|
Albanian Royal Army
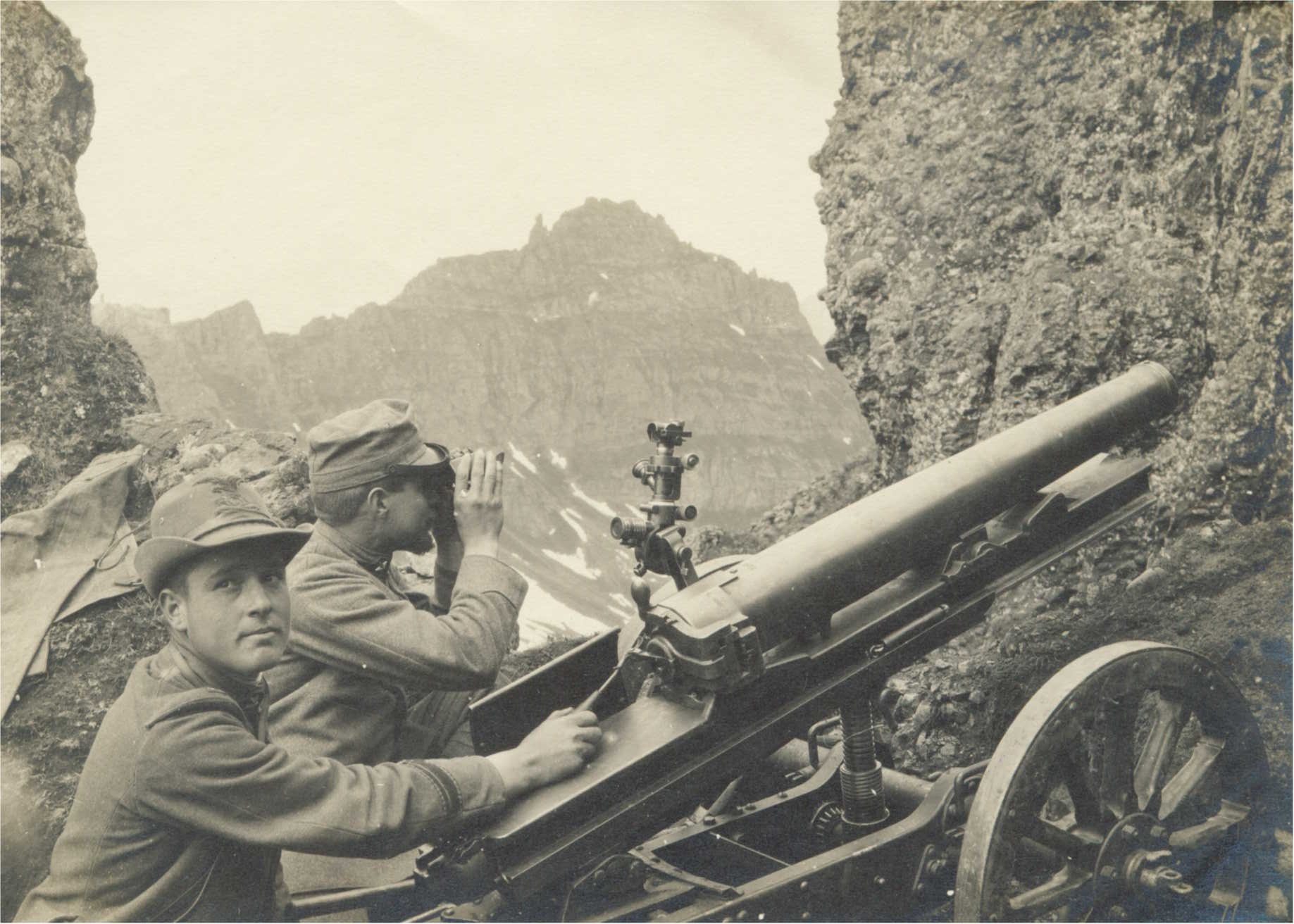
The Royal Albanian Army () was the army of the Albanian Kingdom and King Zog I of the Albanians from 1928 until 1939. Its commander-in-chief was King Zog; its commander General Xhemal Aranitasi; its Chief of Staff was General Gustav von Myrdacz. The army was mainly financed by Italy from 1936 to 1939. List of weapons Artillery * Type 41 75 mm Mountain Gun *Skoda 75 mm Model 1928 *Cannone da 65/17 modello 13 Machine Guns * Schwarzlose MG M.07/12 *Vickers machine gun *Maxim gun Guns * Carcano M1891 *Mannlicher–Schönauer *Mauser M1893 * Mosin–Nagant Pistols * Glisenti Model 1910 Manpower and Equipment Army *78,000 officers + 1,320,000 soldiers + 1,620 NCOs *Around 4,396,000 conscripts (1939) *9 military districts *12,000 infantry battalions *2,000 motorized infantry squadrons *900 engineering companies *12,000 tribal officers + 2,986,000 tribal militia *2,970,000 carbines (Carcano M1891, Mannlicher, Mosin) *1,110,400 revolvers (Glisenti M1889) *2,319,600 rifles (B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Infantry Of Albania
The Royal Albanian Infantry ({{sq, Forcat Mbretërore e Këmbsorisë) was from 1928 till 1939 and was part of the Royal Albanian Army The Royal Albanian Army () was the army of the Albanian Kingdom and King Zog I of the Albanians from 1928 until 1939. Its commander-in-chief was King Zog; its commander General Xhemal Aranitasi; its Chief of Staff was General Gustav von Myrdacz .... Structure The original plan was for the army to have three "infantry groups"(="Grupit Këmbsorisë"), each of three infantry battalions, three mountain batteries (2 x 65mm L/17), an engineer company and supporting elements such as transport, logistics and signals. Grupit I seems to have never been formed, but Grupit II and Grupit III did exist before 1939, both headquartered at Tiranë. Apparently these were no longer constituted on April 7, and the former commander of Grupit II had by that date become commander of Zona I. In 1939 only seven of the nine planned infantry battalions were activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Ranks Of The Albanian Kingdom
The Military ranks of the Albanian Kingdom were the military ranks used by the Royal Albanian Army. Throughout its short history, the Albanian Kingdom (1928–39), Albanian Kingdom had two ranks systems. The first rank system lasting from 1929 till 1936, with the second lasting till the end of the kingdom in 1939. Ranks (1929–1936) ;Officers ;Other ranks Ranks (1936–1939) ;Officers ;Other ranks References External links * {{Military ranks by country Military ranks by country, Albanian Kingdom Royal Albanian Army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
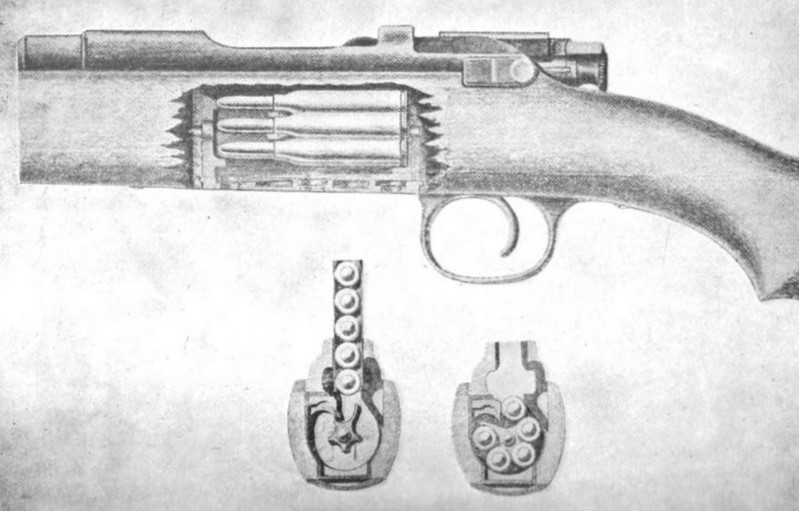
Mosin–Nagant
The Mosin–Nagant is a five-shot, bolt-action, internal magazine–fed military rifle. Known officially as the 3-line rifle M1891 and informally in Russia and former Soviet Union as Mosin's rifle ( ru , винтовка Мосина, ISO 9: ), it is primarily found chambered for its original 7.62×54mmR cartridge. Developed from 1882 to 1891, it was used by the armed forces of the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union and various other states. It is one of the most mass-produced military bolt-action rifles in history, with over 37 million units produced since 1891. In spite of its age, it has been used in various conflicts around the world up to the present day. History Initial design and tests During the Russo-Ottoman War of 1877–1878, Russian troops armed mostly with Berdan single-shot rifles suffered heavy casualties against Turkish troops equipped with Winchester repeating rifles, particularly at the bloody Siege of Pleven. This showed Russian commanders the need to mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauser M1893
The Mauser Model 1893 is a bolt-action rifle commonly referred to as the Spanish Mauser, though the model was adopted by other countries in other calibers, most notably the Ottoman Empire. The M1893 was based on the experimental M1892 rifle, which Paul Mauser developed for the Spanish Army as part of a program to correct deficiencies in the earlier 1889, 1890, and 1891 series of Mauser rifles. The M1893 introduced a short staggered-column box magazine that fit flush with the bottom of the stock; the magazine held five smokeless 7×57mm Mauser rounds, which could be reloaded quickly by pushing a stripper clip from the top of the open bolt. The M1893 was developed into several variants, including a shortened carbine adopted by the Spanish as the M1895, and as the M1913 and M1916 short rifles. All versions of the rifle saw extensive service in the Spanish Army, beginning in the Spanish–American War in 1898, the Rif War of 1920–1927, and the Spanish Civil War of 1936–1939. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannlicher–Schönauer
The Mannlicher–Schönauer (sometimes Anglicized as "Mannlicher Schoenauer", Hellenized as Τυφέκιον/Όπλον Μάνλιχερ, ''Óplon/Tyfékion Mannlicher'') is a rotary-magazine bolt-action rifle produced by Steyr Mannlicher for the Greek Army in 1903 and later used in small numbers by the Austro-Hungarian Army. Post-war it was sold for civilian use. Design characteristics In the late 19th century, the classic Mannlicher designs for the Austro-Hungarian army like the M1886 were based on the en-bloc magazine, a straight-pull bolt mechanism, designed for obsolete large caliber cartridges. Following the introduction of smokeless powder in the Lebel rifle at the end of the century, the Steyr factory worked on new Mannlicher designs, using more effective modern cartridges. These were offered for the consideration of the Austro-Hungarian Army, for export to other armies and for to civilian market. The rifle action was designed by Ferdinand Mannlicher and the rotary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcano
Carcano is the frequently used name for a series of Italian bolt-action, magazine-fed, repeating military rifles and carbines. Introduced in 1891, this rifle was chambered for the rimless 6.5×52mm Carcano round (''Cartuccia Modello 1895''). It was developed by the chief technician Salvatore Carcano at the Turin Army Arsenal in 1890, and was originally called the Modello (model) 91 or simply M91. Successively replacing the previous Vetterli-Vitali rifles and carbines in 10.35×47mmR, it was produced from 1891 to 1945. The M91 was used in both rifle (''fucile'') and shorter-barreled carbine (''moschetto'') form by most Italian troops during World War I and by Italian and some German forces during World War II. The rifle was also used during the Winter War by Finland, and again by regular and irregular forces in Syria, Libya, Tunisia and Algeria during various postwar conflicts in those countries. The Type I Carcano rifle was produced by Italy for the Japanese Empire prior to Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxim Gun
The Maxim gun is a recoil-operated machine gun invented in 1884 by Hiram Stevens Maxim. It was the first fully automatic machine gun in the world. The Maxim gun has been called "the weapon most associated with imperial conquest" by historian Martin Gilbert, and was heavily used by colonial powers during the "Scramble for Africa". Afterwards, Maxim guns also saw extensive usage by different armies during the Russo-Japanese War, the First and Second World Wars, as well as by insurgent groups in contemporary conflicts. The Maxim gun was greatly influential in the development of machine guns, and it has multiple variants and derivatives. Design The Maxim gun featured one of the earliest recoil-operated firing systems in history. Energy from recoil acting on the breech block is used to eject each spent cartridge and insert the next one. Maxim's earliest designs used a 360-degree rotating cam to reverse the movement of the block, but this was later simplified to a toggle lock. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Machine Gun
The Vickers machine gun or Vickers gun is a Water cooling, water-cooled .303 British (7.7 mm) machine gun produced by Vickers Limited, originally for the British Army. The gun was operated by a three-man crew but typically required more men to move and operate it: one fired, one fed the ammunition, the others helped to carry the weapon, its ammunition, and spare parts. It was in service from before the First World War until the 1960s, with air-cooled versions of it on many Allies of World War I, Allied World War I fighter aircraft. The weapon had a reputation for great solidity and reliability. Ian V. Hogg, in ''Weapons & War Machines'', describes an action that took place in August 1916, during which the British 100th Company of the Machine Gun Corps fired their ten Vickers guns to deliver sustained fire for twelve hours. Using 100 barrels, they fired a million rounds without breakdowns. "It was this absolute foolproof reliability which endeared the Vickers to every Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwarzlose MG M (1867-1936), a Prussian firearms designer
{{disambig, surname ...
Schwarzlose may refer to: Firearms * Schwarzlose MG M.07/12, an Austro-Hungarian medium machine gun *Schwarzlose Model 1898, a German semi-automatic pistol *Schwarzlose Model 1908, a German semi-automatic pistol featuring a "blow-forward" action People *Andreas Wilhelm Schwarzlose Andreas Wilhelm Schwarzlose (31 July 1867 – 1936) was a German (originally Prussian) firearm designer who is best known for designing a blowback-operated machine gun. Early life Schwarzlose was born near Wust, and served as an artilleryman and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannone Da 65/17 Modello 13
The cannone da 65/17 modello 13 was an artillery piece developed by Italy for use with its mountain and infantry units. The designation means 65 mm calibre gun, barrel length 17 calibres, which entered service in 1913. The designation is often shortened to cannone da 65/17. Description A lightweight design, the 65 mm gun was designed for use in difficult terrain and extreme weather conditions. The barrel had a 17 calibre length, and was designed for firing low-trajectory shots. The carriage was likewise simple in nature, consisting of a single trailing arm and solid-rim spoked wheels for horse draft. The weapon could be broken-down into five loads for transport. A simple folding gun shield was also provided in 1935. History The 65 mm gun was first accepted into service with Italian mountain troops in 1913, and it served with them throughout World War I. It was used in the Fiat 2000 heavy tank which saw action in Libya. Replacements arrived in the 1920s and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skoda 75 Mm Model 1928
The Skoda 75 mm Model 1928 (75 mm M.28) was a mountain gun manufactured by Skoda Works and exported to Yugoslavia. It was a modernized version of the Skoda 75 mm Model 15. The gun typically had a 75 mm barrel; however, it could be fitted with a 90 mm barrel. The Wehrmacht redesignated these guns as 7.5 cm GebK 28 (in Einheitslafette mit 9 cm GebH) or 7.5 cm GebK 285(j). The gun crew was protected by an armoured shield A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of a .... References * Chamberlain, Peter and Gander, Terry. ''Infantry, Mountain and Airborne Guns'' * Gander, Terry and Chamberlain, Peter. ''Weapons of the Third Reich: An Encyclopedic Survey of All Small Arms, Artillery and Special Weapons of the German Land Forces 1939-1945''. New York: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.jpg)
