|
Adso Of Montier-en-Der
Adso of Montier-en-Der ( la, Adso Dervensis) (910/920 – 992) was abbot of the Benedictine monastery of Montier-en-Der in France, and died on a pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Biographical information on Adso comes mainly from one single source and has come under question, but the traditional biography depicts him as an abbot who enacted important monastic reform, as a scholar, and as a writer of five hagiographies. His best-known work was a biography of Antichrist, titled "''De ortu et tempore Antichristi''", which combined exegetical and Sibylline lore. This letter became one of the best-known medieval descriptions of Antichrist, copied many times and of great influence on all later apocalyptic tradition, in part because, rather than as an exegesis of apocalyptic texts, he chose to describe Antichrist in the style of a hagiography. Biography Biographical knowledge of Adso is limited to the comments made by a chronicler from his abbey, who wrote a half century after him; a successor of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
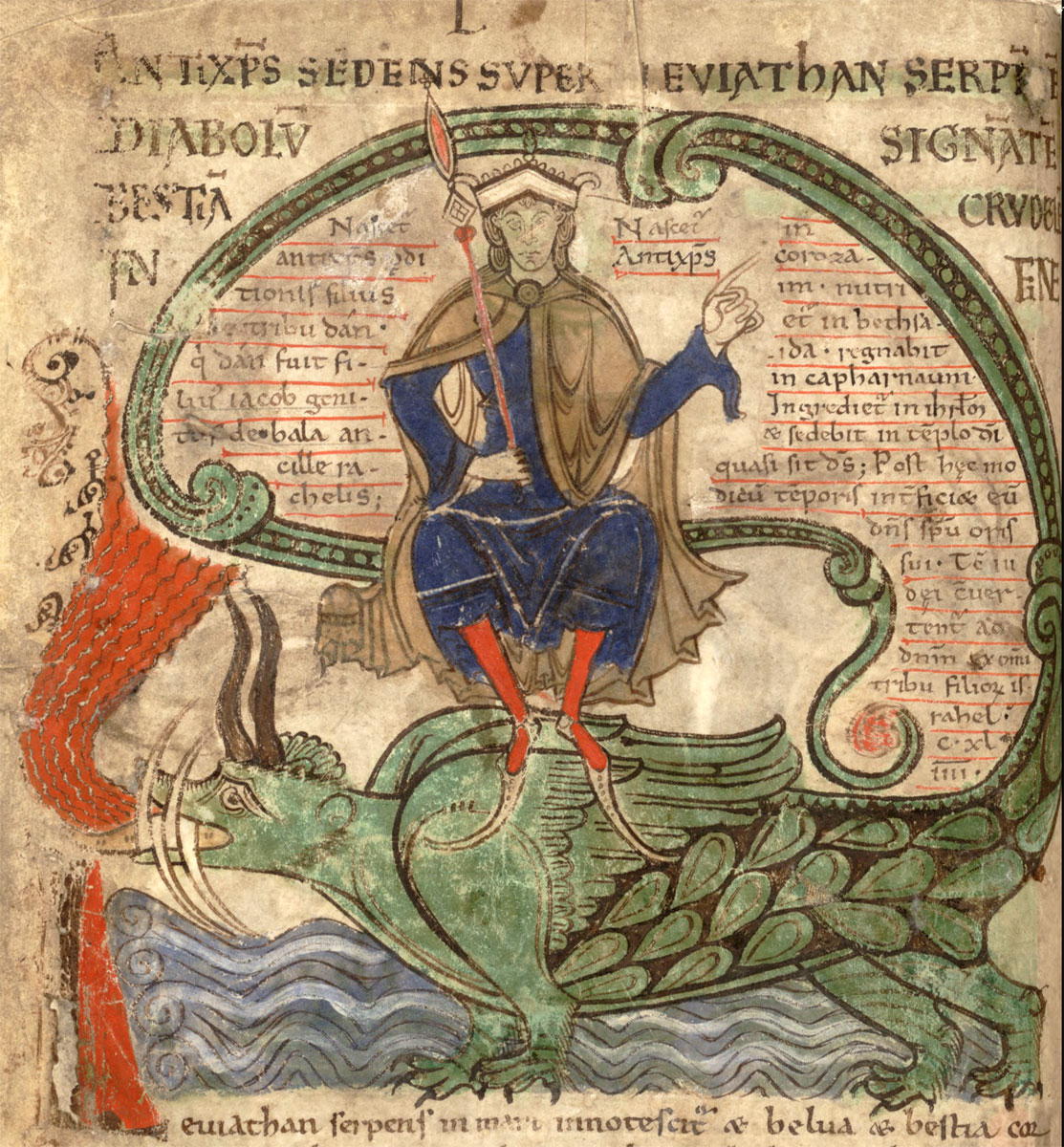
Liber Floridus-1120-Leviathan-p135
In ancient Roman religion and mythology, Liber ( , ; "the free one"), also known as Liber Pater ("the free Father"), was a god of viticulture and wine, male fertility and freedom. He was a patron deity of Rome's plebeians and was part of their Aventine Triad. His festival of Liberalia (March 17) became associated with free speech and the rights attached to coming of age. His cult and functions were increasingly associated with Romanised forms of the Greek Dionysus/Bacchus, whose mythology he came to share. Etymology The name ''Līber'' ('free') stems from Proto-Italic ''*leuþero'', and ultimately from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₁leudʰero'' ('belonging to the people', hence 'free'). Origins and establishment Before his official adoption as a Roman deity, Liber was companion to two different goddesses in two separate, archaic Italian fertility cults; Ceres, an agricultural and fertility goddess of Rome's Hellenised neighbours, and Libera, who was Liber's female equivalent. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leodegar
Leodegar of Poitiers ( la, Leodegarius; french: Léger; 615 – October 2, 679 AD) was a martyred Burgundian Bishop of Autun. He was the son of Saint Sigrada and the brother of Saint Warinus. Leodegar was an opponent of Ebroin, the Frankish Mayor of the Palace of Neustria, and the leader of the faction of Burgundian nobles. His torture and death made him a martyr and saint. Early life Leodegar was the son of a high-ranking Burgundian nobleman, Bodilon, Count of Poitiers and Paris Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ... and Saint Sigrada, St. Sigrada of Alsace, who later became a nun in the convent of Sainte-Marie at Soissons. His brother was Warinus. He spent his childhood in Paris at the court of Clotaire II, King of the Franks and was educated at the palace school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waldebert
Waldebert (also known as Gaubert, Valbert and Walbert), (died 668), was a Frankish count of Guines, Ponthieu and Saint-Pol who became abbot of Luxeuil in the Order of St. Columban, and eventually a canonized saint in the Roman Catholic Church and Eastern Orthodox Church, like several among his kinsmen who protected the Church, enriched it with lands and founded monasteries. Like his predecessor at Luxeuil he was born of the noble Frankish family of Duke Waldelenus of Burgundy, highly influential in seventh-century Frankish politics and served in the military before dedicating himself to the contemplative life and joining the monastery at Luxeuil on the borders of Austrasia and Burgundy (in modern-day France), where he dedicated his weapons and armour, which hung in the abbey church for centuries. He lived as a hermit close to the abbey until the death of the monastery's abbot, Saint Eustace of Luxeuil, when Waldebert was elected Luxeuil's third abbot (c. 628). He was abbot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frobert Of Troyes
Frobert of Troyes, or Frodobert (born in the beginning of the 7th century in Troyes, died 31 January 673 at Saint-André-les-Vergers), was a churchmen and abbot of the Saint-Pierre de Montier-la-Celle Abbey near Saint-André-les-Vergers, an abbey he founded in the middle of the 7th century on part of a royal domain granted him by Clovis II. He began building in 660, and dedicated the church to Saint Peter. He is recognized as a saint by the Catholic church and the Orthodox Church. A hagiography was written by Adso of Montier-en-Der. References External linksSaint Frobert from the Roman Martyrology The ''Roman Martyrology'' ( la, Martyrologium Romanum) is the official martyrology of the Catholic Church. Its use is obligatory in matters regarding the Roman Rite liturgy, but dioceses, countries and religious institutes may add duly approved ... French abbots Canons (priests) 673 deaths 7th-century French priests French Roman Catholic saints French theologians Colomba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansuetus (bishop Of Toul)
Saint Mansuetus (french: Mansuy; died 375) was the first Bishop of Toul. Life Mansuetus is thought to have been of Irish or Scottish origin. After religious studies in Rome, he was sent by Pope Damasus I to evangelize Gaul, becoming the first Bishop of Toul in 365. Mansuetus built in the woods a dwelling of interwoven twigs, where he spent his days in prayer and meditation. Near this he raised an oratory dedicated to St. Peter. It was believed that he had the gift of healing. Tradition holds that he was responsible for the healing of lepers and for restoring the life of the drowned son of the prince of Toul.Rev. S. Baring-Gould, ''The Lives of the Saints'' (John Hodges: 1875), 36 He erected two churches in Toul: one in honor of St. John the Baptist, and the other dedicated to the Blessed Virgin and Saint Stephen. The latter became the cathedral, later rebuilt by Gerard of Toul. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne. Founded by the Gauls, Reims became a major city in the Roman Empire. Reims later played a prominent ceremonial role in French monarchical history as the traditional site of the coronation of the kings of France. The royal anointing was performed at the Cathedral of Reims, which housed the Holy Ampulla of chrism allegedly brought by a white dove at the baptism of Frankish king Clovis I in 496. For this reason, Reims is often referred to in French as ("the Coronation City"). Reims is recognized for the diversity of its heritage, ranging from Romanesque to Art-déco. Reims Cathedral, the adjacent Palace of Tau, and the Abbey of Saint-Remi were listed together as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1991 because of their outstanding Romanesque and Gothi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verzy
Verzy () is a commune in the Marne department in north-eastern France. Champagne The village's vineyards are located in the Montagne de Reims subregion of Champagne, and are classified as Grand Cru (100%) in the Champagne vineyard classification. See also *Communes of the Marne department *Classification of Champagne vineyards *Montagne de Reims Regional Natural Park *Faux de Verzy A ''Fau de Verzy'' is either a Dwarf Beech (''Fagus sylvatica'' variety ''tortuosa''), a dwarf oak tree, or a dwarf chestnut tree. These grow in the forest of Verzy, 25 km south of Reims in France. In this forest are less than a thousand d ... are located in forests about 1 km south west of the village. References Communes of Marne (department) Grand Cru Champagne villages {{Marne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerberga Of Saxony
Gerberga of Saxony (c. 913 – 5 May 968/9 or 984?) was a French queen who ruled as regent of France during the minority of her son Lothair in 954–959. She was a member of the Ottonian dynasty. Her first husband was Gilbert, Duke of Lorraine. Her second husband was Louis IV of France. Contemporary sources describe her as a highly educated, intelligent and forceful political player. Life Family Gerberga was born c. 913. She was the second daughter of Henry the Fowler, King of Germany, and his second wife, Matilda (after Hedwig of Saxony, three years her senior). Her older brother was Otto I of Germany. First marriage In 929, Gerberga married her first husband, Gilbert, Duke of Lorraine. They had four children: # Alberade of Lorraine (b. about 929); married Renaud (originally as Ragenold), a Viking chieftain who became the Count of Roucy. # Henry, Duke of Lorraine (b. about 932). # Gerberge of Lorraine (b. about 935); married Adalbert I of Vermandois. # Wiltrude (b. about 93 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clotilde
Clotilde ( 474–545), also known as Clothilde, Clotilda, Clotild, Rotilde etc. (Latin: Chrodechildis, Chlodechildis from Frankish ''*Hrōþihildi'' or perhaps ''*Hlōdihildi'', both "famous in battle"), was a Queen of All the Franks. She was supposedly descended from the Gothic king Athanaric and became the second wife of the Frankish king Clovis I () in 493. The Merovingian dynasty to which her husband belonged ruled Frankish kingdoms for over 200 years (450–758). Venerated as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church as well as by the Eastern Orthodox Church, she played a role in her husband's famous conversion to Christianity and, in her later years, became known for her almsgiving and penitential works of mercy. She is credited with spreading Christianity within western Europe. Biography Clotilde was born at the Burgundian court of Lyon, the daughter of King Chilperic II of Burgundy. Upon the death of Chilperic's father King Gondioc in 473, Chilperic and his brothers G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martyrology Of Usuard
The ''Martyrology of Usuard'' is a work by Usuard, a monk of the Benedictine Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Prés.Thurston, Herbert. "Martyrology of Usuard." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 15. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1912. 12 March 2021 The prologue is dedicated to Charles the Bald indicating that it was undertaken at that monarch's instigation. It was apparently written shortly before the author's death in 875.Bonniwell O.P., W.R., "Introduction", ''The Martyrology of the Sacred Order of Friars Preachers'', The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Sylvester II
Pope Sylvester II ( – 12 May 1003), originally known as Gerbert of Aurillac, was a French-born scholar and teacher who served as the bishop of Rome and ruled the Papal States from 999 to his death. He endorsed and promoted study of Arab and Greco-Roman arithmetic, mathematics and astronomy, reintroducing to Europe the abacus and armillary sphere, which had been lost to Latin Europe since the end of the Greco-Roman era. He is said to be the first in Europe to introduce the decimal numeral system using the Hindu-Arabic numeral system. He is credited with the invention of the first mechanical clock in 996. Early life Gerbert was born about 946 in the town of Belliac, near the present-day commune of Saint-Simon, Cantal, France. Around 963, he entered the Monastery of St. Gerald of Aurillac. In 967, Count Borrell II of Barcelona (947–992) visited the monastery, and the abbot asked the count to take Gerbert with him so that the lad could study mathematics in Catalonia and acquir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |