|
Aflatoxin Total Synthesis
Aflatoxin total synthesis concerns the total synthesis of a group of organic compounds called aflatoxins. These compounds occur naturally in several fungi. As with other chemical compound targets in organic chemistry, the organic synthesis of aflatoxins serves various purposes. Traditionally it served to prove the structure of a complex biocompound in addition to evidence obtained from spectroscopy. It also demonstrates new concepts in organic chemistry (reagents, reaction types) and opens the way to molecular derivatives not found in nature. And for practical purposes, a synthetic biocompound is a commercial alternative to isolating the compound from natural resources. Aflatoxins in particular add another dimension because it is suspected that they have been mass-produced in the past from biological sources as part of a biological weapons program. The synthesis of racemic aflatoxin B1 has been reported by Buechi et al. in 1967 and that of racemic aflatoxin B2 by Roberts et al. in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aflatoxin B1
Aflatoxin B1 is an aflatoxin produced by ''Aspergillus flavus'' and '' A. parasiticus''. It is a very potent carcinogen with a TD50 3.2 μg/kg/day in rats. This carcinogenic potency varies across species with some, such as rats and monkeys, seemingly much more susceptible than others. Aflatoxin B1 is a common contaminant in a variety of foods including peanuts, cottonseed meal, corn, and other grains; as well as animal feeds. Aflatoxin B1 is considered the most toxic aflatoxin and it is highly implicated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in humans. In animals, aflatoxin B1 has also been shown to be mutagenic, teratogenic, and to cause immunosuppression. Several sampling and analytical methods including thin-layer chromatography (TLC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), among others, have been used to test for aflatoxin B1 contamination in foods. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CBS Catalyst
The CBS catalyst or Corey–Bakshi–Shibata catalyst is an Chiral synthesis, asymmetric catalyst derived from proline. It finds many uses in organic reactions such as the CBS reduction, Diels-Alder reactions and (3+2) cycloadditions. Proline, a naturally occurring Optical isomerism, chiral compound, is readily and cheaply available. It transfers its stereocenter to the catalyst which in turn is able to drive an organic reaction selectively to one of two possible enantiomers. This selectivity is due to steric strain in the transition state that develops for one enantiomer but not for the other. Synthesis The CBS catalyst can be prepared from diphenylprolinol, condensed with a phenylboronic acid, or with borane (as shown below). The CBS catalyst then complexes ''in situ'' with borane to give the active catalyst. Use The general outline for the organic synthesis of a CBS catalyst is shown below. The first leg of the reaction sequence starts from the Azeotropic distill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' is methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Oxidation
Organic reductions or organic oxidations or organic redox reactions are redox reactions that take place with organic compounds. In organic chemistry oxidations and reductions are different from ordinary redox reactions, because many reactions carry the name but do not actually involve electron transfer.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Instead the relevant criterion for organic oxidation is gain of oxygen and/or loss of hydrogen, respectively.''Organic Redox Systems: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications'', Tohru Nishinaga 2016 Simple functional groups can be arranged in order of increasing oxidation state. The oxidation numbers are only an approximation: When methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide its oxidation number changes from −4 to +4. Classical reductions include alkene reduction to alkanes and classical oxidations include oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes. In oxidations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are common and play important roles in the technology and biological spheres. Structure and bonding Aldehydes feature a carbon center that is connected by a double bond to oxygen and a single bond to hydrogen and single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The C=O bond length is about 120-122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes are more soluble in water, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde completely so. The volatile aldehydes have pungent odors. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reaction
The Grignard reaction () is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides ( Grignard reagent) is added to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction of an organic halide with magnesium is ''not'' a Grignard reaction, but provides a Grignard reagent. : Grignard reactions and reagents were discovered by and are named after the French chemist François Auguste Victor Grignard (University of Nancy, France), who published it in 1900 and was awarded the 1912 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work. Reaction mechanism Because carbon is more electronegative than magnesium, the carbon attached to magnesium functions as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom that is present within the polar bond of a carbonyl group. The addition of the Grignard reagent to the carbonyl typically proceeds through a six-membered ring transition state. Based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
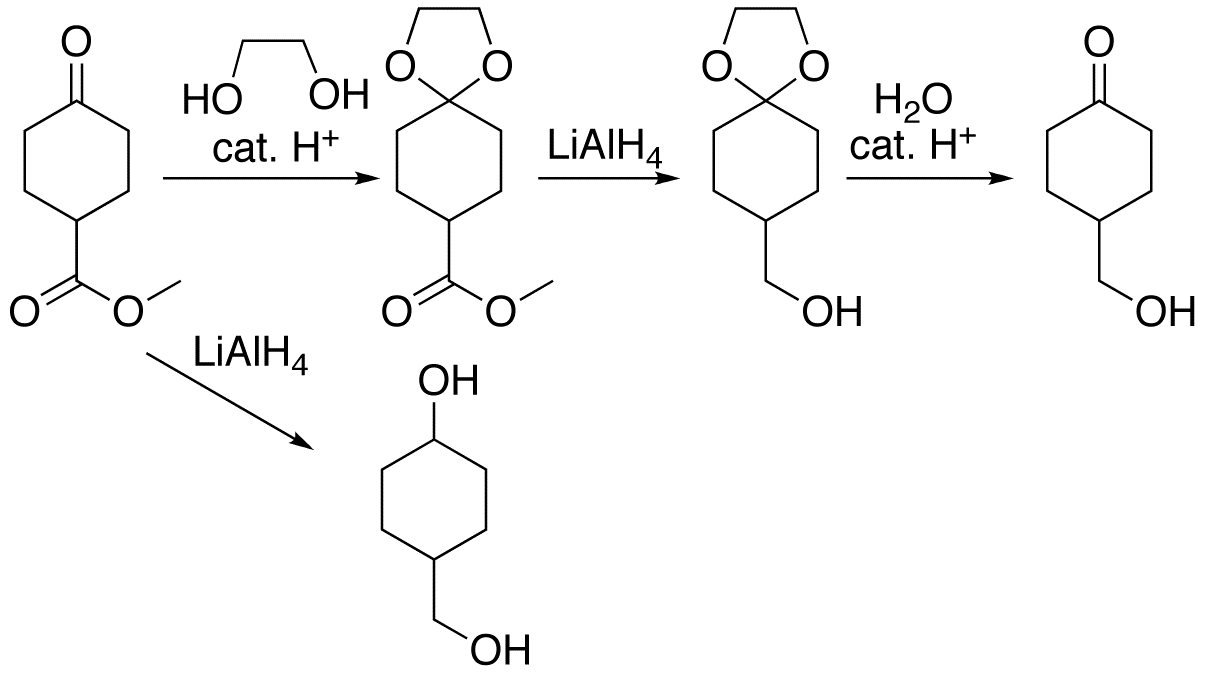
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the acet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triflic Acid
Triflic acid, the short name for trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, TFMS, TFSA, HOTf or TfOH, is a sulfonic acid with the chemical formula CF3SO3H. It is one of the strongest known acids. Triflic acid is mainly used in research as a catalyst for esterification. It is a hygroscopic, colorless, slightly viscous liquid and is soluble in polar solvents. Synthesis Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid is produced industrially by electrochemical fluorination (ECF) of methanesulfonic acid: : CH3SO3H + 4 HF ->CF3SO2F + H2O + 3 H2 The resulting CF3SO2F is hydrolyzed, and the resulting triflate salt is reprotonated. Alternatively, trifluoromethanesulfonic acid arises by oxidation of trifluoromethyl sulfenyl chloride: :CF3SCl + 2 Cl2 + 3 H2O -> CF3SO3H + 5 HCl Triflic acid is purified by distillation from triflic anhydride. Historical Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid was first synthesized in 1954 by Robert Haszeldine and Kidd by the following reaction: : Reactions As an acid In the laboratory, trifl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triflic Anhydride
Trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride, also known as triflic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CF3SO2)2O. It is the acid anhydride derived from triflic acid. This compound is a strong electrophile, useful for introducing the triflyl group, CF3SO2. Abbreviated Tf2O, triflic anhydride is the acid anhydride of the strong acid triflic acid, CF3SO2OH. Preparation and uses Triflic anhydride is prepared by dehydration of triflic acid using P4O10. Triflic anhydride is useful for converting ketones into enol triflates. In a representative application, is used to convert an imine into a NTf group. It will convert phenols into a triflic ester, which enables cleavage of the C-O bond. Assay The typical impurity in triflic anhydride is triflic acid, which is also a colorless liquid. Samples of triflic anhydride can be assayed by 19F NMR spectroscopy: −72.6 ppm vs. −77.3 for TfOH (std CFCl3). Safety It is an aggressive electrophile and readily hydrolyzes to the strong ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters typically have a pleasant smell; those of low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and are found in essential oils and pheromones. They perform as high-grade solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, and are one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. Polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties. '' Nomenclature Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |