|
Agha Muhammad Reza
Mirza Agha Muhammad Reza Baig ( bn, а¶Ѓа¶ња¶∞аІНа¶Ьа¶Ља¶Њ а¶Жа¶Ча¶Њ а¶ЃаІЛа¶єа¶Ња¶ЃаІНඁබ а¶∞аІЗа¶Ьа¶Ља¶Њ а¶ђаІЗа¶Ч, fa, ўЕўКЎ±Ў≤ЎІ ЎҐЎЇЎІ ўЕЎ≠ўЕЎѓ Ў±ЎґЎІ Ў®џМЏѓ), also known by his followers as Pir Ferutupi ( bn, ඙аІАа¶∞ а¶ЂаІЗа¶∞аІБа¶ЯаІБ඙ග),. was a Mughal nobleman and Shia Sufi pir from Sylhet, of Iranian origin. He overthrew the Kachari Kingdom and revolted against the East India Company with the assistance of the local peasantry. Early life and background The honorific title ''Mirza'' was added before his name and ''Baig'' as a suffix. This was the historical naming convention for the descendants of the Mughal dynasty. The Mughal Empire was defeated by the East India Company in the Battle of Plassey of 1757, and an anti-British sentiment was common among the natives of the Indian subcontinent and especially those related to and being descended from the noble dynasty such as Reza. His parents were Iranians and he was an adherent of Shia Islam. Reza was based in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackets
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or 'right' bracket or, alternatively, an "opening bracket" or "closing bracket", respectively, depending on the Writing system#Directionality, directionality of the context. Specific forms of the mark include parentheses (also called "rounded brackets"), square brackets, curly brackets (also called 'braces'), and angle brackets (also called 'chevrons'), as well as various less common pairs of symbols. As well as signifying the overall class of punctuation, the word "bracket" is commonly used to refer to a specific form of bracket, which varies from region to region. In most English-speaking countries, an unqualified word "bracket" refers to the parenthesis (round bracket); in the United States, the square bracket. Glossary of mathematical sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, а¶ђа¶Ња¶Ва¶≤а¶Њ/а¶ђа¶ЩаІНа¶Ч, translit=BƒБnglƒБ/B√іng√і, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predominantly covering present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal. Geographically, it consists of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta system, the largest river delta in the world and a section of the Himalayas up to Nepal and Bhutan. Dense woodlands, including hilly rainforests, cover Bengal's northern and eastern areas, while an elevated forested plateau covers its central area; the highest point is at Sandakphu. In the littoral southwest are the Sundarbans, the world's largest mangrove forest. The region has a monsoon climate, which the Bengali calendar divides into six seasons. Bengal, then known as Gangaridai, was a leading power in ancient South Asia, with extensive trade networks forming connections to as far away as Roman Egypt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
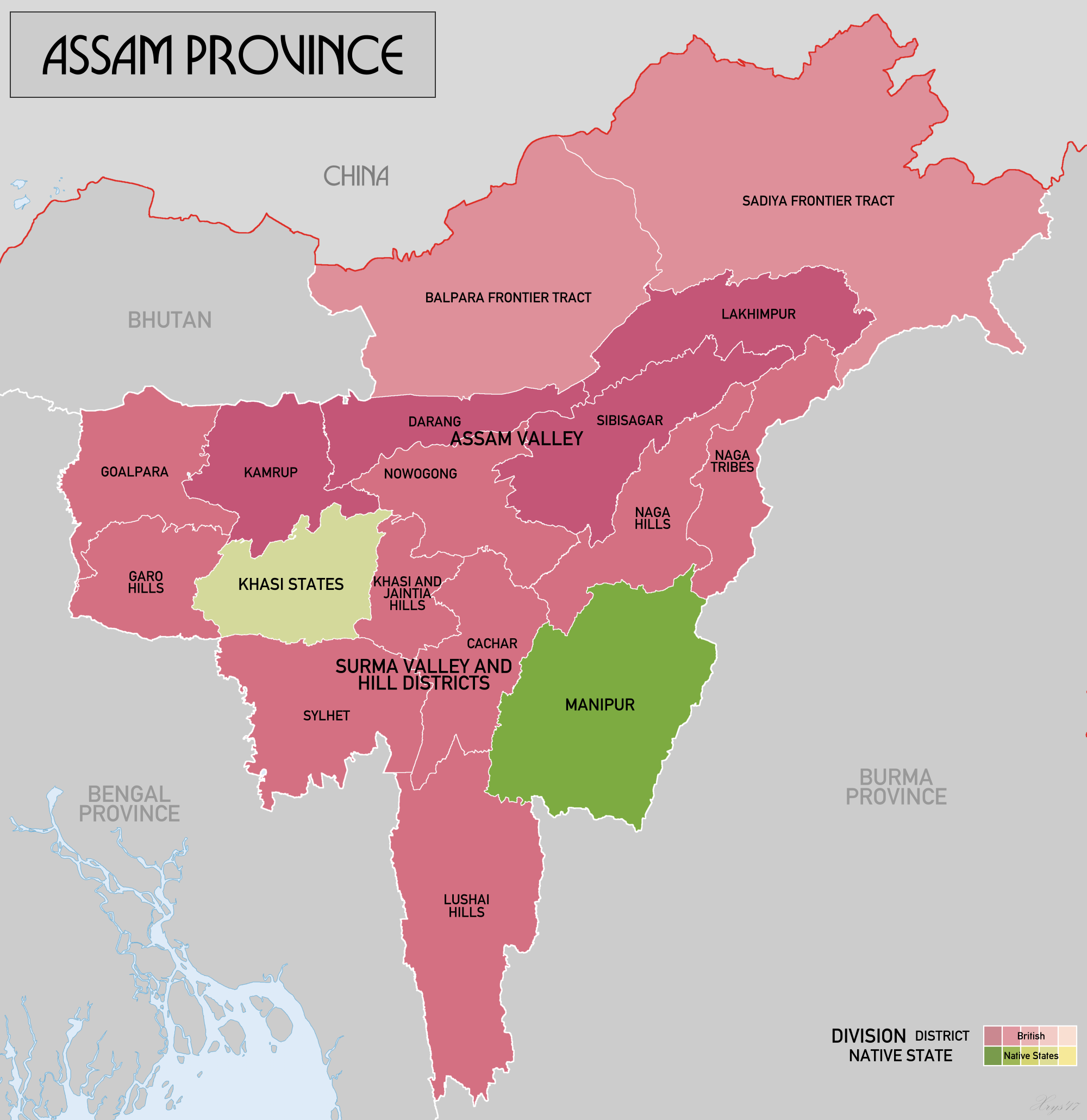
Sylhet Division
Sylhet Division ( bn, а¶Єа¶ња¶≤аІЗа¶Я а¶ђа¶ња¶≠а¶Ња¶Ч) is the northeastern division of Bangladesh. It is bordered by the Indian states of Meghalaya, Assam and Tripura to the north, east and south respectively, and by the Bangladeshi divisions of Chittagong to the southwest and Dhaka and Mymensingh to the west. Prior to 1947, it included the subdivision of Karimganj (presently in Barak Valley, India). However, Karimganj (including the thanas of Badarpur, Patharkandi and Ratabari) was inexplicably severed from Sylhet by the Radcliffe Boundary Commission. According to Niharranjan Ray, it was partly due to a plea from a delegation led by Abdul Matlib Mazumdar. Etymology and names The name ''Sylhet'' is an anglicisation of ''Shilhot'' (පගа¶≤а¶єа¶Я). Its origins seem to come from the Sanskrit words පගа¶≤а¶Њ ''≈ЫilƒБ'' (meaning 'stone') and а¶єа¶ЯаІНа¶Я ''haбє≠бє≠a'' (meaning 'marketplace'). These words match the landscape and topography of the hilly region. The shila stones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subaltern (military)
A subaltern () is a primarily British military term for a junior officer. Literally meaning "subordinate", subaltern is used to describe commissioned officers below the rank of captain and generally comprises the various grades of lieutenant. United Kingdom In the British Army, the senior subaltern rank was captain-lieutenant, obsolete since the 18th century. Before the Cardwell Reforms of the British Army in 1871, the ranks of cornet and ensign were the junior subaltern ranks in the cavalry and infantry respectively, and were responsible for the flag. A subaltern takes temporary command of proceedings during Trooping the Colour. Within the ranks of subaltern, in a battalion or regiment, a Senior Subaltern may be appointed, usually by rank and seniority, who is responsible for discipline within the junior officer ranks and is responsible to the adjutant for this duty, although the adjutant is ultimately responsible to the commanding officer for the discipline of all the junior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuki People
The Kuki people are an ethnic group native to the Mizo Hills (formerly Lushai), a mountainous region in the southeastern part of Mizoram and Manipur in India. The Kuki constitute one of several hill tribes within India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. In Northeast India, they are present in all states except Arunachal Pradesh. Some fifty tribes of Kuki peoples in India are recognised as scheduled tribes, based on the dialect spoken by that particular Kuki community as well as their region of origin. The Chin people of Myanmar and the Mizo people of Mizoram are kindred tribes of the Kukis. Collectively, they are termed the Zo people. History Early history The early history of the Kukis is obscure. The origin of the word "Kuki" is uncertain; it is an exonym: it was not originally as a self-designation by the tribes that are now called Kukis. According to the colonial British writer Adam Scott Reid, the earliest reference to the word Kuki can be dated to 1777 CE, when it first appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naga People
Nagas are various ethnic groups native to northeastern India and northwestern Myanmar. The groups have similar cultures and traditions, and form the majority of population in the Indian states of Nagaland and Manipur and Naga Self-Administered Zone of Myanmar; with significant populations in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in India; Sagaing Region and Kachin State in Myanmar (Burma). The Nagas are divided into various Naga ethnic groups whose numbers and population are unclear. They each speak distinct Naga languages often unintelligible to the others, but all are somehow in a way loosely connected to each other. Etymology The present day Naga people have been called by many names, like 'Noga' by Assamese, 'Hao' by Manipuri and 'Chin' by Burmese. However, over time 'Naga' became the commonly accepted nomenclature, and was also used by the British. According to the Burma Gazetteer, the term 'Naga' is of doubtful origin and is used to describe hill tribes that occupy the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelfth Imam
MuбЄ•ammad ibn al-бЄ§asan al-MahdƒЂ ( ar, ўЕЎ≠ўЕЎѓ Ў®ўЖ ЎІўДЎ≠Ў≥ўЖ ЎІўДўЕўЗЎѓўК) is believed by the Twelver Shia to be the last of the Twelve Imams and the eschatological Mahdi, who will emerge in the end of time to establish peace and justice and redeem Islam. Hasan al-Askari, the eleventh Imam, died in 260 AH (873-874 CE), possibly poisoned by the Abbasids. Immediately after his death, his main representative, Uthman ibn Sa'id, claimed that the eleventh Imam had an infant son named Muhammad, who was kept hidden from the public out of fear of Abbasid persecution. Uthman also claimed to represent Muhammad, who had entered a state of occultation. Other local representatives of al-Askari largely supported these assertions, while the Shia community fragmented into several sects over al-Askari's succession. All these sects, however, are said to have disappeared after a few decades except the Twelvers, who accept the son of al-Askari as the twelfth and final Imam in occultation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hijrat
The Hijrah or Hijra () was the journey of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his followers from Mecca to Medina. The year in which the Hijrah took place is also identified as the epoch of the Lunar Hijri and Solar Hijri calendars; its date equates to 16 July 622 in the Julian calendar. The Arabic word ''hijra'' means "departure" or "migration", among other definitions. It has been also transliterated as Hegira in medieval Latin, a term still in occasional use in English. Early in Muhammad's preaching of Islam, his followers only included his close friends and relatives. Following the spread of his religion, Muhammad and his small faction of Muslims faced several challenges including a boycott of Muhammad's clan, torture, killing, and other forms of religious persecution by the Meccans. Toward the end of the decade, Abu Talib, Muhammad's uncle, who supported him amidst the leaders of Mecca, died. Finally, the leaders of Mecca ordered the assassination of Muhammad, which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jihad
Jihad (; ar, ЎђўЗЎІЎѓ, jihƒБd ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God's guidance, such as struggle against one's evil inclinations, proselytizing, or efforts toward the moral betterment of the Muslim community (''Ummah''), though it is most frequently associated with war. In classical Islamic law (''sharia''), the term refers to armed struggle against unbelievers, while modernist Islamic scholars generally equate military ''jihad'' with defensive warfare. In Sufi circles, spiritual and moral jihad has been traditionally emphasized under the name of ''greater jihad''. The term has gained additional attention in recent decades through its use by various insurgent Islamic extremist, militant Islamist, and terrorist individuals and organizations whose ideology is based on the Islamic notion of ''jihad''. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naib Nazim Of Dhaka
The Naib Nazim of Dhaka, officially the Naib Nazim of Jahangir Nagar, was the chief Mughal political officer in the city of Dhaka, the present-day capital of Bangladesh, between the mid-18th and mid-19th centuries. It was the second highest office in the political hierarchy of Mughal Bengal, including as a nominal position during the British East India Company's occupation of Bengal. The Naib Nazim was the deputy of the Nawab of Bengal, who was based in Murshidabad. The Naib Nazim was responsible for governing territories in eastern Bengal, including for revenue collection, army and navy affairs; and administering justice. In the later period of British rule, the Naib Nazims were heavily influenced by English culture, spoke fluent English and collected Western art. The 19th century office holder Nusrat Jung was described as an anglophile. Dhaka's status as a leading financial and commercial center of Mughal India lent significant influence to the office of the Naib Nazim. The N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryot
Ryot (alternatives: raiyat, rait or ravat) was a general economic term used throughout India for peasant cultivators but with variations in different provinces. While zamindars were landlords, raiyats were tenants and cultivators, and served as hired labour. A raiyat was defined as someone who has acquired a right to hold land for the purpose of cultivating it, whether alone or by members of his family, hired servants, or partners. It also referred to succession rights. Etymology ''Ryot'' originates from the Hindi-Urdu word ''ra`ƒЂyat'' and the Arabic word ''ra`ƒЂyah'', translated as "flock" or "peasants", in turn originating from the word ''ra`ƒБ'', meaning "pasture". Classifications Under the Mughal system of land control there were two types of raiyats: khudkasta and paikasta. The khudkasta raiyats were permanent resident cultivators of the village. Their rights in land were heritable according to Muslim and Hindu laws of succession. The other type of raiyats was called pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakir
Fakir ( ar, ўБўВџМЎ±, translit=faбЄ≥ƒЂr or ''faqƒЂr'') is an Islamic term traditionally used for Sufi Muslim ascetics who renounce their worldly possessions and dedicate their lives to the worship of God. They do not necessarily renounce all relationships and take vows of poverty, some may be poor and some may even be wealthy, but the adornments of the temporal worldly life are kept in perspective and do not detract from their constant dedication to God. The connotations of poverty associated with the term relate to their spiritual neediness, not necessarily their physical neediness. They are characterized by their reverence for ''dhikr'' (a devotional practice which consists of repeating the names of God with various formulas, often performed after the daily prayers). Sufism in the Muslim world emerged during the early Umayyad Caliphate (661вАУ750 CE) See Googlbook search and grew as a mystical tradition in the mainstream Sunni and Shia denominations of Islam, state Eric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_in_Eastern_Bengal_in_the_1860s.jpg)