|
Akita Castle
refers to the ruins of a Nara period fortified settlement located in what is now the city Akita, Akita, Akita, Akita Prefecture, Japan. It is also sometimes referred to as “Fort Akita”. The name is sometimes used wrongly for Kubota Castle, an Edo period Japanese castle which served as the headquarters or the Satake clan, Satake, ''daimyō'' of Kubota Domain that was a domain in the northern part of Dewa Province created by the Tokugawa shogunate. History During the Asuka period, Abe no Hirafu conquered the native Emishi tribes at what are now the cities of Akita and Noshiro, Akita, Noshiro in 658 and established a fortification on the Mogami River. In the year 708 AD, “Dewa Country” was created out of the northern half of Echigo Province and was raised in status to Dewa Province in 712 AD. However, at that time the region was still outside the effective control of the Yamato dynasty, Yamato court based in Nara, Nara, Nara. A number of military expeditions were sent to the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
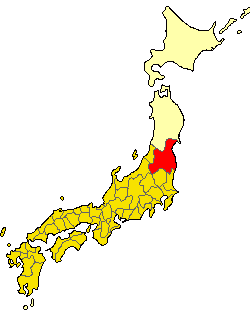
Akita, Akita
'Autumn field' is the capital Cities of Japan, city of Akita Prefecture, Japan, and has been designated a Core cities of Japan, core city since 1 April 1997. , the city has an estimated population of 305,625, 136,628 households and a population density of 340 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . History The area of present-day Akita was part of ancient Dewa Province, and has been inhabited for thousands of years. The Jizōden Site, Jizōden ruins within the city limits are a major archaeological site with artifacts from the Japanese Paleolithic period through the Jōmon period, Jōmon and Yayoi periods. During the Nara period, the Yamato dynasty, Yamato court established Akita Castle in 733 AD to bring the local Emishi tribes under its control. The area was ruled by a succession of local samurai clans in the Sengoku period, before coming under the control of the Satake clan of Kubota Domain during the Edo period. Under the Tokugawa shogunate, a castle town developed ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emishi
The (also called Ebisu and Ezo), written with Chinese characters that literally mean "shrimp barbarians," constituted an ancient ethnic group of people who lived in parts of Honshū, especially in the Tōhoku region, referred to as in contemporary sources. The first mention of the Emishi in literature that can be corroborated with outside sources dates to the 5th century AD, in which they are referred to as (毛人 - "hairy people") in Chinese records. Some Emishi tribes resisted the rule of various Japanese Emperors during the Asuka, Nara and early Heian periods (7th–10th centuries AD). The origin of the Emishi is disputed. They are often thought to have descended from some tribes of the Jōmon people. Some historians believe that they were related to the Ainu people, but others disagree with this theory and see them as a completely distinct ethnicity.Aston, W.G., trans. Nihongi: Chronicles of Japan from the Earliest Times to AD 697. Tokyo: Charles E.Tuttle Co., 1972 (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balhae
Balhae ( ko, 발해, zh, c=渤海, p=Bóhǎi, russian: Бохай, translit=Bokhay, ), also rendered as Bohai, was a multi-ethnic kingdom whose land extends to what is today Northeast China, the Korean Peninsula and the Russian Far East. It was established in 698 by Dae Joyeong (Da Zuorong) and originally known as the Kingdom of Jin (Zhen) until 713 when its name was changed to Balhae. Balhae's early history involved a rocky relationship with the Tang dynasty that saw military and political conflict, but by the end of the 8th century the relationship had become cordial and friendly. The Tang dynasty would eventually recognize Balhae as the "Prosperous Country of the East". Numerous cultural and political exchanges were made. Balhae was conquered by the Khitan-led Liao dynasty in 926. Balhae survived as a distinct population group for another three centuries in the Liao and Jin dynasties before disappearing under Mongol rule. The history of the founding of the state, its e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Nine Years War
The , also known in English as the Former Nine Years' War or the Early Nine Years' War, was fought between the Imperial Court and the Abe clan in Mutsu Province, in Northeast Japan, from 1051 to 1063. It resulted in Imperial Court victory and the surrender of Abe no Sadato. Like the other major conflicts of the Heian period, such as the Gosannen War and the Genpei War, the Zenkunen war was a struggle for power within the samurai clans. Background While most provinces were overseen by just a Governor, Mutsu, in what is now the Tohoku region, had a military general in charge of controlling the Emishi natives, who had been subjugated when the Japanese took over the area in the ninth century. Historically, this post was always held by a member of the Abe clan, and there were many conflicts between the Abe general and the Governor over administrative control of the province. In 1050, the general overseeing the Ainu was Abe no Yoritoki, who levied taxes and confiscated property on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokushi (official)
were provincial officials in Classical Japan. They were nobles sent from the central government in Kyoto to oversee a province, a system that was established as part of the Taika Reform in 645, and enacted by the ''Ritsuryō'' system. There were four classes of ''kokushi'', from the highest to the lowest: ''Kami'' (守), ''Suke'' (介), ''Jō'' (掾), and ''Sakan'' (目). In the Middle Ages, an acting governor called ''mokudai'', the ''daikan'' of the ''kokushi'', took over the local government of the province, while the ''kokushi'' returned to the capital to take on a supervising role. History The oldest reference to the term ''kokushi'' appears on the Seventeen-article constitution from 604. As part of the Taika Reform in 645, a new system of provincial government was established, marking the beginning of the ''kokushi''. Before this, the governors were called ''mikotomochi'' (宰 or 使者). This term was replaced with the ''kanji'' characters 国 (province) and 司 (governo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taga Castle
was a ''jōsaku''-style Japanese castle built in the late Nara period in what is now part of the city of Tagajō in Miyagi prefecture in the Tōhoku region of far northern Honshu, Japan. Bashō tells of his visit to the site in ''Oku no Hosomichi''. The ruins of Taga-jō and its former temple have been designated a since 1922. History In the Nara period, after the establishment of a centralized government under the ''Ritsuryō'' system, the Yamato court sent a number of military expeditions to what is now the Tōhoku region of northern Japan to bring the local Emishi tribes under its control. In what is now Miyagi Prefecture, a civil administration was established in the form of a provincial capital and regional administrative centers in the late 6th century; however, a massive Emishi uprising occurred in 709 AD during which time many of these structures were destroyed. Per the ''Shoku Nihongi'', following a huge earthquake in the year 715 AD, a large number of people migrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abe No Yakamaro
Abe or ABE may refer to: People and fictional characters * Shinzo Abe (1954–2022), former Prime Minister of Japan * Abe (given name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or nickname * Abe (surname), a list of people and fictional characters with the surname * Abe clan, a Japanese clan Languages * Abé language, a language of the Niger-Congo family * abe, the ISO 639-3 code for the Western Abenaki language, a nearly extinct Algonquian language of Canada and the United States * AbE, Aboriginal English spoken in Australia Science and technology * Bolivian Space Agency, Agencia Boliviana Espacial * Associação Brasileira de Estatística, a Brazilian scientific society * Acetone–butanol–ethanol fermentation, or ABE fermentation, a process that produces acetone, biobutanol, and bioethanol from starch * Attribute-based encryption, a collusion-resistant one-to-many encryption scheme Storms * Typhoon Abe (1990) * Typhoon Abe (1993) Transportation * Abe S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamagata Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu. Yamagata Prefecture has a population of 1,079,950 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of 9,325 km² (3,600 sq mi). Yamagata Prefecture borders Akita Prefecture to the north, Miyagi Prefecture to the east, Fukushima Prefecture to the south, and Niigata Prefecture to the southwest. Yamagata is the capital and largest city of Yamagata Prefecture, with other major cities including Tsuruoka, Sakata, and Yonezawa. Yamagata Prefecture is located on Japan's western Sea of Japan coast and its borders with neighboring prefectures are formed by various mountain ranges, with 17% of its total land area being designated as Natural Parks. Yamagata Prefecture formed the southern half of the historic Dewa Province with Akita Prefecture and is home to the Three Mountains of Dewa, which includes the Haguro Five-story Pagoda, a recognised National Treasure of Japan. History The aboriginal people once inhabited the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nara, Nara
is the capital city of Nara Prefecture, Japan. As of 2022, Nara has an estimated population of 367,353 according to World Population Review, making it the largest city in Nara Prefecture and sixth-largest in the Kansai region of Honshu. Nara is a core city located in the northern part of Nara Prefecture bordering the Kyoto Prefecture. Nara was the capital of Japan during the Nara period from 710 to 794 as the seat of the Emperor before the capital was moved to Kyoto. Nara is home to eight temples, shrines, and ruins, specifically Tōdai-ji, Saidai-ji, Kōfuku-ji, Kasuga Shrine, Gangō-ji, Yakushi-ji, Tōshōdai-ji, and the Heijō Palace, together with Kasugayama Primeval Forest, collectively form the Historic Monuments of Ancient Nara, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Etymology By the Heian period, a variety of different characters had been used to represent the name Nara: , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and . A number of theories for the origin of the name "Nara" have been pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamato Dynasty
The , also referred to as the Imperial Family or the House of Yamato, comprises those members of the extended family of the reigning Emperor of Japan who undertake official and public duties. Under the present Constitution of Japan, the Emperor is "the symbol of the State and of the unity of the people". Other members of the Imperial Family perform ceremonial and social duties, but have no role in the affairs of government. The duties as an Emperor are passed down the line to their male children. This Japanese monarchy is the oldest continuous hereditary monarchy in the world. The Imperial House recognizes 126 monarchs, beginning with Emperor Jimmu (traditionally dated to 11 February 660 BC), and continuing up to the current emperor, Naruhito. However, scholars have agreed that there is no evidence of Jimmu's existence, that the traditional narrative of Japan’s founding is mythical, and that Jimmu is a mythical figure. Historical evidence for the first 25 emperors is mythical, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |