|
Alateen
Al-Anon Family Groups, founded in 1951, is an international mutual aid organization for people who have been impacted by another person's alcoholism. In the organization's own words, Al-Anon is a "worldwide fellowship that offers a program of recovery for the families and friends of alcoholics, whether or not the alcoholic recognizes the existence of a drinking problem or seeks help." Alateen "is part of the Al-Anon fellowship designed for the younger relatives and friends of alcoholics through the teen years". Background Al-Anon defines itself as an independent fellowship with the stated purpose of helping relatives and friends of alcoholics. According to the organization, alcoholism is a family illness. Its "Preamble to the Twelve Steps" provides a general description: Not an intervention program, Al-Anon does not have the stated primary purpose of arresting another's compulsive drinking. Members meet in groups. Meetings are usually small (five to twenty-five); in large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community Reinforcement Approach And Family Training
Community reinforcement approach and family training (CRAFT) is a behavior therapy approach in psychotherapy for treating addiction developed by Robert J. Meyers in the late 1970s. Meyers worked with Nathan Azrin in the early 1970s whilst he was developing his own community reinforcement approach (CRA) which uses operant conditioning (also called contingency management) techniques to help people learn to reduce the power of their addictions and enjoy healthy living. Meyers adapted CRA to create CRAFT, which he described as CRA that "works through family members." CRAFT combines CRA with family training to equip concerned significant others (CSOs) of addicts with supportive techniques to encourage their loved ones to begin and continue treatment and provides them with defences against addiction's damaging effects on themselves. Overview "CRA is a time-limited treatment." "In time-limited therapy, a set number of sessions (for example, 16 sessions) or time limit (for example, one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholics Anonymous
Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) is an international mutual aid fellowship of alcoholics dedicated to abstinence-based recovery from alcoholism through its spiritually-inclined Twelve Step program. Following its Twelve Traditions, AA is non-professional and non-denominational, as well as apolitical and unaffiliated. In 2020 AA estimated its worldwide membership to be over two million with 75% of those in the U.S. and Canada. Regarding its effectiveness, a 2020 scientific review saw clinical interventions encouraging increased AA participation resulting in higher abstinence rates over other clinical interventions while probably reducing health costs. On the disease model of alcoholism, AA has no opinion on it—or any other medical matter—but it is often associated with AA due to many members promotion of it. AA dates its start to 1935 with Bill Wilson (Bill W) first commiserating alcoholic to alcoholic with Bob Smith (Dr. Bob) who, along with Wilson, was active in AA's precurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve-step Program
Twelve-step programs are international mutual aid programs supporting recovery from substance addictions, behavioral addictions and compulsions. Developed in the 1930s, the first twelve-step program, Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), aided its membership to overcome alcoholism. Since that time dozens of other organizations have been derived from AA's approach to address problems as varied as drug addiction, compulsive gambling, sex, and overeating. All twelve-step programs utilize a version of AA's suggested twelve steps first published in the 1939 book '' Alcoholics Anonymous: The Story of How More Than One Hundred Men Have Recovered from Alcoholism.'' As summarized by the American Psychological Association (APA), the process involves the following: * admitting that one cannot control one's alcoholism, addiction, or compulsion; * coming to believe in a Higher Power that can give strength; * examining past errors with the help of a sponsor (experienced member); * making amends for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholics Anonymous
Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) is an international mutual aid fellowship of alcoholics dedicated to abstinence-based recovery from alcoholism through its spiritually-inclined Twelve Step program. Following its Twelve Traditions, AA is non-professional, non-denominational, as well as apolitical and unaffiliated. In 2020 AA estimated its worldwide membership to be over two million with 75% of those in the U.S. and Canada. Despite viewing the disease model of alcoholism as an outside issue on which it has no opinion, AA is commonly associated with its popularity since many of its members took a large role in spreading it. Regarding its effectiveness, a 2020 scientific review saw clinical interventions encouraging increased AA participation resulting in higher abstinence rates over other clinical interventions while probably reducing health costs. AA marks 1935 for its start when Bill Wilson (Bill W.) first commiserated alcoholic to alcoholic with Bob Smith (Dr. Bob) who, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve Steps
Twelve-step programs are international mutual aid programs supporting recovery from substance addictions, behavioral addictions and compulsions. Developed in the 1930s, the first twelve-step program, Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), aided its membership to overcome alcoholism. Since that time dozens of other organizations have been derived from AA's approach to address problems as varied as drug addiction, compulsive gambling, sex, and overeating. All twelve-step programs utilize a version of AA's suggested twelve steps first published in the 1939 book '' Alcoholics Anonymous: The Story of How More Than One Hundred Men Have Recovered from Alcoholism.'' As summarized by the American Psychological Association (APA), the process involves the following: * admitting that one cannot control one's alcoholism, addiction, or compulsion; * coming to believe in a Higher Power that can give strength; * examining past errors with the help of a sponsor (experienced member); * making amends for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
501(c)(3)
A 501(c)(3) organization is a United States corporation, trust, unincorporated association or other type of organization exempt from federal income tax under section 501(c)(3) of Title 26 of the United States Code. It is one of the 29 types of 501(c) nonprofit organizations in the US. 501(c)(3) tax-exemptions apply to entities that are organized and operated exclusively for religious, charitable, scientific, literary or educational purposes, for testing for public safety, to foster national or international amateur sports competition, or for the prevention of cruelty to children or animals. 501(c)(3) exemption applies also for any non-incorporated community chest, fund, cooperating association or foundation organized and operated exclusively for those purposes.IR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Theory (sociology)
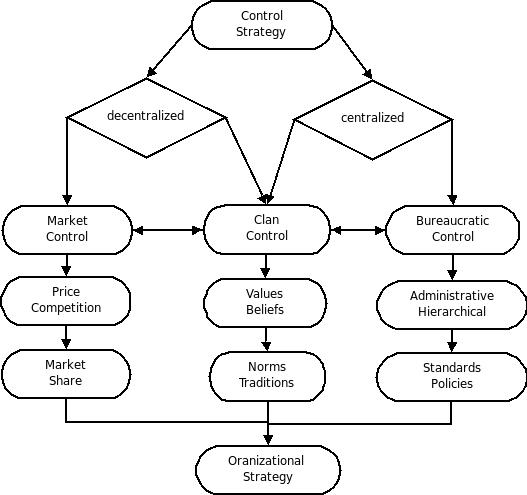
Control theory in sociology is the idea that two control systems—inner controls and outer controls—work against our tendencies to deviate. Control theory can either be classified as centralized or decentralized. Decentralized control is considered market control. Centralized control is considered bureaucratic control. Some types of control such as clan control are considered to be a mixture of both decentralized and centralized control. Decentralized control or market control is typically maintained through factors such as price, competition, or market share. Centralized control such as bureaucratic control is typically maintained through administrative or hierarchical techniques such as creating standards or policies. An example of mixed control is clan control which has characteristics of both centralized and decentralized control. Mixed control or clan control is typically maintained by keeping a set of values and beliefs or norms and traditions. Containment theory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-esteem
Self-esteem is confidence in one's own worth or abilities. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs about oneself (for example, "I am loved", "I am worthy") as well as emotional states, such as triumph, despair, pride, and shame. Smith and Mackie (2007) defined it by saying "The self-concept is what we think about the self; self-esteem, is the positive or negative evaluations of the self, as in how we feel about it." Self-esteem is an attractive psychological construct because it predicts certain outcomes, such as academic achievement, happiness, satisfaction in marriage and relationships, and criminal behavior. Self-esteem can apply to a specific attribute or globally. Psychologists usually regard self-esteem as an enduring personality characteristic (''trait self-esteem''), though normal, short-term variations (''state self-esteem'') also exist. Synonyms or near-synonyms of self-esteem include: self-worth, self-regard, self-respect, and self-integrity. History The concept of self-estee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agency (philosophy)
Agency is the capacity of an actor to act in a given environment. It is independent of the moral dimension, which is called moral agency. In ''sociology'', an agent is an individual engaging with the social structure. Notably, though, the primacy of structure and agency, social structure vs. individual capacity with regard to persons' actions is debated within sociology. This debate concerns, at least partly, the level of reflexivity (social theory), reflexivity an agent may possess. Agency may either be classified as unconscious, involuntary behavior, or purposeful, goal directed activity (intentional action). An agent typically has some sort of immediate awareness of their physical activity and the goals that the activity is aimed at realizing. In ‘goal directed action’ an agent implements a kind of direct control or guidance over their own behavior. Human agency Agency is contrasted to objects reacting to Natural phenomenon, natural forces involving only unthinking dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstinence
Abstinence is a self-enforced restraint from indulging in bodily activities that are widely experienced as giving pleasure. Most frequently, the term refers to sexual abstinence, but it can also mean abstinence from alcohol, drugs, food, etc. Because the regimen is intended to be a conscious act, freely chosen to enhance life, abstinence is sometimes distinguished from the psychological mechanism of repression. The latter is an unconscious state, having unhealthy consequences. Abstinence in religion Abstinence may arise from an ascetic over indulgent, hasidic point of view in natural ways of procreation, present in most faiths, or from a subjective need for spiritual discipline. In its religious context, abstinence is meant to elevate the believer beyond the normal life of desire, to a chosen ideal, by following a path of renunciation. In Judaism, Christianity and Islam, amongst others, pre-marital sex is prohibited. Judaism For Jews, the principal day of fast is Yom Kippur, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill W
William Griffith Wilson (November 26, 1895 – January 24, 1971), also known as Bill Wilson or Bill W., was the co-founder of Alcoholics Anonymous (AA). AA is an international mutual aid fellowship with about two million members worldwide belonging tover 123,000 A.A. groups associations, organizations, cooperatives, and fellowships of alcoholics helping other alcoholics achieve and maintain sobriety. Following AA's Twelfth Tradition of anonymity, Wilson is commonly known as "Bill W." or "Bill". In order to identify each other, members of AA will sometimes ask others if they are "friends of Bill". Although this question can be confusing, because "Bill" is a common name, it does provide a means of establishing the common experience of AA membership. After Wilson's death in 1971, and amidst much controversy within the fellowship, his full name was included in obituaries by journalists who were unaware of the significance of maintaining anonymity within the organization. Wils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
