|
Aelle II Of Northumbria
Aelle, also seen as Ælle, Aella, or Ælla may refer to: *Ælle of Sussex, king of Sussex (r. 477–514) *Ælla of Deira (died 588), king of Deira *Ælla of Northumbria (died 867), king of Northumbria (r. 860s) *Aella (Amazon) In Greek mythology, the Amazons (Ancient Greek: Ἀμαζόνες ''Amazónes'', singular Ἀμαζών ''Amazōn'', via Latin ''Amāzon, -ŏnis'') are portrayed in a number of ancient epic poems and legends, such as the Labours of Hercules, ..., an Amazon in Greek mythology {{given name Old English personal names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ælle Of Sussex
Ælle (also Aelle or Ella) is recorded in early sources as the first king of the South Saxons, reigning in what is now called Sussex, England, from 477 to perhaps as late as 514. According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', Ælle and three of his sons are said to have landed at a place called Cymensora and fought against the local Britons. The chronicle goes on to report a victory in 491, at present day Pevensey, where the battle ended with the Saxons slaughtering their opponents to the last man. Ælle was the first king recorded by the 8th century chronicler Bede to have held "''imperium''", or overlordship, over other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.Bede, ''Ecclesiastical History'', II 5. In the late 9th-century ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' (around four hundred years after his time) Ælle is recorded as being the first bretwalda, or "Britain-ruler", though there is no evidence that this was a contemporary title. Ælle's death is not recorded and although he may have been the founder of a S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ælla Of Deira
Ælla or Ælle is the first known king of the Anglian kingdom of Deira, which he ruled from around 560 until his death in 588. Biography The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' records that Ælla became king in 560.Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, s.a. 560 Anachronistically, the name of his kingdom is given as Northumbria, but the region was actually split between Deira and Bernicia at the time. Ælla's kingdom is identified by Bede as Deira - the use of Northumbria could be based on a tradition whereby the most powerful Anglian king in the region would claim that title. Venning Ælla was almost certainly a pagan - when Pope Gregory the Great encountered two pale-skinned English boys (Deirans) at a slave market in Rome he is said to have remarked that they were "not Angles, but angels, if they were Christian". (''Non Angli, sed angeli, si forent Christiani.'') Zuckermann, Ghil'ad (2003), Language Contact and Lexical Enrichment in Israeli Hebrew. Palgrave Macmillan. //ref>) and upon learning that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
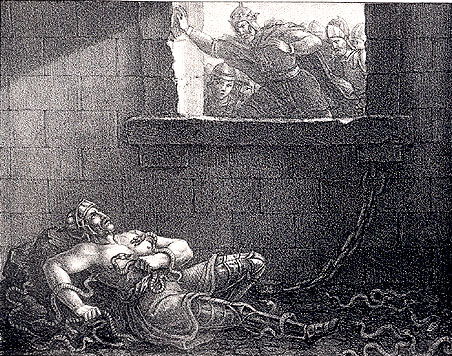
Ælla Of Northumbria
Ælla (or Ælle or Aelle, fl. 866; died 21 March 867) was King of Northumbria, a kingdom in medieval England, during the middle of the 9th century. Sources on Northumbrian history in this period are limited, and so Ælla's ancestry is not known and the dating of the beginning of his reign is questionable. In addition to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', Ælla is also mentioned in Scandinavian sources, such as the Norse sagas. According to the latter, Ælla captured the legendary Swedish-Danish Viking king Ragnar Lodbrok and put him to death in a pit of snakes. The historical invasion of Northumbria in 866 occurred in retaliation for Ragnar's execution, according to ''Ragnarssona þáttr'' (''The Tale of Ragnar's Sons''). While Norse sources claim that Ragnar's sons tortured Ælla to death by the method of the blood eagle, Anglo-Saxon accounts maintain that he died in battle at York on 21 March 867. Concerning the Norse claim, Roberta Frank reviewed the historical evidence for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aella (Amazon)
In Greek mythology, the Amazons (Ancient Greek: Ἀμαζόνες ''Amazónes'', singular Ἀμαζών ''Amazōn'', via Latin ''Amāzon, -ŏnis'') are portrayed in a number of ancient epic poems and legends, such as the Labours of Hercules, the ''Argonautica'' and the ''Iliad''. They were a group of female warriors and hunters, who beat men in physical agility and strength, in archery, riding skills, and the arts of combat. Their society was closed for men and they only raised their daughters, either killing their sons or returning them to their fathers, with whom they would only socialize briefly in order to reproduce. Courageous and fiercely independent, the Amazons, commanded by their queen, regularly undertook extensive military expeditions into the far corners of the world, from Scythia to Thrace, Asia Minor and the Aegean Islands, reaching as far as Arabia and Egypt. Besides military raids, the Amazons are also associated with the foundation of temples and the estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |