|
Aktiubinsk
Aktobe ( kz, Ақтөбе, Aqtöbe; russian: Актобе, Aktobe) is a city on the Ilek River in Kazakhstan. It is the administrative center of Aktobe Region. In 2020, it had a population of 500,757 people. Aktobe is located in the west of Kazakhstan. The area of the city is about 428,469 km2. There are two water reservoirs: Aktobe and Sazdy. Aktobe ranks fourth among the cities of Kazakhstan in terms of population and is the largest city in western Kazakhstan. The city's populace is ethnically diverse, with 79% being Kazakhs and 14.8% being Russians. The predominant religions are Islam and Christianity. The agglomeration of Aktobe is expected to grow up to 1.3 million people, including nearby settlements. Etymology The name "Aktobe" comes from Kazakh "ақ" (white) and "төбе" (hill); the name is a reference to the heights on which the original 19th century settlement was located. Until 1999 it was officially known as Aktyubinsk (russian: Актюбинск). The former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
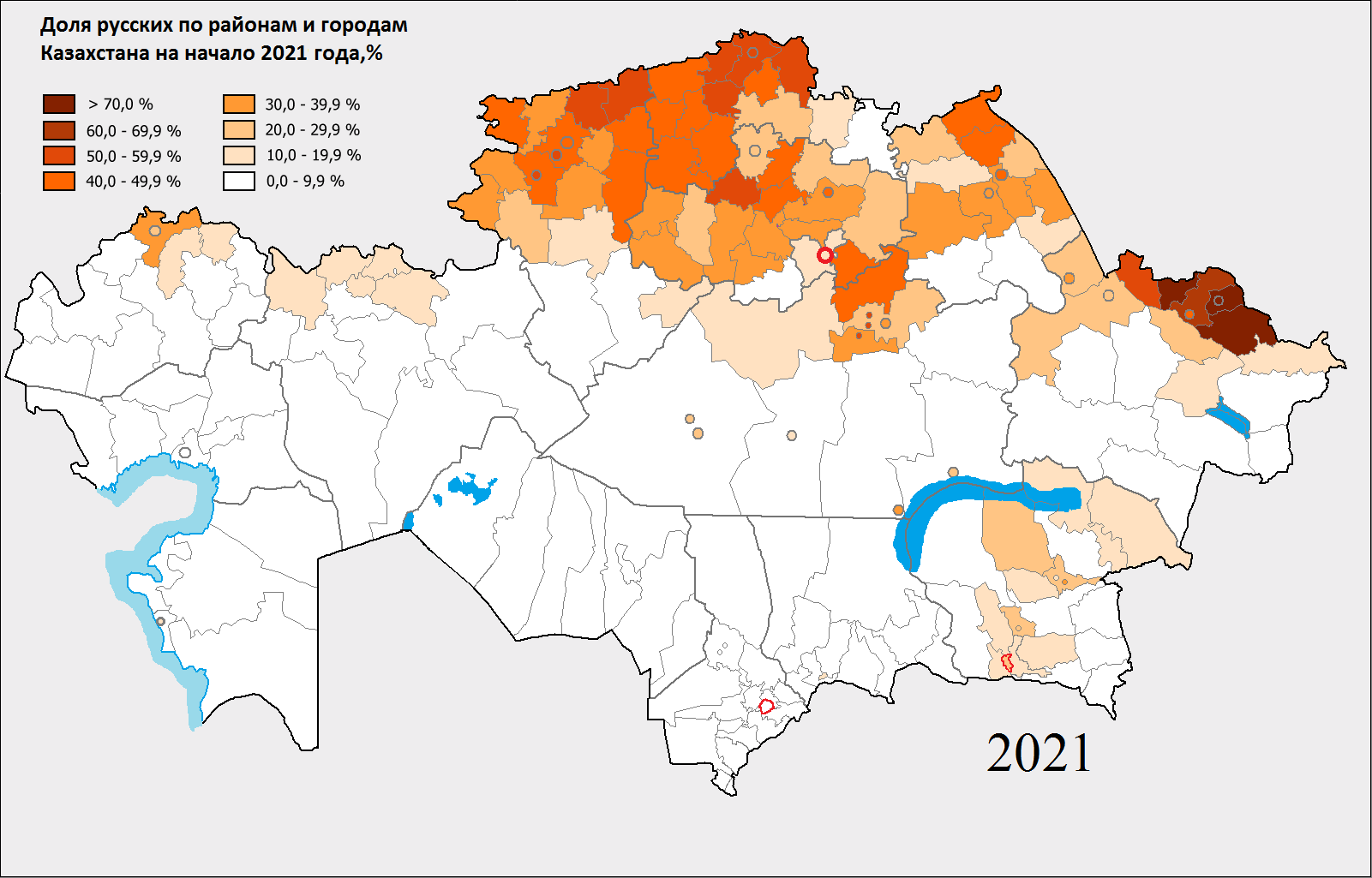
Russians In Kazakhstan
There has been a substantial population of Russians in Kazakhstan since the 19th century. Although their numbers have been reduced since the breakup of the Soviet Union, they remain prominent in Kazakh society today. Russians formed a plurality of the Kazakh SSR's population for several decades. Early colonisation The first Rus' traders and soldiers began to appear on the northwestern edge of modern Kazakhstan territory in the early 16th century, when Cossacks established the forts that later became the cities of Oral (Ural'sk, est. 1520) and Atyrau (Gur'yev). Ural, Siberian and later Orenburg Cossack Hosts gradually established themselves in parts of northern Kazakhstan. In 1710s and 1720s Siberian Cossacks founded Oskemen (Ust-Kamennaya), Semey (Semipalatinsk) and Pavlodar (Fort Koryakovskiy) as border forts and trading posts. Russian imperial authorities followed and were able to seize Kazakh territory because the local khanates were preoccupied by a war with Kalmyks (Oirats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after 1922, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. The army was established in January 1918. The Bolsheviks raised an army to oppose the military confederations (especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army) of their adversaries during the Russian Civil War. Starting in February 1946, the Red Army, along with the Soviet Navy, embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces; taking the official name of "Soviet Army", until its dissolution in 1991. The Red Army provided the largest land force in the Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its invasion of Manchuria assisted the unconditional surrender of Imperial Japan. During operations on the Eastern Front, it accounted for 75–80% of casual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet (council)
Soviets (singular: soviet; rus, сове́т, sovét, , literally "council" in English) were Political organisation, political organizations and governmental bodies of the former Russian Empire, primarily associated with the Russian Revolution, which gave the name to the latter state of the Soviet Union. Soviets were the main form of government in the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, Makhnovshchina, Free Territory, and to a much lesser extent were active in the Russian Provisional Government. It also can mean any workers' council that is Socialism, socialist such as the Irish soviets. Soviets do not inherently need to adhere to the ideology of the later Soviet Union. Etymology "Soviet" is derived from a Russian language, Russian word meaning council, assembly, advice, harmony, or concord, uk, рада (''rada''); pl, rada; be, савет; uz, совет; kk, совет/кеңес; ka, საბჭო; az, совет; lt, taryba; ro, soviet (Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English as the Bolshevists,. It signifies both Bolsheviks and adherents of Bolshevik policies. were a far-left, revolutionary Marxist faction founded by Vladimir Lenin that split with the Mensheviks from the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), a revolutionary socialist political party formed in 1898, at its Second Party Congress in 1903. After forming their own party in 1912, the Bolsheviks took power during the October Revolution in the Russian Republic in November 1917, overthrowing the Provisional Government of Alexander Kerensky, and became the only ruling party in the subsequent Soviet Russia and later the Soviet Union. They considered themselves the leaders of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia. Their beliefs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Revolution Of 1905
The Russian Revolution of 1905,. also known as the First Russian Revolution,. occurred on 22 January 1905, and was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. The mass unrest was directed against the Tsar, nobility, and ruling class. It included worker strikes, peasant unrest, and military mutinies. In response to the public pressure, Tsar Nicholas II enacted some constitutional reform (namely the October Manifesto). This took the form of establishing the State Duma, the multi-party system, and the Russian Constitution of 1906. Despite popular participation in the Duma, the parliament was unable to issue laws of its own, and frequently came into conflict with Nicholas. Its power was limited and Nicholas continued to hold the ruling authority. Furthermore, he could dissolve the Duma, which he often did. The 1905 revolution was primarily spurred by the international humiliation as a result of the Russian defeat in the Russo-Japa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Aral Railway
The broad gauge Trans-Aral Railway (also known as the Tashkent Railway) was built in 1906 connecting Kinel and Tashkent, then both in the Russian Empire. For the first part of the 20th century it was the only railway connection between European Russia and Central Asia. An extensive description of the newly built railway was published in 1910. Construction history There were plans to construct the Orenburg–Tashkent line as early as 1874. Construction work did not start, however, until the autumn of 1900. The railway was simultaneously built from both ends toward a common junction. It opened in January 1906, linking the existing network of Russian and European railways to the Trans-Caspian Railway. On January 1, 1905, the Kinel–Orenburg section of the Samara–Zlatoust line was joined to the Tashkent railway. The Kinel–Tashkent Railway was the first line to be built across the steppe, replacing the multiple routes once used by caravans with a single, steel path. It introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turkic ethnic groups bearing the name "Tatar". Initially, the ethnonym ''Tatar'' possibly referred to the . That confederation was eventually incorporated into the when unified the various steppe tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Peoples
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably dive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caravan (travellers)
A caravan (from Persian ) or cafila (from Arabic ) is a group of people traveling together, often on a trade expedition. Caravans were used mainly in desert areas and throughout the Silk Road, where traveling in groups aided in defense against bandits as well as helped to improve economies of scale in trade. Some of the first caravans on the Silk Road were sent out by Emperor Wu of Han in the 2nd century BCE when this vast network of roads was 'born', and as China began exporting large quantities of silk and other goods west, particularly destined for the Roman Empire. Description In historical times, caravans connecting East Asia and Europe often carried luxurious and lucrative goods, such as silks or jewelry. Caravans could therefore require considerable investment and were a lucrative target for bandits. The profits from a successfully undertaken journey could be enormous, comparable to the later European spice trade. The luxurious goods brought by caravans attracted many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |