|
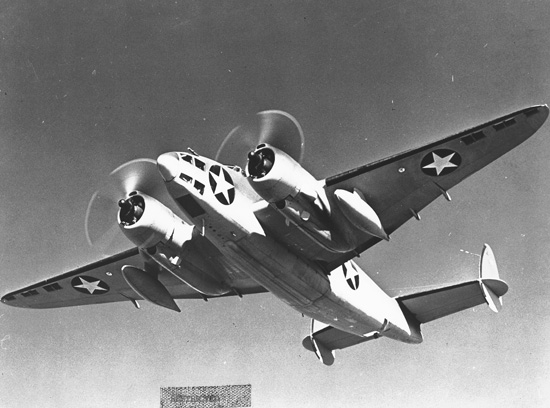
AiRover
The Vega Aircraft Corporation was a subsidiary of the Lockheed Aircraft Company in Burbank, California responsible for much of its parent company's production in World War II. History The company was first formed in August 1937 as the AiRover Company to produce a new light aircraft design. It was renamed in May 1938 to honor Lockheed's first aircraft design, the Vega. The AiRover Model 1 was a Lockheed Altair fitted with a Menasco Unitwin 2-544 engine, which featured two engines driving a single shaft. The AiRover Model 2 was a new design named the Vega Starliner. One Starliner prototype was built and tested, but the design did not go into production. In 1940, with World War II already underway in Europe, Vega changed its focus from light aircraft to military aircraft. The company began by producing five North American NA-35 trainers under license with North American Aviation. Production by Vega really got underway with the Hudson, a patrol bomber designed for use by the Roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menasco Unitwin 2-544
The Menasco Unitwin 2-544 was a coupled piston engine. Menasco Motors Company of Burbank, California was a well known manufacturer of inverted inline four and six cylinder engines. At the request of Lockheed Aircraft designers, Menasco produced an inverted twelve-cylinder air cooled aircraft engine by designing a common crankcase and gearbox for two of the six cylinder engines. The two crankshafts were combined with a unique double clutch gearbox to power a single propeller. This gave reliability of a twin engine aircraft in a single powerplant. It was a success, but did not enter production as no aircraft were produced that used it. Design and development In mid-1935 Lockheed's chief engineer, Hall Hibbard, began discussing with Al Menasco, the president of the Menasco Motors Company in Burbank, the merits of coupling two Menasco C6S Super Buccaneer six-cylinder in-line engines mounted side-by-side, driving a single propeller. In 1937 Lockheed established the AiRover Aircraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Altair
The Lockheed Altair was a single-engined sport aircraft produced by Lockheed Aircraft Limited in the 1930s. It was a development of the Lockheed Sirius with a retractable undercarriage, and was the first Lockheed aircraft and one of the first aircraft designs with a fully retractable undercarriage. Development and design Lockheed designed an alternative wing fitted with a retractable undercarriage for the Lockheed Sirius as a result of a request from Charles Lindbergh, although Lindbergh in the end chose to buy a standard Sirius. The first Altair, converted from a Sirius, flew in September 1930.Francillon 1982, p. 101. Like the Sirius, the Altair was a single-engined, low-winged monoplane of wooden construction. The undercarriage, which was operated by use of a hand crank, retracted inwards. Four Altairs following the prototype were converted Sirii, with another six Altairs built from scratch: three by Lockheed, two by the Detroit Aircraft Corporation, and one by AiRover. The Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
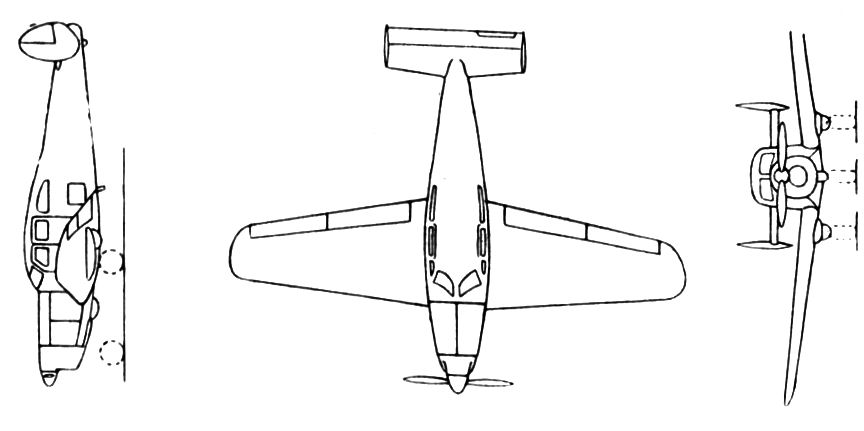
Vega Model 2 Starliner
The Vega Model 2 Starliner was a prototype five-seat feeder airliner produced by the Vega Airplane Company, a subsidiary of Lockheed. It was designed to be powered by an unusual powerplant, consisting of two Menasco piston engines coupled together to drive a single propeller. A single example was built, flying in 1939, but no production followed. Design and development In 1935 Lockheed chief engineer Hall Hibbard discussed with Al Menasco the coupling of two Menasco C6S-4 engines mounted side-by side, driving a single propeller. In 1937, a Lockheed subsidiary, the AiRover Company, designed the Model 2 Starliner, to be powered by the new Menasco U2-544 Unitwin engine. The Starliner was a low-wing monoplane constructed with a light-alloy semi-monocoque structure conventional tail and rearward retracting undercarriage which remained exposed when retracted. The enclosed cabin was available in two cabin layouts: a custom luxury setup for private owners or a "Starliner" five seat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vega Starliner
The Vega Model 2 Starliner was a prototype five-seat feeder airliner produced by the Vega Airplane Company, a subsidiary of Lockheed. It was designed to be powered by an unusual powerplant, consisting of two Menasco piston engines coupled together to drive a single propeller. A single example was built, flying in 1939, but no production followed. Design and development In 1935 Lockheed chief engineer Hall Hibbard discussed with Al Menasco the coupling of two Menasco C6S-4 engines mounted side-by side, driving a single propeller. In 1937, a Lockheed subsidiary, the AiRover Company, designed the Model 2 Starliner, to be powered by the new Menasco U2-544 Unitwin engine. The Starliner was a low-wing monoplane constructed with a light-alloy semi-monocoque structure conventional tail and rearward retracting undercarriage which remained exposed when retracted. The enclosed cabin was available in two cabin layouts: a custom luxury setup for private owners or a "Starliner" five seat c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Air Terminal
Hollywood Burbank Airport, legally and formerly marketed as Bob Hope Airport after entertainer Bob Hope , is a public airport northwest of downtown Burbank, California, Burbank, in Los Angeles County, California, United States.. Federal Aviation Administration. effective November 9, 2017 The airport serves Downtown Los Angeles and the northern Greater Los Angeles area, which include Glendale, California, Glendale, Pasadena, California, Pasadena, and the San Fernando Valley. It is closer to many popular attractions including Griffith Park, Universal Studios Hollywood, Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood, and Downtown Los Angeles than Los Angeles International Airport (LAX), and is the only airport in the area with a direct rail connection to Downtown Los Angeles, with service from two stations: Burbank Airport–North station, Burbank Airport–North and Burbank Airport–South station, Burbank Airport–South. Nonstop flights mostly serve cities in the western United States, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vega Model 40
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only from the Sun, and one of the most luminous stars in the Sun's neighborhood. It is the fifth-brightest star in the night sky, and the second-brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus. Vega has been extensively studied by astronomers, leading it to be termed "arguably the next most important star in the sky after the Sun". Vega was the northern pole star around 12,000 BCE and will be so again around the year 13,727, when its declination will be . Vega was the first star other than the Sun to have its image and spectrum photographed. It was one of the first stars whose distance was estimated through parallax measurements. Vega has functioned as the baseline for calibrating the photometric brightness scale and was one of the stars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing XB-38 Flying Fortress
The XB-38 Flying Fortress was a single example conversion of a production B-17E Flying Fortress, testing whether the Allison V-1710 V type engine could be substituted for the standard Wright R-1820 radial engine during early World War II. Design and development The XB-38 was the result of a modification project undertaken by Vega (a subsidiary of Lockheed) on a Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress to fit it with liquid-cooled Allison V-1710-89 V-12 engines. It was meant as an improved version of the B-17, and a variant that could be used if air-cooled Wright R-1820 radial engines became scarce. Completing the modifications took less than a year, and the XB-38 made its first flight on May 19, 1943. Only one prototype was built, and it was developed from an existing B-17 bomber. While the XB-38 delivered a substantially higher top speed, its service ceiling was lower. After a few flights it had to be grounded due to a problem with engine manifold joints leaking exhaust gases. Following t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing YB-40 Flying Fortress
The Boeing YB-40 Flying Fortress was a modification for operational testing purposes of the B-17 Flying Fortress bomber aircraft, converted to act as a heavily armed Gunship#Bomber escort, gunship to support other bombers during World War II. At the time of its development, long-range fighter aircraft such as the North American P-51 Mustang were just entering quantity production, and thus were not yet available to accompany bombers all the way from England to Germany and back. Design and development Work on the prototype, Project V-139, began in September 1942 by converting the second production B-17F-1-BO (serial number 41-24341) built. Conversion work was done by Lockheed's Vega company. The aircraft differed from the standard B-17 in that a second manned Gun turret#Aircraft, dorsal turret was installed in the former radio compartment, just behind the bomb bay and forward of the ventral ball turret's location. The single .50-caliber light-barrel (12.7 mm) M2 Browning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Ventura
The Lockheed Ventura is a twin-engine medium bomber and patrol bomber of World War II. The Ventura first entered combat in Europe as a bomber with the RAF in late 1942. Designated PV-1 by the United States Navy (US Navy), it entered combat in 1943 in the Pacific. The bomber was also used by the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), which designated it the Lockheed B-34 (''Lexington'') and B-37 as a trainer. British Commonwealth forces also used it in several guises, including antishipping and antisubmarine search and attack. The Ventura was developed from the Lockheed Model 18 Lodestar transport, as a replacement for the Lockheed Hudson bombers then in service with the Royal Air Force. Used in daylight attacks against occupied Europe, they proved to have weaknesses and were removed from bomber duty and some used for patrols by Coastal Command. After USAAF monopolization of land-based bombers was removed, the US Navy ordered a revised design which entered service as the PV-2 H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Aircraft Company
The Douglas Aircraft Company was an American aerospace manufacturer based in Southern California. It was founded in 1921 by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. and later merged with McDonnell Aircraft in 1967 to form McDonnell Douglas; it then operated as a division of McDonnell Douglas. McDonnell Douglas later merged with Boeing in 1997. History 1920s The company was founded as the Douglas Company by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. on July 22, 1921 in Santa Monica, California, following dissolution of the Davis-Douglas Company. An early claim to fame was the first circumnavigation of the world by air in Douglas airplanes in 1924. In 1923, the U.S. Army Air Service was interested in carrying out a mission to circumnavigate the Earth for the first time by aircraft, a program called "World Flight". Donald Douglas proposed a modified Douglas DT to meet the Army's needs. The two-place, open cockpit DT biplane torpedo bomber had previously been produced for the U.S. Navy.Rumerman, Judy. "The Dougla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California During World War II
California during World War II was a major contributor to the World War II effort. California's long Pacific Ocean coastline provided the support needed for the Pacific War. California also supported the war in Europe. After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941, most of California's manufacturing was shifted to the war effort. California became a major ship builder and aircraft manufacturer. Existing military installations were enlarged and many new ones were built. California trained many of the troops before their oversea deployment. Over 800,000 Californians served in the United States Armed Forces. California agriculture, ranches and farms were used to feed the troops around the world. California's long coastline also put the state in fear, as an attack on California seemed likely. California was used for the temporary and permanent internment camps for Japanese Americans. The population of California grew significantly, largely due to servicemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Corporation
The Lockheed Corporation was an American aerospace manufacturer. Lockheed was founded in 1926 and later merged with Martin Marietta to form Lockheed Martin in 1995. Its founder, Allan Lockheed, had earlier founded the similarly named but otherwise-unrelated Loughead Aircraft Manufacturing Company, which was operational from 1912 to 1920. History Origins Allan Loughead and his brother Malcolm Loughead had operated an earlier aircraft company, Loughead Aircraft Manufacturing Company, which was operational from 1912 to 1920. The company built and operated aircraft for paying passengers on sightseeing tours in California and had developed a prototype for the civil market, but folded in 1920 due to the flood of surplus aircraft deflating the market after World War I. Allan went into the real estate market while Malcolm had meanwhile formed a successful company marketing brake systems for automobiles. On December 13, 1926, Allan Lockheed, Jack Northrop, John Northrop, Kenneth K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_JP7769673.jpg)



