|
Administrative License Suspension
License suspension or revocation traditionally follows conviction for alcohol-impaired or drunk driving. However, under administrative license suspension (ALS) laws, sometimes called administrative license revocation or administrative per se, licenses are confiscated and automatically suspended independent of criminal proceedings whenever a driver either (1) refuses to submit to chemical testing (blood, breath or, in some states, urine), or (2) submits to testing with results indicating a blood alcohol content of 0.08% or higher. Because ALS laws are immediate and require no proof of guilt, proponents such as Mothers Against Drunk Driving argue that they are more effective in reducing drunk driving than are traditional post-conviction sanctions, and that, in any event, driving is only a privilege. However, civil liberties advocates and other critics object to a procedure in which guilt is presumed and punishment is automatically imposed by the officer; they further point out that s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Alcohol Content
Blood alcohol content (BAC), also called blood alcohol concentration or blood alcohol level, is a measurement of alcohol intoxication used for legal or medical purposes; it is expressed as mass of alcohol per volume or mass of blood. For example, a BAC of 0.10 by (0.10% or one tenth of one percent) means that there is 0.10 g of alcohol for every 100 mL of blood, which is the same as 21.7 mmol/L. A BAC of 0.10 by (0.10%) is 0.10 g of alcohol per 100 g of blood (23 mmol/L). A BAC of 0.0 is sober; in different countries the maximum permitted BAC when driving ranges from about 0.04% to 0.08%; BAC levels over 0.08% are considered very impaired; above 0.4% is potentially fatal. Effects by alcohol level Estimation by intake Blood alcohol content can be estimated by a method developed by Swedish professor in the 1920s: :EBAC = \frac\times100\%-\beta\times T where: * is the mass of alcohol consumed. * is the ratio of body water to total weight. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mothers Against Drunk Driving
Mothers Against Drunk Driving (MADD) is a non-profit organization in the United States, Canada and Brazil that seeks to stop drunk driving, support those affected by drunk driving, prevent underage drinking, and strive for stricter impaired driving policy, whether that impairment is caused by alcohol or any other drug. The Irving, Texas–based organization was founded on September 5, 1980, in California by Candace Lightner after her 13-year-old daughter, Cari, was killed by a drunk driver. There is at least one MADD office in every state of the United States and at least one in each province of Canada. These offices offer victim services and many resources involving alcohol safety. MADD has claimed that drunk driving has been reduced by half since its founding. Positions According to MADD's website, "The mission of Mothers Against Drunk Driving is to end drunk driving, help fight drugged driving, support the victims of these violent crimes and prevent underage drinking." General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties may include the Freedom of thought, freedom of conscience, Freedom of the press, freedom of press, freedom of religion, Freedom of speech, freedom of expression, freedom of assembly, the right to security and liberty, freedom of speech, the right to privacy, the right to Equality before the law, equal treatment under the law and due process, the right to a fair trial, and the right to life. Other civil liberties include the Right to property, right to own property, the Self-defense, right to defend oneself, and the right to bodily integrity. Within the distinctions between civil liberties and other types of liberty, distinctions exist between positive liberty/Negative and positive rights, positive rights and negative liberty/Negative and positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Due Process
Due process of law is application by state of all legal rules and principles pertaining to the case so all legal rights that are owed to the person are respected. Due process balances the power of law of the land and protects the individual person from it. When a government harms a person without following the exact course of the law, this constitutes a due process violation, which offends the rule of law. Due process has also been frequently interpreted as limiting laws and legal proceedings (see substantive due process) so that judges, instead of legislators, may define and guarantee fundamental fairness, justice, and liberty. That interpretation has proven controversial. Analogous to the concepts of natural justice and procedural justice used in various other jurisdictions, the interpretation of due process is sometimes expressed as a command that the government must not be unfair to the people or abuse them physically. The term is not used in contemporary English law, but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Jeopardy
In jurisprudence, double jeopardy is a procedural defence (primarily in common law jurisdictions) that prevents an accused person from being tried again on the same (or similar) charges following an acquittal or conviction and in rare cases prosecutorial and/or judge misconduct in the same jurisdiction. Double jeopardy is a common concept in criminal law. In civil law, a similar concept is that of . Variation in common law countries is the peremptory plea, which may take the specific forms of ('previously acquitted') or ('previously convicted'). These doctrines appear to have originated in ancient Roman law, in the broader principle ('not twice against the same'). Availability as a legal defence If a double-jeopardy issue is raised, evidence will be placed before the court, which will typically rule as a preliminary matter whether the plea is substantiated; if it is, the projected trial will be prevented from proceeding. In some countries certain exemptions are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
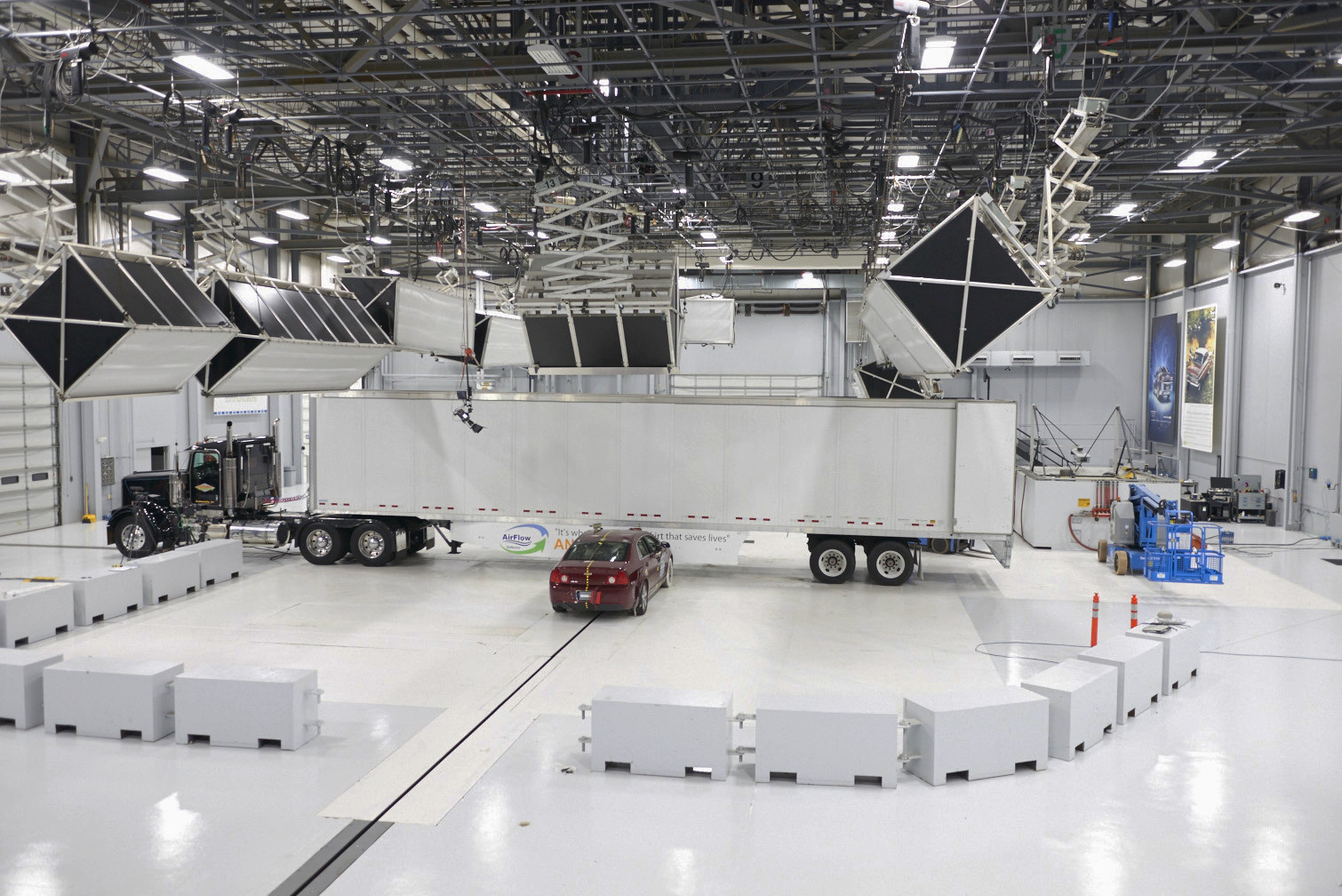
Insurance Institute For Highway Safety
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) is a U.S. nonprofit organization funded by auto insurance companies, established in 1959 and headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It works to reduce the number of motor vehicle traffic collisions, and the rate of injuries and amount of property damage in the crashes that still occur. It carries out research and produces ratings for popular passenger vehicles as well as for certain consumer products such as child car booster seats. It also conducts research on road design and traffic regulations, and has been involved in promoting policy decisions. Frontal crash tests The IIHS evaluates six individual categories, assigning each a "Good", "Acceptable", "Marginal", or "Poor" rating before determining the vehicle's overall frontal impact rating. Moderate overlap frontal test The moderate overlap test (formerly frontal offset test), introduced in January 1995, differs from that of the U.S. government's National Highway Traffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
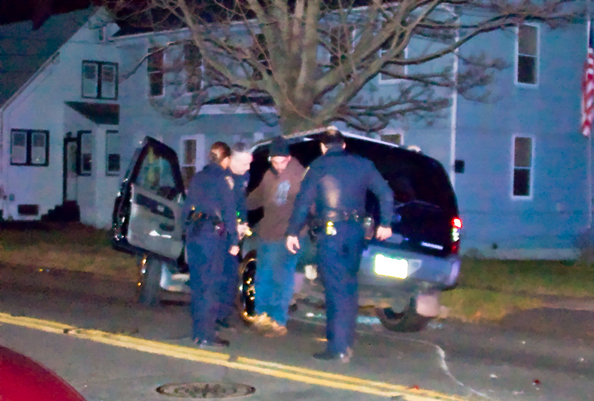
Drunk Driving
Drunk driving (or drink-driving in British English) is the act of driving under the influence of alcohol. A small increase in the blood alcohol content increases the relative risk of a motor vehicle crash. In the United States, alcohol is involved in 30% of all traffic fatalities. Effects of alcohol on cognitive processes Alcohol has a very significant effect on the functions of the body which are vital to driving and being able to function. Alcohol is a depressant, which mainly affects the function of the brain. Alcohol first affects the most vital components of the brain and "when the brain cortex is released from its functions of integrating and control, processes related to judgment and behavior occur in a disorganized fashion and the proper operation of behavioral tasks becomes disrupted." Alcohol weakens a variety of skills that are necessary to perform everyday tasks. One of the main effects of alcohol is severely impairing a person's ability to shift attention fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Law Judge
An administrative law judge (ALJ) in the United States is a judge and trier of fact who both presides over trials and adjudicates claims or disputes involving administrative law. ALJs can administer oaths, take testimony, rule on questions of evidence, and make factual and legal determinations. In the United States, the United States Supreme Court has recognized that the role of a federal administrative law judge is "functionally comparable" to that of an Article III judge. An ALJ's powers are often, if not generally, comparable to those of a trial judge, as ALJs may issue subpoenas, rule on proffers of evidence, regulate the course of the hearing, and make or recommend decisions. Depending upon the agency's jurisdiction, proceedings may have complex multi-party adjudication, as is the case with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, or simplified and less formal procedures, as is the case with the Social Security Administration. Federal appointment and tenure The Admini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Law
The law of Texas is derived from the ''Constitution of Texas'' and consists of several levels, including constitutional, statutory, and regulatory law, as well as case law and local laws and regulations. Sources The Constitution of Texas is the foremost source of state law. Legislation is enacted by the Texas Legislature, published in the '' General and Special Laws'', and codified in the ''Texas Statutes''. State agencies publish regulations (sometimes called administrative law) in the '' Texas Register'', which are in turn codified in the '' Texas Administrative Code''. The Texas legal system is based on common law, which is interpreted by case law through the decisions of the Supreme Court, the Court of Criminal Appeals, and the Courts of Appeals, which are published in the ''Texas Cases'' and ''South Western Reporter''. Counties and municipal governments may also promulgate local ordinances. Constitution The Constitution of Texas is the foundation of the government of Texa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Under The Influence
Driving under the influence (DUI)—also called driving while impaired, impaired driving, driving while intoxicated (DWI), drunk driving, operating while intoxicated (OWI), operating under the influence (OUI), operating vehicle under the influence (OVI), and drink-driving (UK/Ireland)—is the offense of driving, operating, or being in control of a vehicle while impaired by alcohol or other drugs (including recreational drugs and those prescribed by physicians), to a level that renders the driver incapable of operating a motor vehicle safely. Terminology The name of the offense varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction and from legal to colloquial terminology. In the United States, the specific criminal offense is usually called driving under the influence, but states may use other names for the offense including "driving while intoxicated" (DWI), "operating while impaired" (OWI) or "operating while ability impaired", and "operating a vehicle under the influence" (OVI). Such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Law
Traffic codes are laws that generally include provisions relating to the establishment of authority and enforcement procedures, statement of the Traffic#Rules of the road, rules of the road, and other safety provisions. Administrative regulations for driver license, driver licensing, vehicle ownership and Registry of Motor Vehicles, registration, insurance, vehicle safety inspections and parking violations may also be included, though not always directly related to driving safety. Violations of traffic code (i.e., a "moving violation") are often dealt with by forfeiting a Fine (penalty), fine in response to receiving a valid citation ("getting a Ticket (notification), ticket"). Other violations, such as drunk driving or vehicular homicide are handled through the Criminal law, criminal courts, although there may also be lawsuit, civil and administrative cases that arise from the same violation (including payment of damages and loss of driving privileges). In some jurisdictions, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |