|
Alaska Statehood Act
The Alaska Statehood Act () was a statehood admission law, introduced by Delegate E.L. Bob Bartlett and signed by President Dwight D. Eisenhower on July 7, 1958, allowing Alaska to become the 49th U.S. state on January 3, 1959. The law was the result of a multiple decade effort from many Alaskans such as Bartlett, Ernest Gruening, Bill Egan, Bob Atwood and Ted Stevens. The law was first introduced by James Wickersham in 1916, shortly after the First Organic Act. However, due to a lack of interest from Alaskans, the bill was never introduced. Efforts ramped up in 1943, with Bartlett's rendition of the act being first introduced in 1947 & 1950, with the backing of President Harry Truman. However, due to opposition from powerful southern U.S. Congressmen, it took until 1958 to pass the law, with the convincing of Bob Bartlett. Gruening worked on rallying support from Alaskans, launching the Alaskan Constitutional Convention in 1956, which elected Bill Egan & Gruening as Shadow U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signing Of The Alaska Statehood Act
Signing may refer to: * Using sign language * Signature, placing one's name on a document * Signature (other) * Manual communication, signing as a form of communication using the hands in place of the voice * Digital signature A digital signature is a mathematical scheme for verifying the authenticity of digital messages or documents. A valid digital signature, where the prerequisites are satisfied, gives a recipient very high confidence that the message was created b ..., signing as a method of authenticating digital information See also * Wikipedia:Sign your posts on talk pages, the Wikipedia policy of signing Talk pages {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Government Of The United States
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a federal district (the city of Washington in the District of Columbia, where most of the federal government is based), five major self-governing territories and several island possessions. The federal government, sometimes simply referred to as Washington, is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executive, and judicial, whose powers are vested by the U.S. Constitution in the Congress, the president and the federal courts, respectively. The powers and duties of these branches are further defined by acts of Congress, including the creation of executive departments and courts inferior to the Supreme Court. Naming The full name of the republic is "United States of America". No other name appears in the Constitution, and this i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Gruening At Lathrop High School Assembly, 1957-58 School Year (cropped)
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include: People *Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor *Ernest, Margrave of Austria (1027–1075) *Ernest, Duke of Bavaria (1373–1438) *Ernest, Duke of Opava (c. 1415–1464) *Ernest, Margrave of Baden-Durlach (1482–1553) *Ernest, Landgrave of Hesse-Rheinfels (1623–1693) *Ernest Augustus, Elector of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1629–1698) *Ernest, Count of Stolberg-Ilsenburg (1650–1710) *Ernest Augustus, King of Hanover (1771–1851), son of King George III of Great Britain *Ernest II, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1818–1893), sovereign duke of the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha *Ernest Augustus, Crown Prince of Hanover (1845–1923) *Ernest, Landgrave of Hesse-Philippsthal (1846–1925) *Ernest Augustus, Prince of Hanover (1914–1987) *Prince Ernst August of Hanover (born 1954) * Prince Ernst Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juneau, Alaska
The City and Borough of Juneau, more commonly known simply as Juneau ( ; tli, Dzánti K'ihéeni ), is the capital city of the state of Alaska. Located in the Gastineau Channel and the Alaskan panhandle, it is a unified municipality and the second- largest city in the United States by area. Juneau was named the capital of Alaska in 1906, when the government of what was then the District of Alaska was moved from Sitka as dictated by the U.S. Congress in 1900. The municipality unified on July 1, 1970, when the city of Juneau merged with the city of Douglas and the surrounding Greater Juneau Borough to form the current municipality, which is larger by area than both Rhode Island and Delaware. Downtown Juneau () is nestled at the base of Mount Juneau and across the channel from Douglas Island. As of the 2020 census, the City and Borough had a population of 32,255, making it the third-most populous city in Alaska after Anchorage and Fairbanks. Juneau experiences a daily influx o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Howard Taft
William Howard Taft (September 15, 1857March 8, 1930) was the 27th president of the United States (1909–1913) and the tenth chief justice of the United States (1921–1930), the only person to have held both offices. Taft was elected president in 1908, the chosen successor of Theodore Roosevelt, but was defeated for reelection in 1912 by Woodrow Wilson after Roosevelt split the Republican vote by running as a third-party candidate. In 1921, President Warren G. Harding appointed Taft to be chief justice, a position he held until a month before his death. Taft was born in Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1857. His father, Alphonso Taft, was a U.S. attorney general and secretary of war. Taft attended Yale and joined the Skull and Bones, of which his father was a founding member. After becoming a lawyer, Taft was appointed a judge while still in his twenties. He continued a rapid rise, being named solicitor general and a judge of the Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals. In 1901, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinchot–Ballinger Controversy
The Pinchot–Ballinger controversy, also known as the "Ballinger Affair", was a dispute between U.S. Forest Service Chief Gifford Pinchot and U.S. Secretary of the Interior Richard A. Ballinger that contributed to the split of the Republican Party before the 1912 presidential election and helped to define the U.S. conservation movement in the early 20th century. Ballinger's appointment In March 1909, President William Howard Taft began his administration by replacing Theodore Roosevelt's Secretary of the Interior, James Rudolph Garfield, with Richard A. Ballinger, a former Mayor of Seattle who had served as Commissioner of the General Land Office (GLO) under Secretary Garfield. Ballinger's appointment was a disappointment to conservationists, who interpreted the replacement of Garfield as a break with Roosevelt administration policies on conservationism. Within weeks of taking office, Ballinger reversed some of Garfield's policies, restoring 3 million acres (12,000 km² ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Guggenheim
John Simon Guggenheim (December 30, 1867 – November 2, 1941) was an American businessman, politician and philanthropist. Life Born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania of Jewish descent, Simon Guggenheim was the son of Meyer Guggenheim and Barbara Guggenheim, and was the younger brother of Daniel Guggenheim and Solomon R. Guggenheim. He attended Central High School and the Peirce School of Business Administration before settling in Pueblo, Colorado, where he worked as the chief ore buyer for his father's mining and smelting operation, M. Guggenheim's Sons. Guggenheim moved to Denver in 1892 and married Olga Hirsch on November 24, 1898, at the iconic Waldorf Astoria New York in Manhattan. To celebrate their marriage, the Guggenheims provided a Thanksgiving dinner to 5,000 poor Manhattan children. He was the Republican candidate for Governor of Colorado early in the 1898 campaign but withdrew after riots broke out at the State Convention in Colorado Springs, during which one man w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
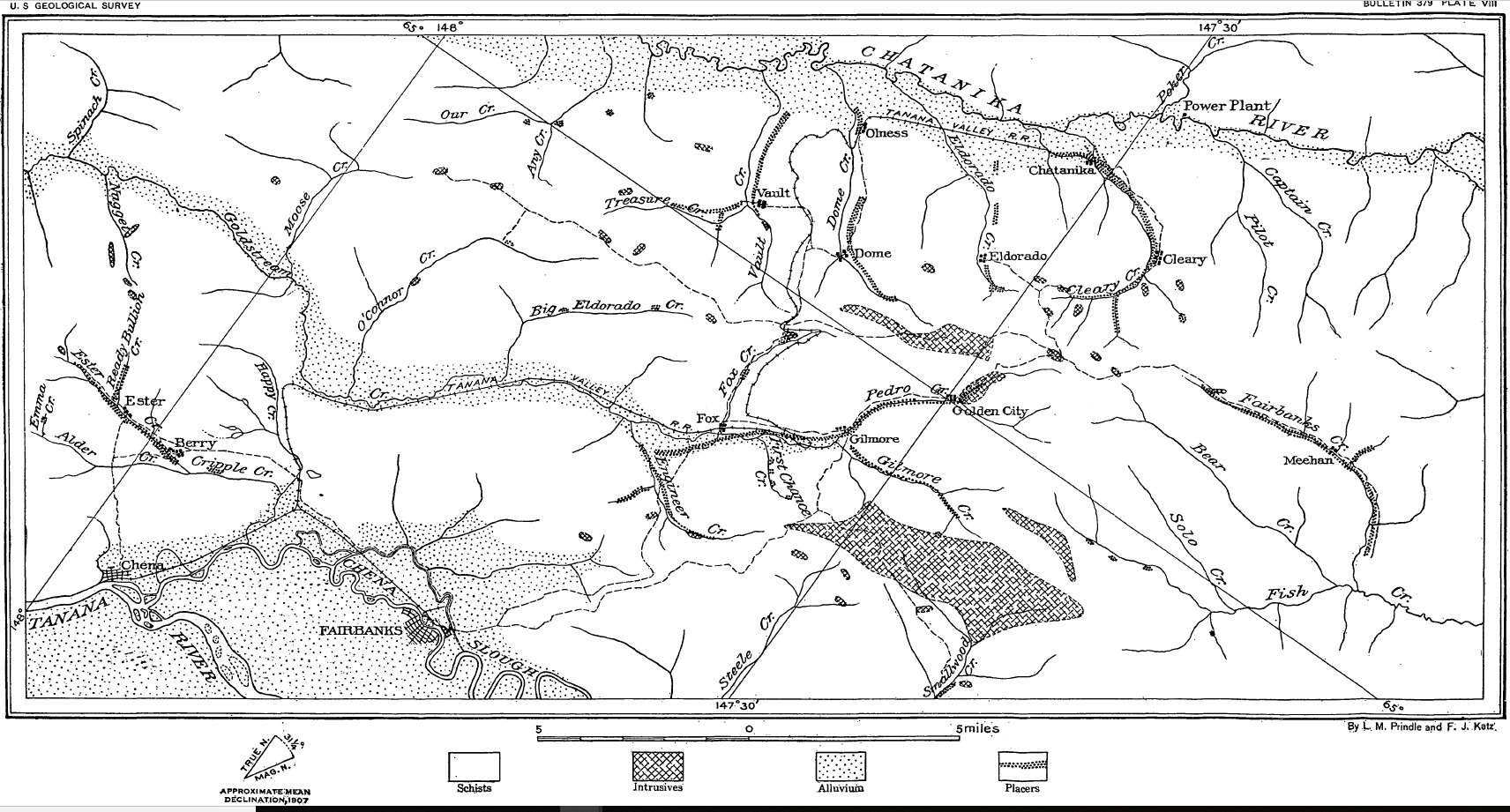
Fairbanks Gold Rush
The Fairbanks Gold Rush was a gold rush that took place in Fairbanks, Alaska in the early 1900s. Fairbanks was a city largely built on gold rush fervor at the turn of the 20th century. Discovery and exploration continue to thrive in and around modern-day Fairbanks. History Felix Pedro spent years searching for gold. He tried to find gold in the creeks and valleys of the Tanana Valley where Fairbanks would begin before he found the "American Klondike". A trader named E.T. Barnette and his wife, Isabelle, were aboard the riverboat ''Lavelle Young'' in August 1901, trying to establish a trading post at Tanacross on the Tanana River. Low water conditions stopped the journey before Barnette could reach his destination. Co-owner of the Lavelle Young, Captain Charles Adams, turned into the Chena River, a tributary of the Tanana, instead. Shallow water stopped the Lavelle Young, and Adams refused to go further, so the Barnettes set up shop there. Barnette opened a trading post on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nome Gold Rush
The Nome Gold Rush was a gold rush in Nome, Alaska, approximately 1899–1909.. It is separated from other gold rushes by the ease with which gold could be obtained. Much of the gold was lying in the beach sand of the landing place and could be recovered without any need for a claim. Nome was a sea port without a harbor, and the biggest town in Alaska. Together with the Klondike Gold Rush (1896–1899) and Fairbanks Gold Rush (1903–1911), Nome was among the biggest gold rushes north of 60 degrees latitude on the North American continent. It shared prospectors with both Klondike and later rushes like Fairbanks. It is memorialized in films like ''North to Alaska''. Nome City still exists and the area is mined as Nome mining district and by tourists. Total production of gold from the area is estimated to be 112 metric tons. History Prehistory The center of the Nome Gold Rush was the town of Nome at the outlet of Snake River on the Seward Peninsula at Norton Sound of the Berin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New Zealand, Brazil, Chile, South Africa, the United States, and Canada while smaller gold rushes took place elsewhere. In the 19th century, the wealth that resulted was distributed widely because of reduced migration costs and low barriers to entry. While gold mining itself proved unprofitable for most diggers and mine owners, some people made large fortunes, and merchants and transportation facilities made large profits. The resulting increase in the world's gold supply stimulated global trade and investment. Historians have written extensively about the mass migration, trade, colonization, and environmental history associated with gold rushes. Gold rushes were typically marked by a general buoyant feeling of a "free-for-all" in income mob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |