|
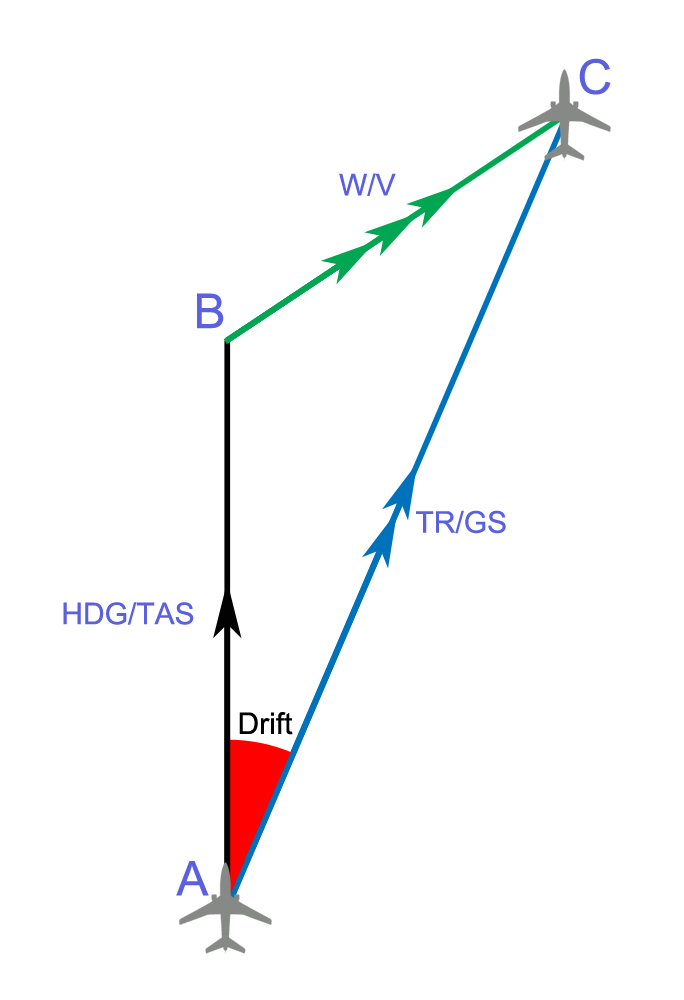
Aircraft Heading
In navigation, the heading of a vessel or aircraft is the compass direction in which the craft's bow or nose is pointed. Note that the heading may not necessarily be the direction that the vehicle actually travels, which is known as its ''course'' or ''track''. Any difference between the heading and course is due to the motion of the underlying medium, the air or water, or other effects like skidding or slipping. The difference is known as the ''drift'', and can be determined by the '' wind triangle''. At least seven ways to measure the heading of a vehicle have been described. Notation Heading is typically based on cardinal directions, so 0° (or 360°) indicates a direction toward true north, 90° true east, 180° true south, and 270° true west. TVMDC TVMDC is a mnemonic for converting true, magnetic and compass headings. TVMDC is a mnemonic initialism for true heading, variation, magnetic heading, deviation, compass heading. The most common use of the TVMDC method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Drift
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their spatial scale, their speed and direction, the forces that cause them, the regions in which they occur, and their effect. Winds have various a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Magnetic North Pole. The North Pole is by definition the northernmost point on the Earth, lying antipodally to the South Pole. It defines geodetic latitude 90° North, as well as the direction of true north. At the North Pole all directions point south; all lines of longitude converge there, so its longitude can be defined as any degree value. No time zone has been assigned to the North Pole, so any time can be used as the local time. Along tight latitude circles, counterclockwise is east and clockwise is west. The North Pole is at the center of the Northern Hemisphere. The nearest land is usually said to be Kaffeklubben Island, off the northern coast of Greenland about away, though some perhaps semi-permanent gravel banks lie slightly clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heading Indicator
The heading indicator (HI), also known as a directional gyro (DG) or direction indicator (DI), is a flight instrument used in an aircraft to inform the pilot of the aircraft's heading. Use The primary means of establishing the heading in most small aircraft is the magnetic compass, which, however, suffers from several types of errors, including that created by the "dip" or downward slope of the Earth's magnetic field. Dip error causes the magnetic compass to read incorrectly whenever the aircraft is in a bank, or during acceleration or deceleration, making it difficult to use in any flight condition other than unaccelerated, perfectly straight and level. To remedy this, the pilot will typically maneuver the airplane with reference to the heading indicator, as the gyroscopic heading indicator is unaffected by dip and acceleration errors. The pilot will periodically reset the heading indicator to the heading shown on the magnetic compass.Bowditch, NathanielAmerican Practica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bearing (navigation)
In navigation, bearing or azimuth is the horizontal angle between the direction of an object and north or another object. The angle value can be specified in various angular units, such as degrees, mils, or grad. More specifically: * Absolute bearing refers to the angle between the magnetic north (''magnetic bearing'') or true north (''true bearing'') and an object. For example, an object to due east would have an absolute bearing of 90 degrees. Thus, it is the same as azimuth.U.S. Army, ''Advanced Map and Aerial Photograph Reading'', Headquarters, War Department, Washington, D.C. (17 September 1941), pp. 24-2/ref> * #Relative, Relative bearing refers to the angle between the craft's forward direction ( heading) and the location of another object. For example, an object relative bearing of 0 degrees would be immediately in front; an object relative bearing 180 degrees would be behind. Bearings can be measured in mils, points, or degrees. Thus, it is the same as an ''a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth. The plastic matrix may be a thermoset polymer matrix—most often based on thermosetting polymers such as epoxy, polyester resin, or vinyl ester resin—or a thermoplastic. Cheaper and more flexible than carbon fiber, it is stronger than many metals by weight, non- magnetic, non- conductive, transparent to electromagnetic radiation, can be molded into complex shapes, and is chemically inert under many circumstances. Applications include aircraft, boats, automobiles, bath tubs and enclosures, swimming pools, hot tubs, septic tanks, water tanks, roofing, pipes, cladding, orthopedic casts, surfboards, and external door skins. Other common names for fiberglass are glass-reinforced plastic (GRP), glass-fiber reinforced plastic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Deviation
Magnetic deviation is the error induced in a compass by ''local'' magnetic fields, which must be allowed for, along with magnetic declination, if accurate bearings are to be calculated. (More loosely, "magnetic deviation" is used by some to mean the same as "magnetic declination". This article is about the former meaning.) Compass readings Compasses are used to determine the direction of true North. However, the compass reading must be corrected for two effects. The first is magnetic declination or variation—the angular difference between ''magnetic North'' (the local direction of the Earth's magnetic field) and true North.Admiralty Manual of Navigation Vol 1 1964 p12 The second is ''magnetic deviation''—the angular difference between magnetic North and the compass needle due to nearby sources of interference such as magnetically permeable bodies, or other magnetic fields within the field of influence. Sources In navigation manuals, ''magnetic deviation'' refers specificall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compass Rose
A compass rose, sometimes called a wind rose, rose of the winds or compass star, is a figure on a compass, map, nautical chart, or monument used to display the orientation of the cardinal directions (north, east, south, and west) and their intermediate points. It is also the term for the graduated markings found on the traditional magnetic compass. Today, a form of compass rose is found on, or featured in, almost all navigation systems, including nautical charts, non-directional beacons (NDB), VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) systems, global-positioning systems (GPS), and similar equipment. Types Linguistic anthropological studies have shown that most human communities have four points of cardinal direction. The names given to these directions are usually derived from either locally-specific geographic features (e.g. "towards the hills", "towards the sea") or from celestial bodies (especially the sun) or from atmospheric features (winds, temperature). Most mobile populations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonic Line
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph of the function f(x,y) parallel to the (x,y)-plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value. In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines, for example a topographic map, which thus shows valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. The gradient of the function is always perpendicular to the contour lines. When the lines are close together the magnitude of the grad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Variation
Magnetic declination, or magnetic variation, is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north (the direction the north end of a magnetized compass needle points, corresponding to the direction of the Earth's magnetic field lines) and true north (the direction along a meridian towards the geographic North Pole). This angle varies depending on position on the Earth's surface and changes over time. Somewhat more formally, Bowditch defines variation as “the angle between the magnetic and geographic meridians at any place, expressed in degrees and minutes east or west to indicate the direction of magnetic north from true north. The angle between magnetic and grid meridians is called grid magnetic angle, grid variation, or grivation.” By convention, declination is positive when magnetic north is east of true north, and negative when it is to the west. '' Isogonic lines'' are lines on the Earth's surface along which the declination has the same constant value, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Deviation
Magnetic deviation is the error induced in a compass by ''local'' magnetic fields, which must be allowed for, along with magnetic declination, if accurate bearings are to be calculated. (More loosely, "magnetic deviation" is used by some to mean the same as "magnetic declination". This article is about the former meaning.) Compass readings Compasses are used to determine the direction of true North. However, the compass reading must be corrected for two effects. The first is magnetic declination or variation—the angular difference between ''magnetic North'' (the local direction of the Earth's magnetic field) and true North.Admiralty Manual of Navigation Vol 1 1964 p12 The second is ''magnetic deviation''—the angular difference between magnetic North and the compass needle due to nearby sources of interference such as magnetically permeable bodies, or other magnetic fields within the field of influence. Sources In navigation manuals, ''magnetic deviation'' refers specificall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic North
The north magnetic pole, also known as the magnetic north pole, is a point on the surface of Earth's Northern Hemisphere at which the planet's magnetic field points vertically downward (in other words, if a magnetic compass needle is allowed to rotate in three dimensions, it will point straight down). There is only one location where this occurs, near (but distinct from) the geographic north pole. The geomagnetic north pole is the northern antipodal pole of an ideal dipole model of the Earth's magnetic field, which is the most closely fitting model of Earth's actual magnetic field. The north magnetic pole moves over time according to magnetic changes and flux lobe elongation in the Earth's outer core. In 2001, it was determined by the Geological Survey of Canada to lie west of Ellesmere Island in northern Canada at . It was situated at in 2005. In 2009, while still situated within the Canadian Arctic at , it was moving toward Russia at between per year. As of 2021, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |