|
Adrianichthyoidei
The ricefishes are a family (Adrianichthyidae) of small ray-finned fish that are found in fresh and brackish waters from India to Japan and out into the Malay Archipelago, most notably Sulawesi (where the Lake Poso and Lore Lindu species are known as buntingi). The common name ricefish derives from the fact that some species are found in rice paddies. This family consists of about 37 species in two genera (some recognize a third, '' Xenopoecilus''). Several species are rare and threatened, and some 2–4 may already be extinct. Description Most of these species are quite small, making them of interest for aquaria. ''Adrianichthys'' reach lengths of depending on the exact species involved, while the largest ''Oryzias'' reaches up to . Most ''Oryzias'' species are less than a half this length, with the smallest being up to only long. They have a number of distinctive features, including an unusual structure to the jaw, and the presence of an additional bone in the tail. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beloniformes
Beloniformes is an order composed of six families (and about 264 species) of freshwater and marine ray-finned fish: * Adrianichthyidae (ricefish and medakas) * Belonidae (needlefish) * Exocoetidae (flyingfishes) * Hemiramphidae (halfbeaks) * Scomberesocidae (sauries) * Zenarchopteridae (viviparous halfbeaks) With the exception of the Adrianichthyidae, these are streamlined, medium-sized fishes that live close to the surface of the water, feeding on algae, plankton, or smaller animals including other fishes. Most are marine, though a few needlefish and halfbeaks inhabit brackish and fresh waters. The order is sometimes divided up into two suborders, the Adrianichthyoidei and the Belonoidei, although this clade is referred to as Exocoetoidei in the 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World''. The Adrianichthyoidei contain only a single family, the Adrianichthyidae. Originally, the Adrianichthyidae were included in the Cyprinodontiformes and assumed to be closely related to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Paddies
A paddy field is a flooded field of arable land used for growing semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro. It originates from the Neolithic rice-farming cultures of the Yangtze River basin in southern China, associated with pre-Austronesian and Hmong-Mien cultures. It was spread in prehistoric times by the expansion of Austronesian peoples to Island Southeast Asia, Southeast Asia including Northeastern India, Madagascar, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. The technology was also acquired by other cultures in mainland Asia for rice farming, spreading to East Asia, Mainland Southeast Asia, and South Asia. Fields can be built into steep hillsides as terraces or adjacent to depressed or steeply sloped features such as rivers or marshes. They require a great deal of labor and materials to create and need large quantities of water for irrigation. Oxen and water buffalo, adapted for life in wetlands, are important working animals used extensively in paddy field farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
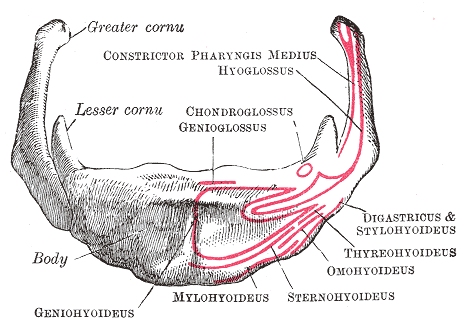
Hyoid
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones nearby. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the front, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprinodontiformes
Cyprinodontiformes is an order (biology), order of Actinopterygii, ray-finned fish, comprising mostly small, freshwater fish. Many popular aquarium fish, such as killifish and Poeciliidae, live-bearers, are included. They are closely related to the Atheriniformes and are occasionally included with them. A colloquial term for the order as a whole is toothcarps, though they are not actually close relatives of the true carps – the latter belong to the superorder Ostariophysi, while the toothcarps are Acanthopterygii. The families of Cyprinodontiformes can be informally divided into three groups based on reproductive strategy: Viviparity, viviparous and Ovoviviparity, ovoviviparous (all species give live birth), and Oviparity, oviparous (all species are egg-laying). The live-bearing groups differ in whether the young are carried to term within (ovoviviparous) or without (viviparous) an enclosing eggshell. Phylogeny, Phylogenetically however, one of the two suborders – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, wikt:ordo#Latin, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between Family_(biology), family and Class_(biology), class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as spacetime. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. Debates concerning the nature, essence and the mode of existence of space date back to antiquity; namely, to treatises like the ''Timaeus'' of Plato, or Socrates in his reflections on what the Greeks called ''khôra'' (i.e. "space"), or in the ''Physics'' of Aristotle (Book IV, Delta) in the definition of ''topos'' (i.e. place), or in the later "geometrical conception of place" as "spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. Perspectives The main processes involved in the embryogenesis, embryonic development of animals are: tissue patterning (via regional specification and patterned cellular differentiation, cell differentiation); tissue growth; and tissue morphogenesis. * Regional specification refers to the processes that create the spatial patterns in a ball or sheet of initially similar cells. This generally involves the action of cytoplasmic determinants, located within parts of the fertilized egg, and of inductive signals emitted from signaling centers in the embryo. The early stages of regional specification do not generate functional differentiated cells, but cell populations committed to developing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Rice Fish
The Japanese rice fish (''Oryzias latipes''), also known as the medaka, is a member of genus ''Oryzias'' ( ricefish), the only genus in the subfamily Oryziinae. This small (up to about ) native of East Asia is a denizen of rice paddies, marshes, ponds, slow-moving streams and tide pools. It is euryhaline, occurring in both brackish and freshwater. It became popular as an aquarium fish because of its hardiness and pleasant coloration: its coloration varies from creamy-white to yellowish in the wild to white, creamy-yellow, or orange in aquarium-bred individuals. Bright yellow, red or green transgenic populations, similar to GloFish, have also been developed, but are banned from sale in the EU. The medaka has been a popular pet since the 17th century in Japan. After fertilization, the female carries her eggs attached anterior to the anal fin for a period before depositing them on plants or similar things. Ecology Medaka live in small ponds, shallow rivers, and rice fields. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarium
An aquarium (plural: ''aquariums'' or ''aquaria'') is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aquatic reptiles, such as turtles, and aquatic plants. The term ''aquarium'', coined by English naturalist Philip Henry Gosse, combines the Latin root , meaning 'water', with the suffix , meaning 'a place for relating to'. The aquarium principle was fully developed in 1850 by the chemist Robert Warington, who explained that plants added to water in a container would give off enough oxygen to support animals, so long as the numbers of animals did not grow too large. The aquarium craze was launched in early Victorian England by Gosse, who created and stocked the first public aquarium at the London Zoo in 1853, and published the first manual, ''The Aquarium: An Unveiling of the Wonders of the Deep Sea'' in 1854.Katherine C. Grier (2008) "Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)