|
Alarm-class Torpedo Gunboat
The ''Alarm''-class torpedo gunboat was the penultimate class of torpedo gunboat built for the Royal Navy. The class was contemporary with the early torpedo boat destroyers, which were faster and thus better suited to pursuit of enemy torpedo boats. By World War I the class had either been sold, converted to submarine depot ships or minesweepers, or reduced to harbour service. Three of the class were lost during World War I while serving in the minesweeping role. Design The ''Alarm'' class was designed by Sir William White in 1889 as an enlarged version of his previous ''Sharpshooter'' class. They had a length overall of , a beam of and a displacement of 810 tons. They were engined with two sets of vertical triple-expansion steam engines, two locomotive-type boilers, and twin screws. This layout produced , giving them a speed of with forced draught. They carried between 100 and 160 tons of coal and were manned by 91 sailors and officers. Thornycroft Special - HMS ''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpshooter-class Torpedo Gunboat
The ''Sharpshooter''-class torpedo gunboat was a class of torpedo gunboat built for the Royal Navy in the late 19th century. One of the class was hulked in 1904, seven were scrapped before World War I and five were converted to minesweepers. Of these minesweepers, ''Seagull'' was lost to a collision in 1918 and the rest survived the war to be broken up in the early 1920s. Design The ''Sharpshooter'' class was designed by Sir William White in 1888. They had a length overall of , a beam of and a displacement of 735 tons. They were engined with two sets of Belliss and Morcom triple-expansion steam engines, two locomotive-type boilers, and twin screws. This layout produced with natural draught and with forced draught, giving them a top speed of . They carried 100 tons of coal, giving them a range of about at and were manned by 91 sailors and officers. The following ''Alarm'' class were essentially an enlarged version of the ''Sharpshooters''. From 1895 to 1898 a series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Defence Act 1889
The Naval Defence Act 1889 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It received the Royal Assent on 31 May 1889 and formally adopted the "two-power standard" and increased the United Kingdom's naval strength. The standard called for the Royal Navy to maintain a number of battleships at least equal to the combined strength of the next two largest navies in the world, which then were France and Russia. An extra £20 million over the following four years were provided for ten new battleships, thirty-eight new cruisers, eighteen new torpedo boats and four new fast gunboats. The two-power standard was maintained until disarmament began during the inter-war period. Background It was passed under the government of Lord Salisbury and facilitated spending £21,500,000 over five years toward fleet expansion. Initially, Parliament opposed the increase in naval expenditures for several reasons. Expert naval opinions presented to Parliament in December 1888 and February 1889 ren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
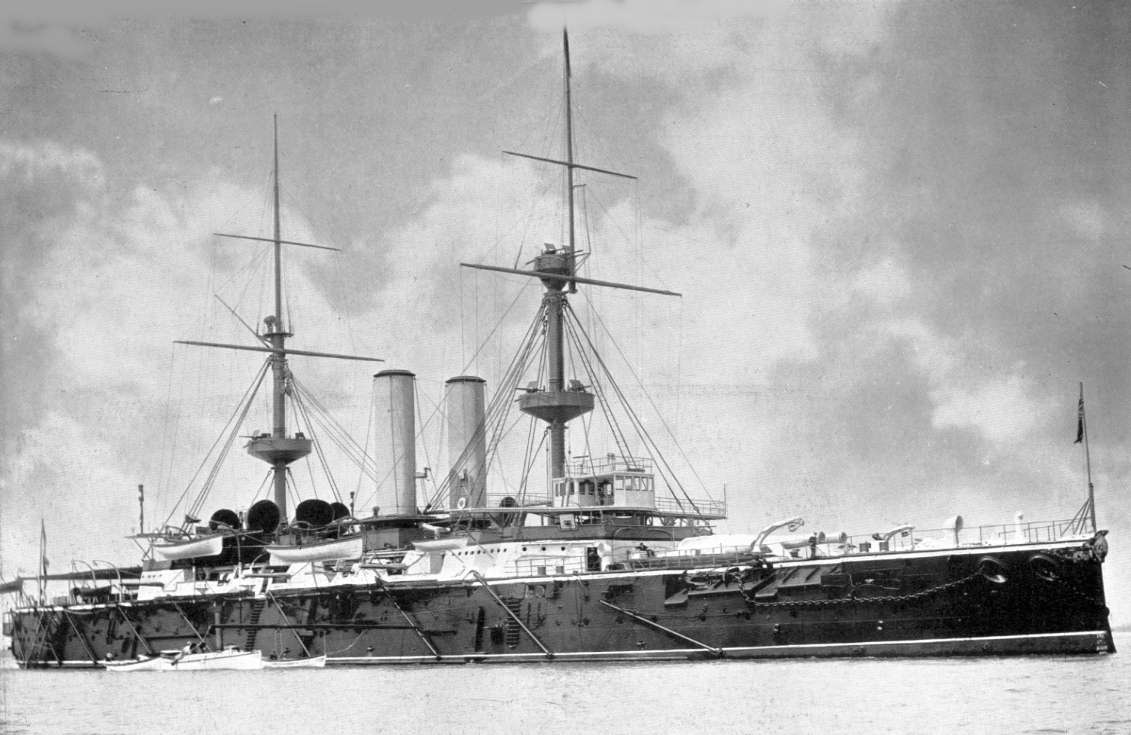
Ship Classes Of The Royal Navy
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SM U-12 (Germany)
SM ''U-12'' was a German submarine, built in 1911 and sunk off Scotland in 1915. It was the first submarine to launch a plane at sea. ''U-12'' was a Type U 9 U-boat built for the Imperial German Navy. Her construction was ordered on 15 July 1908 and her keel was laid down by Kaiserliche Werft in Danzig. She was launched on 6 May 1910 and commissioned on 13 August 1911. The German Empire was the first nation to experiment with submarine aircraft carriers. Oberleutnant zur See Friedrich von Arnauld de la Perière of the Naval Air Service and ''U-12s Kapitanleutnant Walther Forstmann theorised that they could increase the range of their seaplanes by carrying the aircraft out to sea on the deck of submarine and launching the seaplanes after the sub partially submerged, allowing the plane to float off. Service history On 15 January 1915 ''U-12'' left Zeebrugge transporting a Friedrichshafen FF.29 seaplane on its deck. Once beyond the safety of the breakwater, the captain real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Speedy (5041431448)
Nine ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Speedy'': * was a 14 gun sloop-of-war, launched in 1782. She was captured by the French in 1794, retaken by in 1795 and commanded by Thomas Cochrane in 1801. The French captured her again in 1801, whilst she was in the Mediterranean Sea, and donated her to the Papal Navy, She was struck in 1806. * was a gunboat serving on the Canadian Great Lakes. She was launched in 1798 and foundered in 1804. * was a brig-sloop, formerly ''George Herbert'', purchased in 1803 and sold in 1818 for use as a floating chapel. The chapel was used until 1834 then she was broken up. * was a six-gun cutter launched in 1828, converted to a dockyard mooring lighter in 1853 and renamed ''YC.11'' and broken up in 1866. * was a wood screw gunboat of the , launched in 1860 and broken up in 1889. * was a torpedo gunboat launched in 1893 and sunk by a mine in the Humber estuary in 1914. * was an launched in 1918 and sunk on 24 September 1922 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
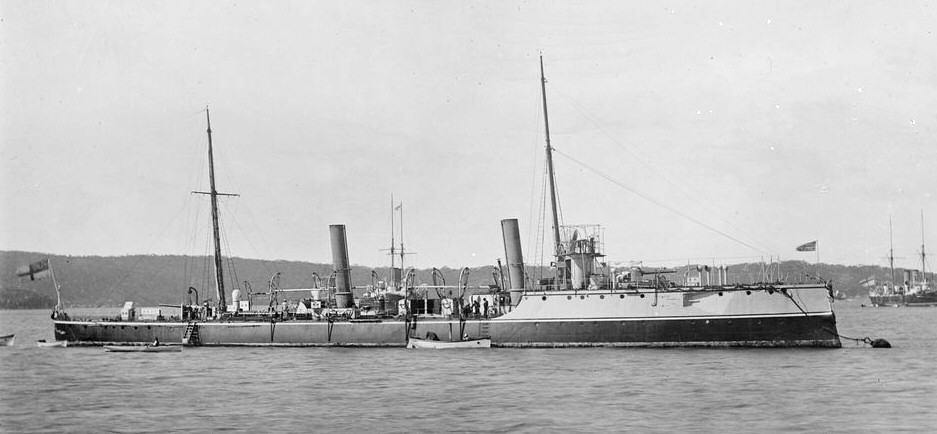
HMS Niger (1892)
HMS ''Niger'' was a torpedo gunboat launched in 1892, converted to a minesweeper in 1909, and sunk in 1914 by the German submarine near Deal. Early history The ship was ordered from Naval Construction & Armament, Barrow, and laid down on 17 September 1891. She was launched on 17 December 1892 and commissioned on 25 April 1893. ''Niger'' was the training ship for and tender to . In 1902 she had a major refit at the Palmers Shipbuilding Company, where she was fitted with new and larger engines, and with Reed water tube boilers. On her completion she relieved as tender to ''Vernon''. Sinking of HMS ''Niger'' On the morning of 11 November a U-boat attack occurred off Deal. Around noon there was an explosion and black smoke rose from HMS ''Niger''. ''Niger'' was at anchor about off the pier at Deal when she was torpedoed and sunk before noon on 11 November 1914 by the German submarine . ''Niger'' was the first ship sunk by U-boat commander Walther Forstmann. Forstmann was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Speedy (1893) Launch
Nine ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Speedy'': * was a 14 gun sloop-of-war, launched in 1782. She was captured by the French in 1794, retaken by in 1795 and commanded by Thomas Cochrane in 1801. The French captured her again in 1801, whilst she was in the Mediterranean Sea, and donated her to the Papal Navy, She was struck in 1806. * was a gunboat serving on the Canadian Great Lakes. She was launched in 1798 and foundered in 1804. * was a brig-sloop, formerly ''George Herbert'', purchased in 1803 and sold in 1818 for use as a floating chapel. The chapel was used until 1834 then she was broken up. * was a six-gun cutter launched in 1828, converted to a dockyard mooring lighter in 1853 and renamed ''YC.11'' and broken up in 1866. * was a wood screw gunboat of the , launched in 1860 and broken up in 1889. * was a torpedo gunboat launched in 1893 and sunk by a mine in the Humber estuary in 1914. * was an launched in 1918 and sunk on 24 September 1922 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiswick
Chiswick ( ) is a district of west London, England. It contains Hogarth's House, the former residence of the 18th-century English artist William Hogarth; Chiswick House, a neo-Palladian villa regarded as one of the finest in England; and Fuller's Brewery, London's largest and oldest brewery. In a meander of the River Thames used for competitive and recreational rowing, with several rowing clubs on the river bank, the finishing post for the Boat Race is just downstream of Chiswick Bridge. Old Chiswick was an St Nicholas Church, Chiswick, ancient parish in the county of Middlesex, with an agrarian and fishing economy beside the river; from the Early Modern period, the wealthy built imposing riverside houses on Chiswick Mall. Having good communications with London, Chiswick became a popular country retreat and part of the suburban growth of London in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was made the Municipal Borough of Brentford and Chiswick in 1932 and part of Greater Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I
John I may refer to: People * John I (bishop of Jerusalem) * John Chrysostom (349 – c. 407), Patriarch of Constantinople * John of Antioch (died 441) * Pope John I, Pope from 523 to 526 * John I (exarch) (died 615), Exarch of Ravenna * John I of Naples (died c. 719) * John of Abkhazia (ruled 878/879–880) * John I of Gaeta (died c. 933) * John I Tzimiskes (c. 925 – 976), Byzantine Emperor * John I of Amalfi (died 1007) * John I of Ponthieu (c. 1147 – 1191) * John I (archbishop of Trier) (c. 1140-1212), Archbishop of Trier from 1190 to 1212 * John of England (1166–1216), King of England, Lord of Ireland, Duke of Normandy and Aquitaine and Count of Anjou * John I of Sweden (c. 1201 – 1222) * John of Brienne (c. 1148 – 1237), king of Jerusalem * John I of Trebizond (died 1238) * John I of Dreux (1215–1249) * John I of Avesnes (1218–1257), Count of Hainaut * John of Brunswick, Duke of Lüneburg (c. 1242–1277) * John I, Count of Blois (died 1280) * John I, Duke of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpshooter Class Torpedo Gunboat
The ''Sharpshooter''-class torpedo gunboat was a class of torpedo gunboat built for the Royal Navy in the late 19th century. One of the class was hulked in 1904, seven were scrapped before World War I and five were converted to minesweepers. Of these minesweepers, ''Seagull'' was lost to a collision in 1918 and the rest survived the war to be broken up in the early 1920s. Design The ''Sharpshooter'' class was designed by Sir William White in 1888. They had a length overall of , a beam of and a displacement of 735 tons. They were engined with two sets of Belliss and Morcom triple-expansion steam engines, two locomotive-type boilers, and twin screws. This layout produced with natural draught and with forced draught, giving them a top speed of . They carried 100 tons of coal, giving them a range of about at and were manned by 91 sailors and officers. The following ''Alarm'' class were essentially an enlarged version of the ''Sharpshooters''. From 1895 to 1898 a series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryad-class Torpedo Gunboat
The ''Dryad''-class torpedo gunboat was the last class of torpedo gunboat built for the Royal Navy. This type of vessel was rapidly replaced by the faster torpedo boat destroyer, and all of the class were converted to minesweepers during World War I, with the exception of ''Hazard'', which became a submarine depot ship. Design Ordered under the Naval Defence Act of 1889, which established the "Two-Power Standard", the ships were contemporary with the first torpedo boat destroyers, a type which subsequently superseded the torpedo gunboats. With a length overall of , a beam of and a displacement of 1,070 tons, these torpedo gunboats were not small ships by the standard of the time; they were larger than the majority of World War I destroyers. Machinery They were equipped with two sets of vertical triple-expansion steam engines, with two locomotive-type boilers, driving through twin screws. This layout produced giving them a speed of ; ''Halcyon'' was uprated to produce 600 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)