|
Aggregation Problem
In economics, an ''aggregate'' is a summary measure. It replaces a vector that is composed of many real numbers by a single real number, or a scalar. Consequently, there occur various problems that are inherent in the formulations that use aggregated variables.Franklin M. Fisher (1987). "aggregation problem," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 1, pp.53-55 The aggregation problem is the problem of finding a valid way to treat an empirical or theoretical aggregate as if it reacted like a less-aggregated measure, say, about behavior of an individual agent as described in general microeconomic theory (see representative agent and heterogeneity in economics). The second meaning of "aggregation problem" is the theoretical difficulty in using and treating laws and theorems that include aggregate variables. A typical example is the aggregate production function. Another famous problem is Sonnenschein-Mantel-Debreu theorem. Most of macroeconomic statements comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gross Output
In economics, gross output (GO) is a measure of the value of production of new goods and services during an accounting period. Gross output represents the total value of ''sales'' by producing enterprises (their gross revenue or turnover) in an accounting period (a quarter or a year), before subtracting the value of intermediate goods used up in production from the value of sales. Gross output can also be defined as the value of net output (the gross value-added or GDP) ''plus'' the value of intermediate consumption. Gross output is therefore a broader measure of the value of production than gross domestic product (GDP), which measures only the net value of final output (finished goods and services). , for example, the Bureau of Economic Analysis estimated gross output in the United States to be $50.9 trillion, compared to $29.3 trillion for GDP. Gross output and net output are complementary measures of the value of production. The components of gross output provide extra in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Franklin Fisher
Franklin Marvin Fisher (December 13, 1934 – April 29, 2019) was an American economist. He taught economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology from 1960 to 2004. Biography Fisher attended Harvard University, where he was inducted into Phi Beta Kappa in 1955 and received a Bachelor of Arts degree (''summa cum laude'') in 1956, followed by a Master's degree in 1957 and a Ph.D. in Economics from Harvard in 1960. His doctoral thesis was entitled ''A Priori Information and Time Series Analysis''. Fisher married Ellen Paradise Fisher in 1958. They had three children and eight grandchildren. He was Teaching Fellow at Harvard from 1956 to 1957, Junior Fellow of the Society of Fellows at Harvard (1957–59), Assistant Professor of Economics at the University of Chicago (1959–60), Assistant Professor of Economics at MIT (1960–62), Associate Professor of Economics at MIT (1962–65), and Professor of Economics at MIT from 1965 to 2004. He retired as the Jane Berkowitz Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Utility Function
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings. * In a Normative economics, normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish to maximize, i.e., an objective function. This kind of utility bears a closer resemblance to the original Utilitarianism, utilitarian concept, developed by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. * In a Positive economics, descriptive context, the term refers to an ''apparent'' objective function; such a function is Revealed preference, revealed by a person's behavior, and specifically by their preferences over Lottery (decision theory), lotteries, which can be any quantified choice. The relationship between these two kinds of utility functions has been a source of controversy among both Economics, economists and Ethics, ethicists, with most maintaining that the two are distinct but generally re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Composite Good
In economics, a composite good is an abstraction that represents all but one of the goods in the relevant budget.* ''Deardorff's Glossary of International Economics''"Composite good."/ref> Purpose Consumer demand theory shows how the composite may be treated as if it were only a single good as to properties hypothesized about demand. The composite good represents what is given up along consumer's budget constraint to consume more of the first good. Reason for use Budget constraints are designed to show the maximum amount of a good, or combination of goods, that can be purchased by a consumer given a limited budget. In a single-good world, the cost of a good cannot be related to any other opportunities. Therefore, opportunity costs cannot be calculated. The addition of one new good to a single-good market allows for opportunity costs to be determined ''only'' in relation to that other good. However, its weakness is that it ignores ''all other possible choices''. Trying to solve t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
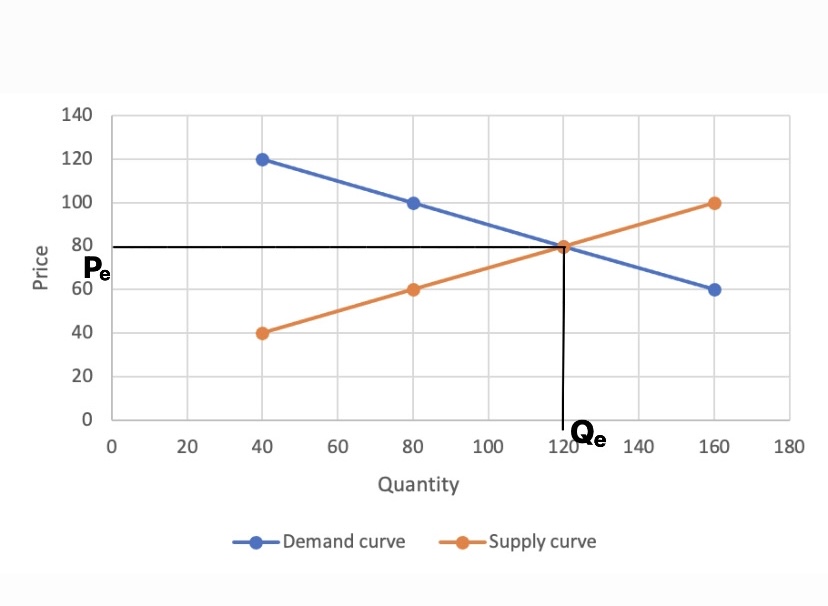
Law Of Demand
In microeconomics, the law of demand is a fundamental principle which states that there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. In other words, "conditional on ceteris paribus, all else being equal, as the price of a Goods, good increases (↑), quantity demanded will decrease (↓); conversely, as the price of a good decreases (↓), quantity demanded will increase (↑)". Alfred Marshall worded this as: "When we say that a person's demand for anything increases, we mean that he will buy more of it than he would before at the same price, and that he will buy as much of it as before at a higher price". The law of demand, however, only makes a qualitative statement in the sense that it describes the direction of change in the amount of quantity demanded but not the magnitude of change. The law of demand is represented by a graph called the demand curve, with quantity demanded on the x-axis and price on the y-axis. Demand curves are downward sloping by defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Waiting Staff
Waiting staff ( BrE), waiters () / waitresses (), or servers (AmE) are those who work at a restaurant, a diner, or a bar and sometimes in private homes, attending to customers by supplying them with food and drink as requested. Waiting staff follow rules and guidelines determined by the manager. Waiting staff carry out many different tasks, such as taking orders, food-running, polishing dishes and silverware, helping bus tables, entertaining patrons, restocking working stations with needed supplies, and handing out the bill. Waiting on tables is part of the service sector and among the most common occupations. In the United States, the Bureau of Labor Statistics estimated that, , there were about people employed as servers in the country. Many restaurants choose a specific uniform for their waiting staff to wear. Waiting staff may receive tips as a minor or major part of their earnings, with customs varying widely from country to country. Terminology An individual ''waitin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unemployment Rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period. Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, which is the number of people who are unemployed as a percentage of the labour force (the total number of people employed added to those unemployed). Unemployment can have many sources, such as the following: * the status of the economy, which can be influenced by a recession * competition caused by globalization and international trade * new technologies and inventions * policies of the government * regulation and market * war, civil disorder, and natural disasters Unemployment and the status of the economy can be influenced by a country through, for example, fiscal policy. Furthermore, the monetary authority of a country, such as the central bank, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
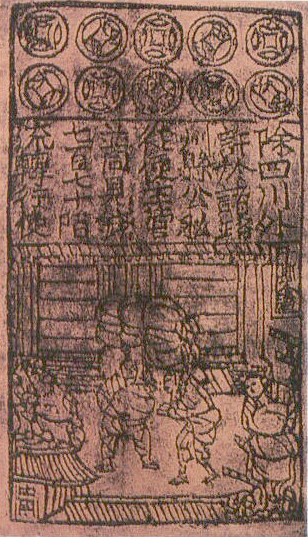
Paper Money
Paper money, often referred to as a note or a bill (North American English), is a type of negotiable promissory note that is payable to the bearer on demand, making it a form of currency. The main types of paper money are government notes, which are directly issued by political authorities, and banknotes issued by banks, namely banks of issue including central banks. In some cases, paper money may be issued by other entities than governments or banks, for example merchants in pre-modern China and Japan. "Banknote" is often used synonymously for paper money, not least by collectors, but in a narrow sense banknotes are only the subset of paper money that is issued by banks. Paper money is often, but not always, legal tender, meaning that courts of law are required to recognize them as satisfactory payment of money debts. Counterfeiting, including the forgery of paper money, is an inherent challenge. It is countered by anticounterfeiting measures in the printing of paper money. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vault Cash
Bank reserves are a commercial bank's cash holdings physically held by the bank, and deposits held in the bank's account with the central bank. In most countries, the Central bank may set minimum reserve requirements that mandate commercial banks under their purview to hold cash or deposits at the central bank equivalent to at least a prescribed percentage of their liabilities, such as customer deposits. Such sums are usually termed required reserves, and any funds above the required amount are called excess reserves. These reserves are prescribed to ensure that, in the normal events, there is sufficient liquidity in the banking system to provide funds to bank customers wishing to withdraw cash. Even when there are no reserve requirements, banks often as a matter of prudent management hold reserves in case of unexpected events, such as unusually large net withdrawals by customers (such as before Christmas) or bank runs. Traditionally, central banks do not pay interest on reserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Savings Deposits
A savings account is a bank account at a retail bank. Common features include a limited number of withdrawals, a lack of cheque and linked debit card facilities, limited transfer options and the inability to be overdrawn. Traditionally, transactions on savings accounts were widely recorded in a passbook, and were sometimes called passbook savings accounts, and bank statements were not provided; however, currently such transactions are commonly recorded electronically and accessible online. People deposit funds in savings account for a variety of reasons, including a safe place to hold their cash. Savings accounts normally pay interest as well: almost all of them accrue compound interest over time. Several countries require savings accounts to be protected by deposit insurance and some countries provide a government guarantee for at least a portion of the account balance. There are many types of savings accounts, often serving particular purposes. These may include accounts for y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Money Supply
In macroeconomics, money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of money held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circulation (i.e. physical cash) and demand deposits (depositors' easily accessed assets on the books of financial institutions). Money supply data is recorded and published, usually by the national statistical agency or the central bank of the country. Empirical money supply measures are usually named M1, M2, M3, etc., according to how wide a definition of money they embrace. The precise definitions vary from country to country, in part depending on national financial institutional traditions. Even for narrow aggregates like M1, by far the largest part of the money supply consists of deposits in commercial banks, whereas currency (banknotes and coins) issued by central banks only makes up a small part of the total money supply in modern economies. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |