|
Adversarial Machine Learning
Adversarial machine learning is the study of the attacks on machine learning algorithms, and of the defenses against such attacks. A recent survey exposes the fact that practitioners report a dire need for better protecting machine learning systems in industrial applications. To understand, note that most machine learning techniques are mostly designed to work on specific problem sets, under the assumption that the training and test data are generated from the same statistical distribution (IID). However, this assumption is often dangerously violated in practical high-stake applications, where users may intentionally supply fabricated data that violates the statistical assumption. Some of the most common threat models in adversarial machine learning include evasion attacks, data poisoning attacks, Byzantine attacks and model extraction. History In 2004, Nilesh Dalvi and others noted that linear classifiers used in spam filters could be defeated by simple " evasion attacks" as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making predicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesla, Inc
Tesla, Inc. ( or ) is an American multinational automotive and clean energy company headquartered in Austin, Texas. Tesla designs and manufactures electric vehicles ( electric cars and trucks), battery energy storage from home to grid-scale, solar panels and solar roof tiles, and related products and services. Tesla is one of the world's most valuable companies and remains the world's most valuable automaker with a market capitalization of more than US$550 billion. In 2021, the company had the most worldwide sales of battery electric vehicles and plug-in electric vehicles, capturing 21% of the battery-electric (purely electric) market and 14% of the plug-in market (which includes plug-in hybrids). Through its subsidiary Tesla Energy, the company develops and is a major installer of photovoltaic systems in the United States. Tesla Energy is also one of the largest global suppliers of battery energy storage systems, with 3.99 gigawatt-hours (GWh) installed in 2021 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overfitting
mathematical modeling, overfitting is "the production of an analysis that corresponds too closely or exactly to a particular set of data, and may therefore fail to fit to additional data or predict future observations reliably". An overfitted model is a mathematical model that contains more parameters than can be justified by the data. The essence of overfitting is to have unknowingly extracted some of the residual variation (i.e., the noise) as if that variation represented underlying model structure. Underfitting occurs when a mathematical model cannot adequately capture the underlying structure of the data. An under-fitted model is a model where some parameters or terms that would appear in a correctly specified model are missing. Under-fitting would occur, for example, when fitting a linear model to non-linear data. Such a model will tend to have poor predictive performance. The possibility of over-fitting exists because the criterion used for selecting the model is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Box (software Engineering)
A white box (or glass box, clear box, or open box) is a subsystem whose internals can be viewed but usually not altered.Patrick J. Driscoll, "Systems Thinking," in Gregory S. Parnell, Patrick J. Driscoll, and Dale L. Henderson (eds.), ''Decision Making in Systems Engineering and Management'', 2nd. ed., Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2011, 40. The term is used in systems engineering as well as in software engineering. Having access to the subsystem internals in general makes the subsystem easier to understand, but also easier to hack; for example, if a programmer can examine source code, weaknesses in an algorithm are much easier to discover. That makes white-box testing much more effective than black-box testing but considerably more difficult from the sophistication needed on the part of the tester to understand the subsystem. See also * Black box * White-box cryptography * White-box testing White-box testing (also known as clear box testing, glass box testing, transparent box tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Box
In science, computing, and engineering, a black box is a system which can be viewed in terms of its inputs and outputs (or transfer characteristics), without any knowledge of its internal workings. Its implementation is "opaque" (black). The term can be used to refer to many inner workings, such as those of a transistor, an engine, an algorithm, the human brain, or an institution or government. To analyse an open system with a typical "black box approach", only the behavior of the stimulus/response will be accounted for, to infer the (unknown) ''box''. The usual representation of this ''black box system'' is a data flow diagram centered in the box. The opposite of a black box is a system where the inner components or logic are available for inspection, which is most commonly referred to as a white box (sometimes also known as a "clear box" or a "glass box"). History The modern meaning of the term "black box" seems to have entered the English language around 1945. In electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
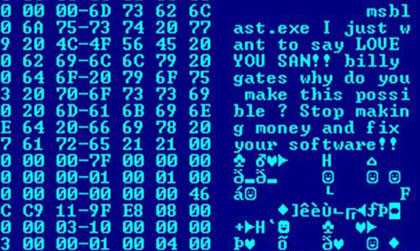
Image Spam
Image-based spam,Giorgio Fumera, Ignazio Pillai, Fabio Roli, Journal of Machine Learning Research (special issue on Machine Learning in Computer Security), vol. 7, pp. 2699-2720, 12/2006.Battista Biggio, Giorgio Fumera, Ignazio Pillai, Fabio Roli, Volume 32, Issue 10, 15 July 2011, Pages 1436-1446, ISSN 0167-8655. or image spam, is a kind of email spam where the textual spam message is embedded into images, that are then attached to spam emails. Since most of the email clients will display the image file directly to the user, the spam message is conveyed as soon as the email is opened (there is no need to further open the attached image file). Technique The goal of image spam is clearly to circumvent the analysis of the email’s textual content performed by most spam filters (e.g., SpamAssassin, RadicalSpam, Bogofilter, SpamBayes). Accordingly, for the same reason, together with the attached image, often spammers add some “bogus” text to the email, namely, a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malware
Malware (a portmanteau for ''malicious software'') is any software intentionally designed to cause disruption to a computer, server, client, or computer network, leak private information, gain unauthorized access to information or systems, deprive access to information, or which unknowingly interferes with the user's computer security and privacy. By contrast, software that causes harm due to some deficiency is typically described as a software bug. Malware poses serious problems to individuals and businesses on the Internet. According to Symantec's 2018 Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR), malware variants number has increased to 669,947,865 in 2017, which is twice as many malware variants as in 2016. Cybercrime, which includes malware attacks as well as other crimes committed by computer, was predicted to cost the world economy $6 trillion USD in 2021, and is increasing at a rate of 15% per year. Many types of malware exist, including computer viruses, worms, Trojan horses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
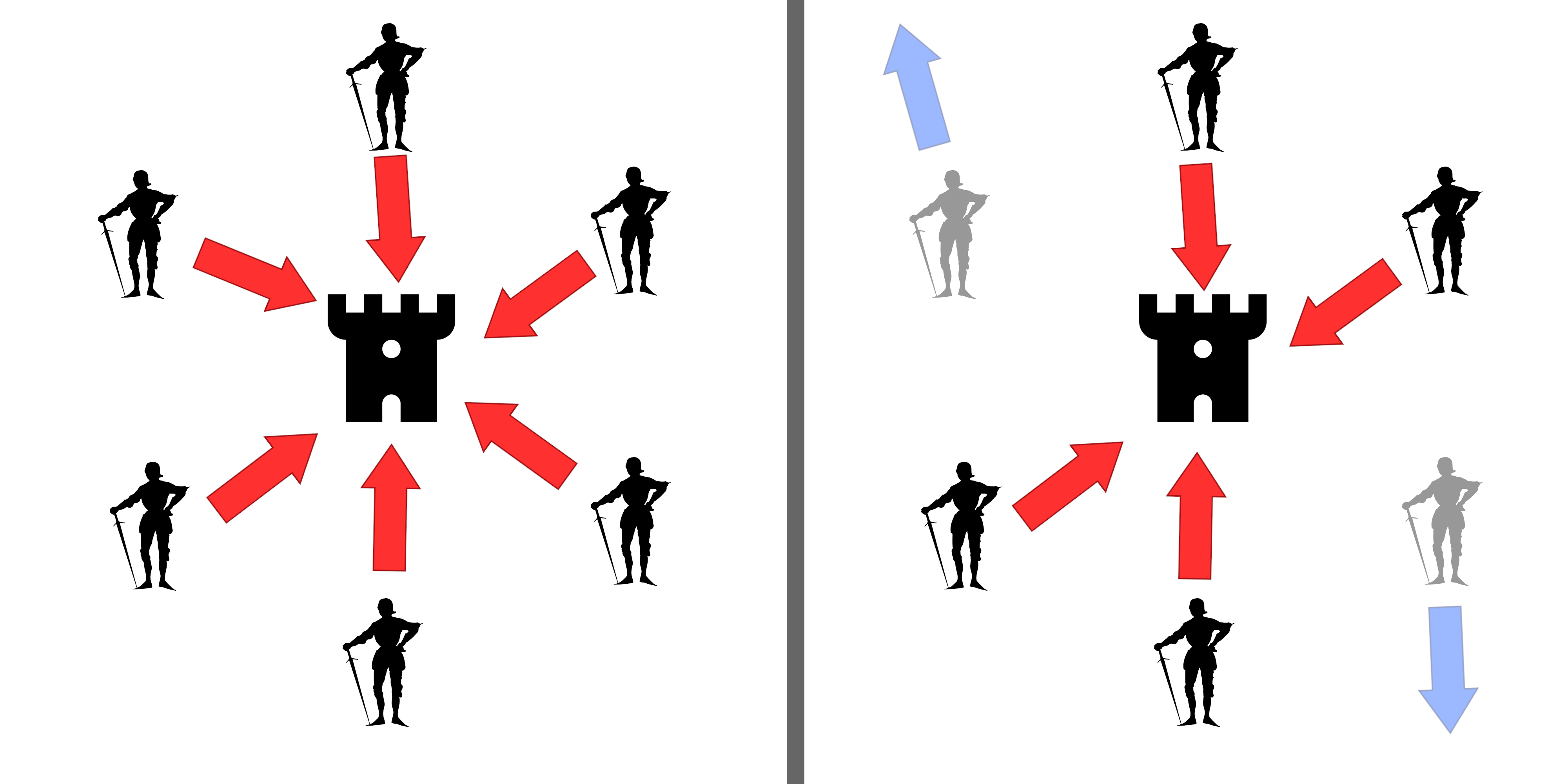
Byzantine Fault
A Byzantine fault (also Byzantine generals problem, interactive consistency, source congruency, error avalanche, Byzantine agreement problem, and Byzantine failure) is a condition of a computer system, particularly distributed computing systems, where components may fail and there is imperfect information on whether a component has failed. The term takes its name from an allegory, the "Byzantine generals problem", developed to describe a situation in which, in order to avoid catastrophic failure of the system, the system's actors must agree on a concerted strategy, but some of these actors are unreliable. In a Byzantine fault, a component such as a server can inconsistently appear both failed and functioning to failure-detection systems, presenting different symptoms to different observers. It is difficult for the other components to declare it failed and shut it out of the network, because they need to first reach a consensus regarding which component has failed in the first pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
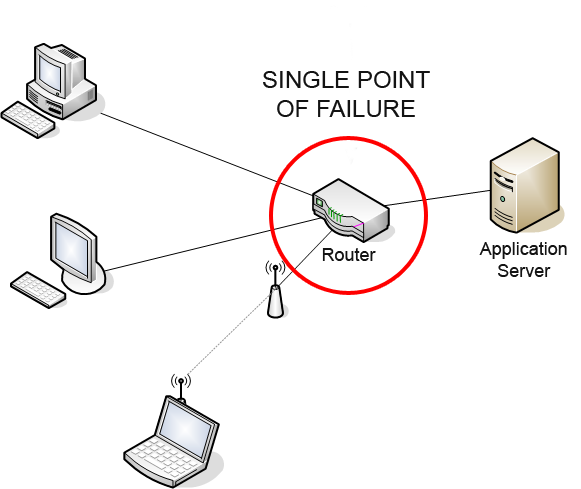
Single Point Of Failure
A single point of failure (SPOF) is a part of a system that, if it fails, will stop the entire system from working. SPOFs are undesirable in any system with a goal of high availability or reliability, be it a business practice, software application, or other industrial system. Overview Systems can be made robust by adding redundancy in all potential SPOFs. Redundancy can be achieved at various levels. The assessment of a potential SPOF involves identifying the critical components of a complex system that would provoke a total systems failure in case of malfunction. Highly reliable systems should not rely on any such individual component. For instance, the owner of a small tree care company may only own one woodchipper. If the chipper breaks, he may be unable to complete his current job and may have to cancel future jobs until he can obtain a replacement. The owner of the tree care company may have spare parts ready for the repair of the wood chipper, in case it fails. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federated Learning
Federated learning (also known as collaborative learning) is a machine learning technique that trains an algorithm across multiple decentralized edge devices or servers holding local data samples, without exchanging them. This approach stands in contrast to traditional centralized machine learning techniques where all the local datasets are uploaded to one server, as well as to more classical decentralized approaches which often assume that local data samples are identically distributed. Federated learning enables multiple actors to build a common, robust machine learning model without sharing data, thus allowing to address critical issues such as data privacy, data security, data access rights and access to heterogeneous data. Its applications are spread over a number of industries including defense, telecommunications, IoT, and pharmaceutics. A major open question at the moment is how inferior models learned through federated data are relative to ones where the data are pooled. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrusion Detection System
An intrusion detection system (IDS; also intrusion prevention system or IPS) is a device or software application that monitors a network or systems for malicious activity or policy violations. Any intrusion activity or violation is typically reported either to an administrator or collected centrally using a security information and event management (SIEM) system. A SIEM system combines outputs from multiple sources and uses alarm filtering techniques to distinguish malicious activity from false alarms. IDS types range in scope from single computers to large networks. The most common classifications are network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) and host-based intrusion detection systems (HIDS). A system that monitors important operating system files is an example of an HIDS, while a system that analyzes incoming network traffic is an example of an NIDS. It is also possible to classify IDS by detection approach. The most well-known variants are signature-based detection (recogni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backdoor (computing)
A backdoor is a typically covert method of bypassing normal authentication or encryption in a computer, product, embedded device (e.g. a home router), or its embodiment (e.g. part of a cryptosystem, algorithm, chipset, or even a "homunculus computer" —a tiny computer-within-a-computer such as that found in Intel's Intel Active Management Technology, AMT technology). Backdoors are most often used for securing remote access to a computer, or obtaining access to plaintext in cryptographic systems. From there it may be used to gain access to privileged information like passwords, corrupt or delete data on hard drives, or transfer information within autoschediastic networks. A backdoor may take the form of a hidden part of a program, a separate program (e.g. Back Orifice may subvert the system through a rootkit), code in the hardware backdoor, firmware of the hardware, or parts of an operating system such as Microsoft Windows, Windows. Trojan horse (computing), Trojan horses can be u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)