|
Alba Augusta
Alba-la-Romaine (; oc, Aps) is a commune in the Ardèche department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of southern France. The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Albains'' or ''Albaines'' Geography ''Alba-la-Romaine'' is located some 5 km west of Montelimar on a mountain ridge overlooking the Rhone river valley. The commune can be accessed on Highway N102 running west from Le Teil and through the northern part of the commune and continuing west to Saint-Jean-le-Centenier. Local Road D253 enters the commune from Sceautres in the north and runs south crossing the N102 before continuing to the village of Alba-la-Romaine and then continuing south to Valvigneres. Another district road the D107 commences from the village and goes south to Saint-Thome. There is an extensive network of small country roads throughout the commune. There are extensive areas of farmland in the commune especially following the ridge line from north to south as well as steep mountain sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helvii
The Helvii (also Elui, ancient Greek Ἑλουοί) were a relatively small Celtic polity west of the Rhône river on the northern border of Gallia Narbonensis. Their territory was roughly equivalent to the Vivarais, in the modern French department of Ardèche. Alba Helviorum was their capital, possibly the Alba Augusta mentioned by Ptolemy, and usually identified with modern-day Alba-la-Romaine (earlier Aps). In the 5th century the capital seems to have been moved to Viviers. From the mid-2nd to mid-1st century BC, Helvian territory was on the northern border of the Roman province of Gallia Transalpina (later the Narbonensis). As a border people, the Helvii played a crucial if limited role in the Gallic Wars under the leadership of Gaius Valerius Caburus, who had held Roman citizenship since 83 BC, and his sons Troucillus and Domnotaurus. Julius Caesar calls the Helvii a ''civitas,'' a polity with at least small-scale urban centers ('' oppida''), and not a ''pagus'' ("sub-tribe") ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cultural practices. There existed several different types of citizenship, determined by one's gender, class, and political affiliations, and the exact duties or expectations of a citizen varied throughout the history of the Roman Empire. History The oldest document currently available that details the rights of citizenship is the Twelve Tables, ratified c. 449 BC. Much of the text of the Tables only exists in fragments, but during the time of Ancient Rome the Tables would be displayed in full in the Roman Forum for all to see. The Tables detail the rights of citizens in dealing with court proceedings, property, inheritance, death, and (in the case of women) public behavior. Under the Roman Republic, the government conducte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allobroges
The Allobroges (Gaulish: *''Allobrogis'', 'foreigner, exiled'; grc, Ἀλλοβρίγων, Ἀλλόβριγες) were a Gallic people dwelling in a large territory between the Rhône river and the Alps during the Iron Age and the Roman period. The Allobroges came relatively late to Gaul compared to most other tribes of Gallia Narbonensis; they first appear in historical records in connection with Hannibal's crossing of the Alps in 218 BC. Their territory was subsequently annexed to Rome in 121 BC by Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus and Quintus Fabius Maximus Allobrogicus. An attempted revolt was crushed by in 61 BC. However, they had rejected the second Catilinarian conspiracy in 63 BC. During the Gallic Wars, the Allobroges did not side with Vercingetorix at the Battle of Alesia in 52 BC. Name Attestations They are mentioned as ''A̓llobrígōn'' ( Ἀλλοβρίγων) by Polybius (2nd c. BC) and Strabo (early 1st c. AD),Polybius. ''Historíai'3:49–51 Strabo4:1:11 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segusiavi
The Segusiavī (Gaulish: *''Segusiauī/Segusiawī'') were a Gallic tribe dwelling around the modern city of Feurs (Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes) during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Name They are mentioned as ''Segusiavis'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), as ''Segosianō͂n'' (Σεγοσιανῶν) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), as ''Segusiavi'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), and as ''Segousō̃antoi'' (Σεγουσῶαντοι) by Ptolemy (2nd c. AD).Ptolemy. ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', 2:8:11., s.v. ''Segusiavi'' and ''Forum Segusiavorum''. The etymology of the Gaulish ethnonym *''Segusiauī/Segusiawī'' is unclear. It probably stems from the Gaulish root ''sego-'' ('victory, force'), but the second element is problematic. Irish folklorist Dáithí Ó hÓgáin tentatively translates their name as the 'Victorious Ones'. Since the ''Segusiavi'' possessed a wide area just north of the Greek colony of Massalia (Marseille) at the time of Aristotle, he has proposed to see their name as an al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Fabius Maximus Allobrogicus
Quintus Fabius Maximus Allobrogicus, was a Roman statesman and general who was elected consul in 121 BC. During his consulship he fought against the Arverni and the Allobroges whom he defeated in 120 BC. He was awarded a triumph and the agnomen Allobrogicus for his victory over the Gauls. Career Fabius Maximus Allobrogicus was the son of Quintus Fabius Maximus Aemilianus, the Roman consul of 145 BC, and a member of the patrician ''gens Fabia''.Allobrogicus was a member of the ''gens Fabia'' through the adoption of his father; his paternal grandfather was Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus. His first appearance was during the elections for quaestor in 134 BC; he was recommended to the voters as a candidate by his biological uncle Scipio Aemilianus, and after Allobrogicus was elected, Scipio took him as his quaestor to Hispania Citerior where they fought in the Second Numantine War. While there, Allobrogicus was placed in charge of 4,000 volunteers. By 124 BC, he had been elected t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
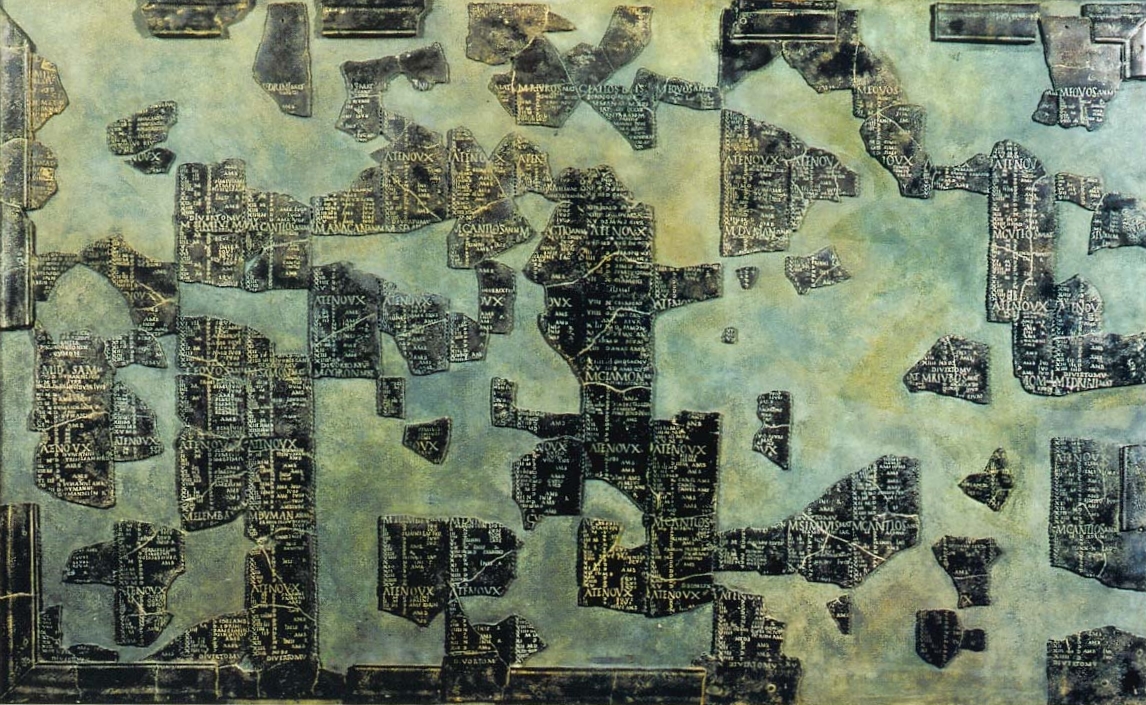
La Tène Culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscans, and the Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences. La Tène culture's territorial extent corresponded to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Austria, England, Southern Germany, the Czech Republic, parts of Northern Italy and Central Italy, Slovenia and Hungary, as well as adjacent parts of the Netherlands, Slovakia, Serbia, Croatia, Transylvania (western Romania), and Transcarpathia (western Ukraine). The Celtiberians of western Iberia shared many aspects of the culture, though not generally the artistic style. To the north extended the contemporary Pre-Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
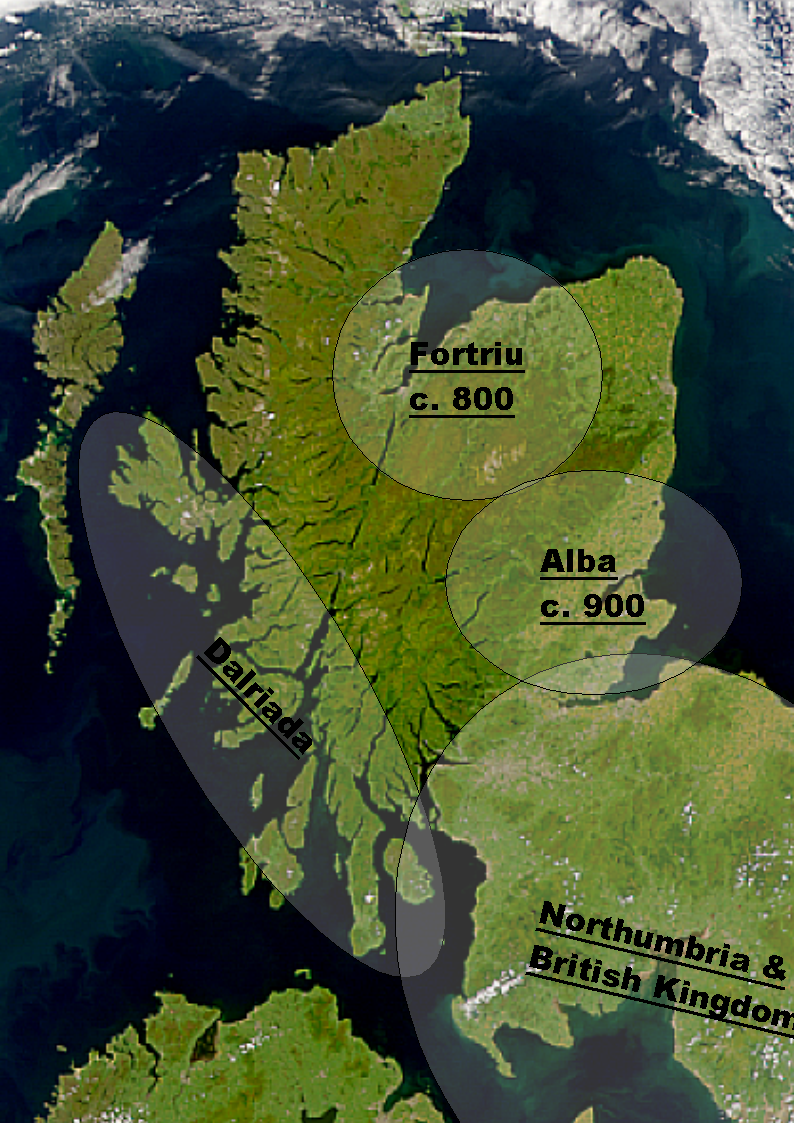
Kingdom Of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba ( la, Scotia; sga, Alba) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the First War of Scottish Independence. Alba included Dalriada, but not large parts of the present day Scottish Lowlands, which were then divided between Strathclyde and Northumbria as far north as the Firth of Forth. Fortriu, a Pictish kingdom in the north, was added to Alba in the tenth century. Until the early 13th century, Moray was not considered part of Alba, which was seen as extending only between the Firth of Forth and the River Spey. The name of Alba is one of convenience, as throughout this period both the ruling and lower classes of the Kingdom were predominantly Pictish-Gaels, later Pictish-Gaels and Scoto-Normans. This differs markedly from the period of the House of Stuart, beginning in 1371, in which the ruling classe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albion
Albion is an alternative name for Great Britain. The oldest attestation of the toponym comes from the Greek language. It is sometimes used poetically and generally to refer to the island, but is less common than 'Britain' today. The name for Scotland in most of the Celtic languages is related to Albion: ''Alba'' in Scottish Gaelic, ''Albain'' (genitive ''Alban'') in Irish language, Irish, ''Nalbin'' in Manx language, Manx and ''Alban'' in Welsh language, Welsh and Cornish language, Cornish. These names were later Latinisation of names, Latinised as ''Albania'' and Anglicisation, Anglicised as ''Albany'', which were once alternative names for Scotland. ''New Albion'' and ''Albionoria'' ("Albion of the North") were briefly suggested as name of Canada, names of Canada during the period of the Canadian Confederation. Sir Francis Drake gave the name New Albion to what is now California when he landed there in 1579. Etymology The toponym is thought to derive from the Greek word , L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aube (river)
The Aube () is a river in France, a right tributary of the Seine. It is long. The river gives its name to the Aube department. Its source is in the Haute-Marne department, on the plateau of Langres, near the town of Auberive. It flows through the departments of Haute-Marne, Côte-d'Or, Aube, and Marne. It flows into the river Seine near Marcilly-sur-Seine. Cities along the river include Bar-sur-Aube and Arcis-sur-Aube. Main tributaries * Aubette * Aujon * Landon * Voire * Ravet * Meldançon * Puits * Huitrelle * Herbissonne * Barbuise * Salon * Superbe Departments and towns crossed * Haute-Marne: Auberive * Côte-d'Or: Montigny-sur-Aube * Aube: Bar-sur-Aube, Brienne-le-Château, Ramerupt, Arcis-sur-Aube * Marne: Anglure See also * The Albian Age in the Cretaceous Period of geological time is named for the River Aube (after the Latin name for the river, Alba) * Rivers of France This is a list of rivers that are at least partially in France. The rivers are group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaulish Language
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switzerland, Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the west bank of the Rhine). In a wider sense, it also comprises varieties of Celtic that were spoken across much of central Europe (" Noric"), parts of the Balkans, and Anatolia (" Galatian"), which are thought to have been closely related. The more divergent Lepontic of Northern Italy has also sometimes been subsumed under Gaulish. Together with Lepontic and the Celtiberian spoken in the Iberian Peninsula, Gaulish helps form the geographic group of Continental Celtic languages. The precise linguistic relationships among them, as well as between them and the modern Insular Celtic languages, are uncertain and a matter of ongoing debate because of their sparse at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |