|
Aikido Techniques
Aikido techniques are frequently referred to as ''waza'' 技 (which is Japanese for technique, art or skill). Aikido training is based primarily on two partners practicing pre-arranged forms ('' kata'') rather than freestyle practice. The basic pattern is for the receiver of the technique (''uke'') to initiate an attack against the person who applies the technique—the 取り '' tori'', or ''shite'' , (depending on aikido style) also referred to as ( ''nage'' (when applying a throwing technique), who neutralises this attack with an aikido technique. Both halves of the technique, that of ''uke'' and that of ''tori'', are considered essential to aikido training. Both are studying aikido principles of blending and adaptation. ''Tori'' learns to blend with and control attacking energy, while ''uke'' learns to become calm and flexible in the disadvantageous, off-balance positions in which ''tori'' places him. This "receiving" of the technique is called ''ukemi''. ''Uke'' continuously s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aikido
Aikido ( , , , ) is a modern Japanese martial art that is split into many different styles, including Iwama Ryu, Iwama Shin Shin Aiki Shuren Kai, Shodokan Aikido, Yoshinkan, Renshinkai, Aikikai and Ki Aikido. Aikido is now practiced in around 140 countries. It was originally developed by Morihei Ueshiba, as a synthesis of his martial studies, philosophy and religious beliefs. Ueshiba's goal was to create an art that practitioners could use to defend themselves while also protecting their attackers from injury. Aikido is often translated as "the way of unifying (with) life energy" or as "the way of harmonious spirit". According to the founder's philosophy, the primary goal in the practice of aikido is to overcome oneself instead of cultivating violence or aggressiveness. Morihei Ueshiba used the phrase to refer to this principle. Aikido's fundamental principles include: (entering), , (breathing control), (triangular principle) and (turning) movements that redirect the oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip. A slashing sword is more likely to be curved and to have a sharpened cutting edge on one or both sides of the blade. Many swords are designed for both thrusting and slashing. The precise definition of a sword varies by historical epoch and geographic region. Historically, the sword developed in the Bronze Age, evolving from the dagger; the earliest specimens date to about 1600 BC. The later Iron Age sword remained fairly short and without a crossguard. The spatha, as it developed in the Late Roman army, became the predecessor of the European sword of the Middle Ages, at first adopted as the Migration Period sword, and only in the High Middle Ages, developed into the classical arming sword with crossguard. The word '' sword'' continue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choku-tsuki
derives from the verb , meaning "to thrust". The second syllable is accented, with Japanese's unvoiced vowels making it pronounced almost like "ski" (but preceded by a "t" sound). In Japanese martial arts and Okinawan martial arts, ''tsuki'' is used to refer to various thrusting techniques. Tsuki in Karate In karate and its variants, the term ''tsuki'' is used as a part of a compound word for any one of a variety of thrusting techniques (usually punches). It is never used as a stand-alone term to describe a discrete technique. For example, ''gyaku seiken chudan-tsuki'', more commonly referred to as ''chudan-tsuki'' (段突), refers to a mid-level (''chudan'') punch (''tsuki'') executed with the rear (''gyaku'') arm. Note that in a compound word, where ''tsuki'' does not come first, its pronunciation and writing changes slightly due to rendaku, and it is pronounced as "''zuki''" (and is sometimes transliterated that way). Performing a Choku-Tsuki (Straight Punch) in Karate T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
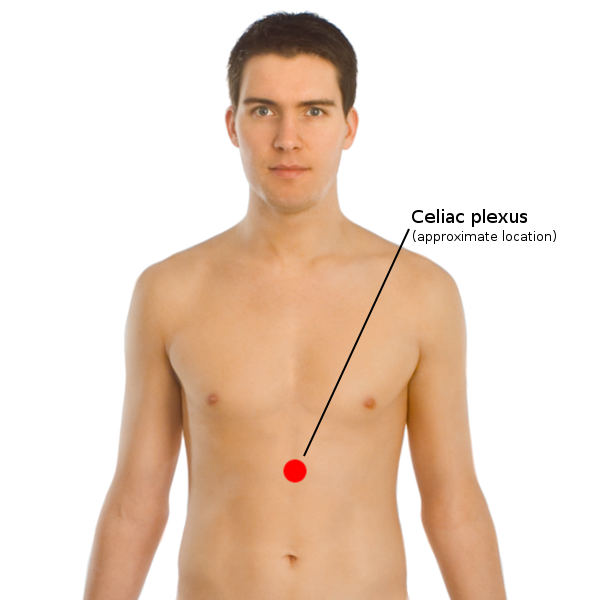
Solar Plexus
The celiac plexus, also known as the solar plexus because of its radiating nerve fibers, is a complex network of nerves located in the abdomen, near where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, and renal arteries branch from the abdominal aorta. It is behind the stomach and the omental bursa, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra. The plexus is formed in part by the greater and lesser splanchnic nerves of both sides, and fibers from the anterior and posterior vagal trunks. The celiac plexus proper consists of the celiac ganglia with a network of interconnecting fibers. The aorticorenal ganglia are often considered to be part of the celiac ganglia, and thus, part of the plexus. Structure The celiac plexus includes a number of smaller plexuses: Other plexuses that are derived from the celiac plexus: Terminology The celiac plexus is often popularly referred to as the solar plexus. In the context of sparring or inj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' "breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torso
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including humans), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a human — is usually divided into the ''thoracic'' segment (also known as the upper torso, where the forelimbs extend), the ''abdominal'' segment (also known as the "mid-section" or "midriff"), and the ''pelvic'' and '' perineal'' segments (sometimes known together with the abdomen as the lower torso, where the hindlimbs extend). Anatomy Major organs In humans, most critical organs, with the notable exception of the brain, are housed within the torso. In the upper chest, the heart and lungs are protected by the rib cage, and the abdomen contains most of the organs responsible for digestion: the stomach, which breaks down partially digested food via gastric acid; the liver, which respectively produces bile necessary for digestion; the large and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punch (strike)
A punch is a striking blow with the fist. It is used in most martial arts and combat sports, most notably boxing, where it is the only type of offensive technique allowed. In sports, hand wraps or other padding such as gloves may be used to protect athletes and practitioners from injuring themselves. The use of punches varies between different martial arts and combat sports. Styles such as boxing, Suntukan or Russian fist fighting use punches alone, while others such as Kickboxing, Muay Thai, Lethwei or karate may use both punches and kicks. Others such as wrestling (excluding professional wrestling) and judo (punches and other striking techniques, atemi, are present in judo kata, but are forbidden in competitions) do not use punches at all. There are many types of punches and as a result, different styles encompass varying types of punching techniques. Basic types This is not a comprehensive list of all punches and may need to be updated, due to the large diversity of schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillary Sinus
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the osteomeatal complex.Human Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209-210 Structure It is the largest air sinus in the body. Found in the body of the maxilla, this sinus has three recesses: an alveolar recess pointed inferiorly, bounded by the alveolar process of the maxilla; a zygomatic recess pointed laterally, bounded by the zygomatic bone; and an infraorbital recess pointed superiorly, bounded by the inferior orbital surface of the maxilla. The medial wall is composed primarily of cartilage. The ostia for drainage are located high on the medial wall and open into the semilunar hiatus of the lateral nasal cavity; because of the position of the ostia, gravity cannot drain the maxillary sinus contents when the head is erect (see pathology). The ostium of the maxillary sinus is high up on the medial wall and on average is 2. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown (anatomy)
The crown is the top portion of the head behind the vertex. The anatomy of the crown varies between different organisms. The human crown is made of three layers of the scalp above the skull. The crown also covers a range of bone sutures, and contains blood vessels and branches of the trigeminal nerve. The structure of the human crown provides a protective cavity for the brain and optimizes the crown's ability to ensure the neocortex is safe. Different parts of the neocortex, such as the frontal lobe and the parietal lobe, are protected by the meninges and bone structures. Other organisms, such as whales, have their blowholes on their crown, causing a flattened head shape. Some bird species have a crest located on their crown, used for communication and courtship. Macroevolution of the human crown has led to different structures between modern and archaic human species, such as significant changes to the cranial vault. The human crown is prone to different injuries and disord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knifehand Strike
In martial arts, a knifehand strike is a strike using the part of the hand opposite the thumb (from the little finger to the wrist), familiar to many people as a karate chop (in Japanese, ''shutō-uchi''). This refers to strikes performed with the side of the knuckle of the small finger. Suitable targets for the knifehand strike include the Carotid Sinus which leads to unconsciousness, mastoid muscles of the neck, the jugular, the throat, the collar bones, ribs, sides of the head, temple, jaw, the third vertebra (key stone of the spinal column), the upper arm, the wrist (knifehand block), the elbow (outside knifehand block), and the knee cap (leg throw). In many Japanese, Korean, and Chinese styles, the knifehand is used to block as well as to strike. Japanese martial arts is a term from Japanese martial arts like aikido and Chinese-Okinawan martial arts like karate and Shorinji Kempo referring to a hand position that resembles that of the blade of a sword. This can be in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kick
A kick is a physical Strike (attack), strike using the leg, in unison usually with an area of the knee or lower using the foot, heel, tibia (shin), ball of the foot, blade of the foot, toes or knee (the latter is also known as a knee (strike), knee strike). This type of attack is used frequently by hoof, hooved animals as well as humans in the context of stand-up fighting. Kicks play a significant role in many forms of martial arts, such as capoeira, kalaripayattu, karate, kickboxing, kung fu, Mixed martial arts, MMA, Muay thai, pankration, pradal serey, savate, sikaran, silat, taekwondo, vovinam, and Yaw-Yan. Kicks are a universal act of aggression among humans. Kicking is also prominent from its use in many sports, especially those called football. The best known of these sports is association football, also known as soccer. History The English verb :wikt:kick, to kick appears only in the late 14th century, apparently as a loan from Old Norse, originally in the sense of a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |