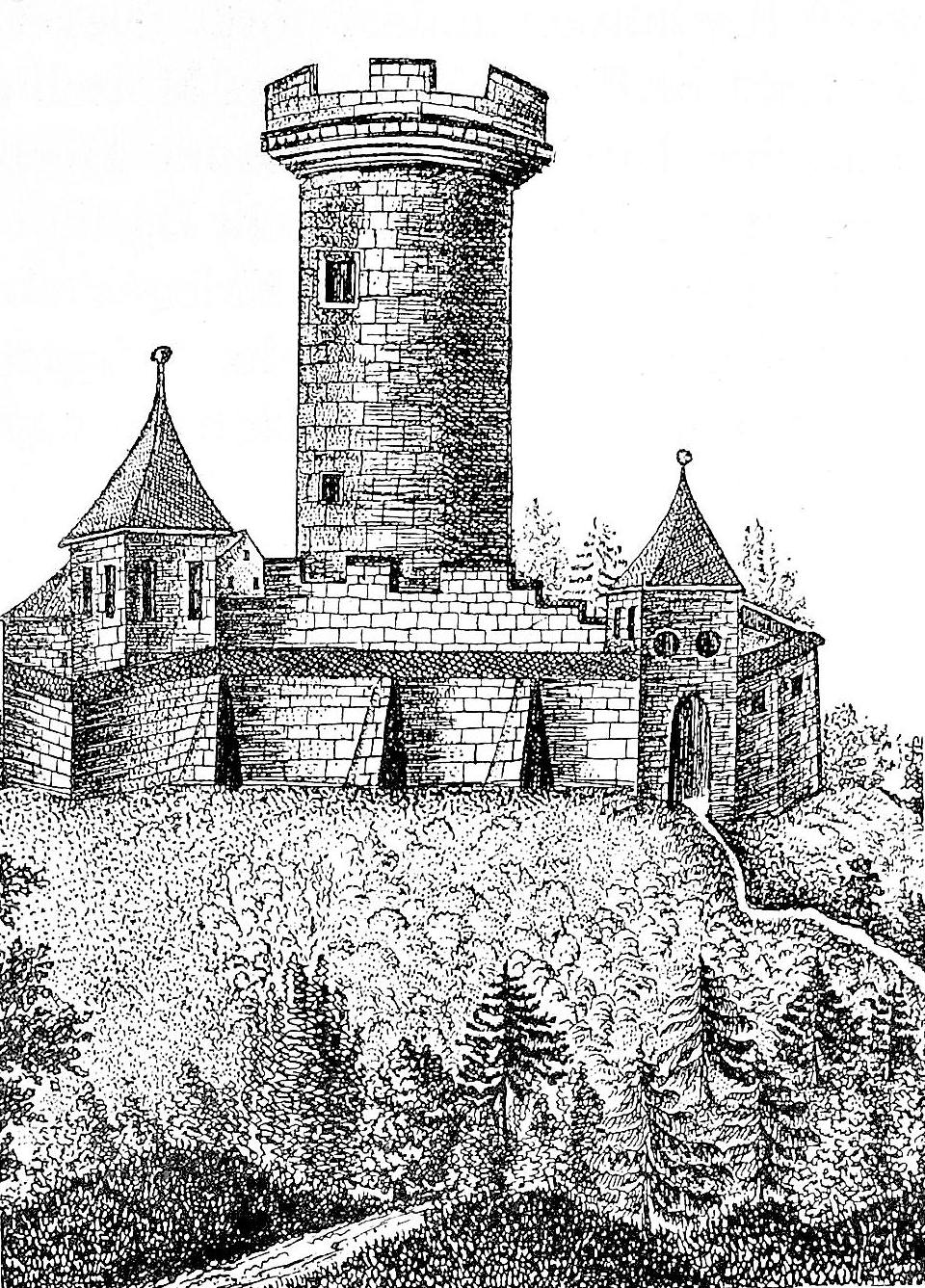
Habsburg Castle
Habsburg Castle (german: Schloss Habsburg, ) is a medieval fortress located in what is now Habsburg, Switzerland, in the canton of Aargau, near the Aar River. At the time of its construction, the location was part of the Duchy of Swabia. Habsburg Castle is the original seat of the House of Habsburg, which became one of the leading imperial and royal dynasties in Europe. It is listed as a Swiss heritage site of national significance. History The castle was built around 1020 by Count Radbot, of the nearby county of Klettgau in the Duchy of Swabia, and Werner, Bishop of Strasbourg. They had the castle erected 35 km southwest of Klettgau, on the Aar, the largest tributary of the High Rhine. It is believed that he named the castle after a hawk (german: Habicht) seen sitting on its walls. Some historians and linguists believe the name may come from the Middle High German word ''hab''/''hap'' meaning ford, as it is located near a ford of the Aar River. The name of "Habsburg" w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1180s Births
118 may refer to: *118 (number) *AD 118 *118 BC *118 (TV series) *118 (film) *118 (Tees) Corps Engineer Regiment *118 (Tees) Field Squadron, Royal Engineers See also *11/8 (other) *Oganesson, synthetic chemical element with atomic number 118 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christians Of The Barons' Crusade
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χριστός), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term ''mashiach'' (מָשִׁיחַ) (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." It does not have a meaning of 'of Christ' or 'related or pertaining to Christ'. According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts Of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Habsburg, french: Maison des Habsbourg and also known as the House of Austriagerman: link=no, Haus Österreich, ; es, link=no, Casa de Austria; nl, Huis van Oostenrijk, pl, dom Austrii, la, Domus Austriæ, french: Maison d'Autriche; hu, Ausztria Háza; it, Casa d'Austria; pt, Casa da Áustria is one of the most prominent and important dynasties in European history. The house takes its name from Habsburg Castle, a fortress built in the 1020s in present-day Switzerland by Radbot of Klettgau, who named his fortress Habsburg. His grandson Otto II was the first to take the fortress name as his own, adding "Count of Habsburg" to his title. In 1273, Count Radbot's seventh-generation descendant Rudolph of Habsburg was elected King of the Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph III, Count Of Habsburg
Rudolph or Rudolf may refer to: People * Rudolph (name), the given name including a list of people with the name Religious figures * Rudolf of Fulda (died 865), 9th century monk, writer and theologian * Rudolf von Habsburg-Lothringen (1788–1831), Archbishop of Olomouc and member of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine Royalty and nobility *Rudolph I (other) * Rudolph II (other) *Rudolph III (other) * Rudolph of France (died 936) * Rudolph I of Germany (1218–1291) * Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor (1552–1612) * Rudolph, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst (1576–1621) * Rudolf, Crown Prince of Austria (1858–1889), son and heir of Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria and Empress Elisabeth of Austria (died at Mayerling) Places * Rudolph Glacier, Antarctica * Rudolph, South Dakota, US * Rudolph, Wisconsin, US, a village * Rudolph (town), Wisconsin, adjacent to the village * Rudolf Island, northernmost island of Europe * Lake Rudolf, now Lake Turkana, in Kenya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theobald I Of Navarre
Theobald I (french: Thibaut, es, Teobaldo; 30 May 1201 – 8 July 1253), also called the Troubadour and the Posthumous, was Count of Champagne (as Theobald IV) from birth and King of Navarre from 1234. He initiated the Barons' Crusade, was famous as a trouvère, and was the first Frenchman to rule Navarre. Rule of Champagne Regency of Champagne Born in Troyes, he was the son of Theobald III of Champagne and Blanche of Navarre, the youngest daughter of Sancho VI of Navarre. His father died less than a week before he was born, and Blanche ruled the county as regent until Theobald turned twenty-one in 1222. He was a notable trouvère, and many of his songs have survived, including some with music. The first half of Theobald's life was plagued by a number of difficulties. His uncle, Count Henry II, had left behind a great deal of debt, which was far from paid off when Theobald's father died. Further, Theobald's right to the succession was challenged by Henry's daughter Philippa an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barons' Crusade
The Barons' Crusade (1239–1241), also called the Crusade of 1239, was a crusade to the Holy Land that, in territorial terms, was the most successful crusade since the First Crusade. Called by Pope Gregory IX, the Barons' Crusade broadly embodied the highest point of papal endeavor "to make crusading a universal Christian undertaking." Gregory IX called for a crusade in France, England, and Hungary with different degrees of success. Although the crusaders did not achieve any glorious military victories, they used diplomacy to successfully play the two warring factions of the Ayyubid dynasty ( as-Salih Ismail in Damascus and as-Salih Ayyub in Egypt) against one another for even more concessions than Frederick II had gained during the more well-known Sixth Crusade. For a few years, the Barons' Crusade returned the Kingdom of Jerusalem to its largest size since 1187. This crusade to the Holy Land is sometimes discussed as two separate crusades: that of King Theobald I of Nav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick II Of Hohenstaufen
Frederick II (German: ''Friedrich''; Italian: ''Federico''; Latin: ''Federicus''; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusalem from 1225. He was the son of emperor Henry VI of the Hohenstaufen dynasty and Queen Constance of Sicily of the Hauteville dynasty. His political and cultural ambitions were enormous as he ruled a vast area, beginning with Sicily and stretching through Italy all the way north to Germany. As the Crusades progressed, he acquired control of Jerusalem and styled himself its king. However, the Papacy became his enemy, and it eventually prevailed. Viewing himself as a direct successor to the Roman emperors of antiquity, he was Emperor of the Romans from his papal coronation in 1220 until his death; he was also a claimant to the title of King of the Romans from 1212 and unopposed holder of that monarchy from 1215. As such, he was King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Bull Of Rimini
The Golden Bull of Rimini was a decree issued by Emperor Frederick II in Rimini in March 1226 that granted and confirmed the privilege of territorial conquest and acquisition for the Teutonic Order in Prussia. According to historian Tomasz Jasiński, the bull was backdated and had actually been issued in 1235. It represents the first of a series of three documents, that include the Treaty of Kruschwitz of 1230 and the Papal Golden Bull of Rieti of 1234. Background The Piast duke Konrad I of Masovia had since 1209 engaged in several military campaigns against the pagan Old Prussians. In 1217 Pope Honorius III authorized bishop Christian of Oliva to designate these conquests as the Prussian Crusade. In 1222/23 Konrad attempted to subdue the Prussian territories of the Culmer Land east of the Vistula River. Backed by his Polish cousins Leszek I the White and Henry I the Bearded, he initially was successful, but was eventually confronted with relentless Prussian counter attacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph II, Count Of Habsburg
Rudolph II (or Rudolph the Kind) (died 10 April 1232) was Count of Habsburg in the Aargau and a progenitor of the royal House of Habsburg. He was the only son of Count Albert III of Habsburg and Ita of Pfullendorf. He married Agnes of Staufen. Rudolph was the father of Count Albert IV of Habsburg and Count Rudolph III of Habsburg and the grandfather of King Rudolph I of Germany Rudolf I (1 May 1218 – 15 July 1291) was the first King of Germany from the House of Habsburg. The first of the count-kings of Germany, he reigned from 1273 until his death. Rudolf's election marked the end of the Great Interregnum which h .... {{DEFAULTSORT:Rudolph 02, Count of Habsburg Counts of Habsburg 1232 deaths Year of birth unknown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Zähringen
The House of Zähringen (german: Zähringer) was a dynasty of Swabian nobility. The family's name derived from Zähringen Castle near Freiburg im Breisgau. The Zähringer in the 12th century used the title of Duke of Zähringen, in compensation for having conceded the title of Duke of Swabia to the Staufer in 1098. The Zähringer were granted the special title of Rector of Burgundy in 1127, and they continued to use both titles until the extinction of the ducal line in 1218. The territories and fiefs held by the Zähringer were known as the 'Duchy of Zähringen' (), but it was not seen as a duchy in equal standing with the old stem duchies. The Zähringer attempted to expand their territories in Swabia and Burgundy into a fully recognized duchy, but their expansion was halted in the 1130s due to their feud with the Welfs. Pursuing their territorial ambitions, the Zähringer founded numerous cities and monasteries on either side of the Black Forest, as well as in the western S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |