|
Adolph II De La Marck (bishop)
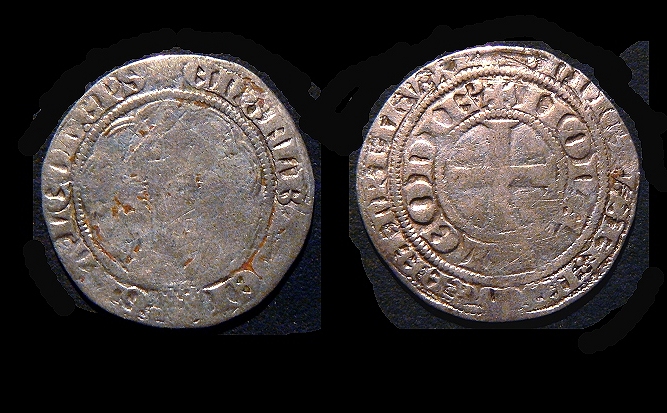
Adolph II von der Mark (English: Adolph II of the Mark) (August 1288 – Clermont-sur-Meuse, 3 November 1344) was the Prince-Bishop of Liège from 1313 until his death in 1344. Adolph was the third son of Count Eberhard I of the Mark and Mary of Loon. Aged only 25, but through the influence of King Philip IV of France, he became Prince-Bishop of Liège in 1313. The people of the Prince-Bishopric opposed his authoritarian way of ruling. In 1316, he was forced to sign the Peace of Fexhe, which has been compared to ''Magna Carta'' and which limited his powers. When he tried to revert the treaty, he was forced to flee from Liège to Huy at the end of 1324. From here, he placed Liège under interdict. In 1333, he sold the Lordship of Mechelen to the Count of Flanders. He intervened in the War of Awans and Waroux and participated in the 1334 siege of Maastricht. When Louis VI of Loon died in 1336 without an heir, he tried to annex the County of Loon, but without success. In 1343, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolph II Of The Marck
Adolf (also spelt Adolph or Adolphe, Adolfo and when Latinised Adolphus) is a given name used in German-speaking countries, Scandinavia, the Netherlands and Flanders, France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Latin America and to a lesser extent in various Central European and East European countries with non-Germanic languages, such as Lithuanian Adolfas and Latvian Ādolfs. Adolphus can also appear as a surname, as in John Adolphus, the English historian. The female forms Adolphine and Adolpha are far more rare than the male names. The name is a compound derived from the Old High German ''Athalwolf'' (or ''Hadulf''), a composition of ''athal'', or ''adal'', meaning "noble" (or '' had(u)''-, meaning "battle, combat"), and ''wolf''. The name is cognate to the Anglo-Saxon name '' Æthelwulf'' (also Eadulf or Eadwulf). The name can also be derived from the ancient Germanic elements "Wald" meaning "power", "brightness" and wolf (Waldwulf). Due to negative associations with Adolf H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eberhard I, Count Of The Mark
Eberhard I (–4 July 1308) was a German nobleman. He was Count of the Mark from 1277 until his death. He was the son of Engelbert I, Count of the Mark and Kunigunde of Blieskastel (died 1265), daughter of Count Henry I of Blieskastel. In 1277, Count Herman of Lohn abducted Eberhard's father Engelbert I, Count of the Mark near Tecklenburg and imprisoned him in the Castle of Bredevoort, where he later died. In 1278 Eberhard took revenge and conquered the castle. From 1281, Eberhard formed an alliance with the Counts of Berg, Cleve and Jülich against the Electorate of Cologne and gained the independence of the County of Mark from the Archbishop of Cologne after the victory in the Battle of Worringen in 1288. He also obtained Brakel, Westhofen and Waltrop. Eberhard died 4 July 1308 and was buried in Fröndenberg Monastery. Marriage and children Eberhard married first about 29 January 1273 to Irmgard of Berg (c.1256–24 March 1294), daughter of Adolf VII of Berg. They had seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Mark
The County of Mark (german: Grafschaft Mark, links=no, french: Comté de La Marck, links=no colloquially known as ) was a county and state of the Holy Roman Empire in the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle. It lay on both sides of the Ruhr River along the Volme and Lenne rivers. The Counts of the Mark were among the most powerful and influential Westphalian lords in the Holy Roman Empire. The name ''Mark'' is recalled in the present-day district in lands south of the Ruhr in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The northern portion (north of the Lippe river) is still called ("Higher Mark"), while the former "Lower Mark" (between the Ruhr and Lippe Rivers) is—for the most part—merged in the present Ruhr area. Geography The County of the Mark enclosed an area of approximately 3,000 km² and extended between the Lippe and Aggers rivers (north-south) and between Gelsenkirchen and Bad Sassendorf (west-east) for about 75 km. The east-west flowing Ruhr separated the cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip IV Of France
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (french: Philippe le Bel), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre as Philip I from 1284 to 1305, as well as Count of Champagne. Although Philip was known to be handsome, hence the epithet ''le Bel'', his rigid, autocratic, imposing, and inflexible personality gained him (from friend and foe alike) other nicknames, such as the Iron King (french: le Roi de fer, link=no). His fierce opponent Bernard Saisset, bishop of Pamiers, said of him: "He is neither man nor beast. He is a statue." Philip, seeking to reduce the wealth and power of the nobility and clergy, relied instead on skillful civil servants, such as Guillaume de Nogaret and Enguerrand de Marigny, to govern the kingdom. The king, who sought an uncontested monarchy, compelled his upstart vassals by wars and restricted their feudal privileges, paving the way for the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardinal Stephen Langton, to make peace between the unpopular king and a group of rebel barons, it promised the protection of church rights, protection for the barons from illegal imprisonment, access to swift justice, and limitations on feudal payments to the Crown, to be implemented through a council of 25 barons. Neither side stood behind their commitments, and the charter was annulled by Pope Innocent III, leading to the First Barons' War. After John's death, the regency government of his young son, Henry III, reissued the document in 1216, stripped of some of its more radical content, in an unsuccessful bid to build political support for their cause. At the end of the war in 1217, it formed part of the pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interdict
In Catholic canon law, an interdict () is an ecclesiastical censure, or ban that prohibits persons, certain active Church individuals or groups from participating in certain rites, or that the rites and services of the church are banished from having validity in certain territories for a limited or extended time. Before 1917 1917 Code of Canon Law Distinctions Under the 1917 Code of Canon Law, interdicts were either ''personal'', if applied directly to a person, wherever this person was, or ''local'', if applied directly to a locality and only indirectly to the people in that place whether permanently or only on a visit. Only the Holy See was empowered to impose a general interdict on a diocese or State or a personal interdict on the people of a diocese or country, but bishops too could impose a general interdict on a parish or on the people of a parish or a particular interdict on a place (such as a church or oratory, an altar or a cemetery) or a person. Effects A l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordship Of Mechelen
The Lordship of Mechelen was until 1795 a small authonomous Lordship in the Low Countries, consisting of the city of Mechelen and some surrounding villages. In the early Middle Ages, it was part of the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, which was confirmed in 910. In practice, the area was ruled by the local Berthout family, against the will of the Prince-Bishops of Liège. The Duchy of Brabant tried to annex the Lordship, but as a reaction, Liège gave the area in 1333 to the County of Flanders. The Flemish also didn't gain complete and permanent control. Mechelen was therefore later considered one of the Seventeen Provinces and then as a province of the Southern Netherlands. The Dukes of Burgundy and later the Habsburg Emperors and Kings were personally Lords of Mechelen and for a while turned the city more or less into the capital of the Netherlands. They established here the highest jurisdictional court of the Seventeen Provinces, called the Great Council of Mechelen. Governess M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Loon
The County of Loon ( , , ) was a county in the Holy Roman Empire, which corresponded approximately with the Belgian province of Limburg. It was named after the original seat of its count, Loon, which is today called Borgloon. During the middle ages the counts moved their court to a more central position in Kuringen, which is today a part of Hasselt, the modern capital of the region. From its beginnings, Loon was associated with the Prince-bishop of Liège and by 1190 the count had come under the bishop's overlordship. In the fourteenth century the male line ended for a second time, at which point the prince-bishops themselves took over the county directly. Loon approximately represented the Dutch-speaking (archaic ) part of the princedom. All of the Dutch-speaking towns in the Prince-Bishopric, with the status of being so-called "Good Cities" (french: bonnes villes), were in Loon, and are in Belgian Limburg today. These were Beringen, Bilzen, Borgloon, Bree, Hamont, Hassel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engelbert III Of The Marck, Archbishop Of Cologne
Engelbert III von der Mark (English: Engelbert III of the Mark) (1304 – 25 August 1368) was the Archbishop-Elector of Cologne from 1364 until 1368 and the Prince-Bishop of Liège (as Engelbert) from 1345 until 1364. Engelbert was the second son of Count Engelbert II of the Mark. Through the influence of his uncle Adolph II of the Marck, Bishop of Liège, he became the Provost of Liège in 1332. Later he was also mentioned as being a Provost in Cologne. After the death of his uncle, he was appointed Prince-Bishop of Liège by Pope Clement VI. In 1362 he applied to become the Archbishop-Elector of Cologne, but his nephew Adolph III gained it in 1363. Nevertheless, after Adolph abdicated in the following year he was appointed Archbishop-Elector in 1364 by Pope Urban V and resigned the Prince-Bishopric of Liège. Engelbert was beset by health problems soon after taking office. In 1366 he accepted coadjutors to assist in the running of the archdiocese, and the Archbishop-Elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of La Marck
The House of La Marck (german: von der Mar(c)k) was a noble family, which from about 1200 appeared as the counts of Mark. History The family history started with Count Adolf I, scion of a cadet branch of the Rhenish Berg dynasty residing at Altena Castle in Westphalia. In the early 13th century Adolf took his residence at his family's estates around Mark, a settlement in present-day Hamm-Uentrop. Adolf had inherited the Mark fortress from his father Count Frederick I of Berg-Altena (d. 1198) together with the older county around Altena and began to call himself count de La Mark. Originally liensmen of the archbishops of Cologne in the Duchy of Westphalia, the family ruled the County of Mark, an immediate state of the Holy Roman Empire, and, at the height of their powers, the four duchies of Julich, Cleves, Berg and Guelders as well as the County of Ravensberg. Members of the family became bishops in the Prince-Bishoprics of Liège, Münster and Osnabrück, and Archbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of The Bishops Of Liège
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)