|
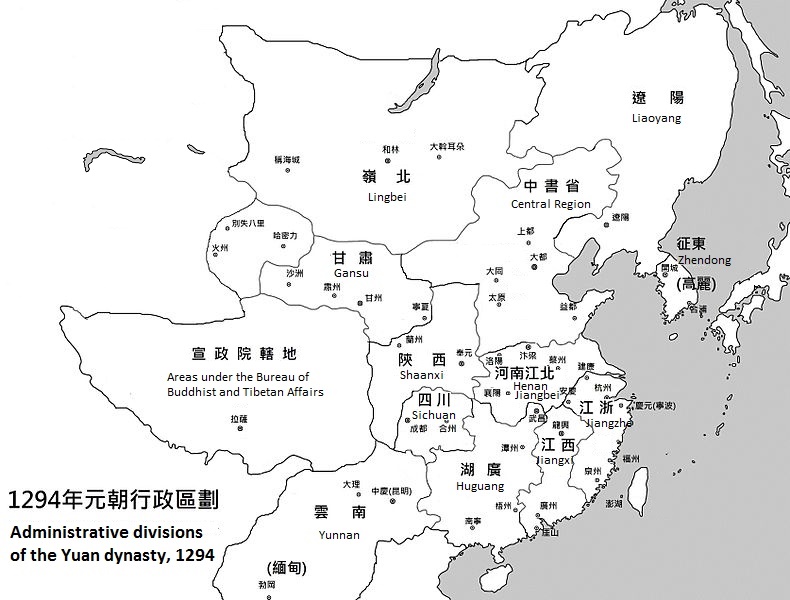
Administrative Divisions Of The Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty was a Mongol-led imperial Chinese dynasty. During its existence, its territory was divided into the Central Region (腹裏) governed by the Central Secretariat (Zhongshu Sheng) and places under control of various provinces (行省) or Branch Secretariats (行中書省), as well as the region under the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs (Xuanzheng Yuan). In addition, the Yuan emperors held nominal suzerainty over the western Mongol khanates, but in reality none of them were governed by the Yuan dynasty due to the division of the Mongol Empire. Overview The most important part of the Yuan Empire was the Central Region, which covered the region of the Yuan capital Khanbaliq (Dadu, modern Beijing). The Central Region consisted of present-day Hebei, Shandong, Shanxi, the south-eastern part of present-day Inner Mongolia and the Henan areas to the north of the Yellow River. Since it was considered the most important region of the dynasty, it was directly governe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty Administrative Division 1330
Yuan may refer to: Currency * Yuan (currency), the basic unit of currency in historic and contemporary mainland China and Taiwan ** Renminbi, the current currency used in mainland China, whose basic unit is yuan ** New Taiwan dollar, the current currency used in Taiwan, whose basic unit is yuán in Mandarin ** Manchukuo yuan, the unit of currency that was used in the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo Governmental organ * " Government branch" or "Court" (), the Chinese name for a kind of executive institution. Government of Taiwan * Control Yuan * Examination Yuan * Executive Yuan * Judicial Yuan * Legislative Yuan Government of Imperial China * Xuanzheng Yuan, or Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs during the Yuan dynasty * Lifan Yuan during the Qing dynasty Dynasties * Yuan dynasty (元朝), a dynasty of China ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan ** Northern Yuan dynasty (北元), the Yuan dynasty's successor state in northern China and the Mongolian Plateau People and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet Under Yuan Rule
Tibet under Mongol rule refers to the Mongol Empire and Yuan dynasty's rule over Tibet from 1244 to 1354. During the Yuan dynasty rule of Tibet, the region was structurally, militarily and administratively controlled by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China. In the history of Tibet, Mongol rule was established after Sakya Pandita got power in Tibet from the Mongols in 1244, following the 1240 Mongol conquest of Tibet led by the Mongol general with the title ''doord darkhan''. It is also called the Sakya dynasty () after the favored Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism. The region retained a degree of political autonomy under the Sakya lama, who was the ''de jure'' head of Tibet and a spiritual leader of the Mongol Empire. However, administrative and military rule of Tibet remained under the auspices of the Yuan government agency known as the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs or Xuanzheng Yuan, a top-level administrative department separate from other Yuan provinces, but still u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amdo
Amdo ( �am˥˥.to˥˥ ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being U-Tsang in the west and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Amdo is also the birthplace of the 14th Dalai Lama. Amdo encompasses a large area from the Machu (Yellow River) to the Drichu (Yangtze). Amdo is mostly coterminous with China's present-day Qinghai province, but also includes small portions of Sichuan and Gansu provinces. Historically, culturally, and ethnically a part of Tibet, Amdo was from the mid-18th century and after administered by a series of local Tibetan rulers. The Dalai Lamas have not directly governed the area since that time. From 1917 to 1928, much of Amdo was occupied intermittently by the Hui Muslim warlords of the Ma clique. In 1928, the Ma Clique joined the Kuomintang (Chinese Nationalist Party), and during the period from 1928 to 1949, much of Amdo was gradually assimilated into the Qingh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan and Loess plateaus and borders Mongolia ( Govi-Altai Province), Inner Mongolia and Ningxia to the north, Xinjiang and Qinghai to the west, Sichuan to the south and Shaanxi to the east. The Yellow River passes through the southern part of the province. Part of Gansu's territory is located in the Gobi Desert. The Qilian mountains are located in the south of the Province. Gansu has a population of 26 million, ranking 22nd in China. Its population is mostly Han, along with Hui, Dongxiang and Tibetan minorities. The most common language is Mandarin. Gansu is among the poorest administrative divisions in China, ranking 31st, last place, in GDP per capita as of 2019. The State of Qin originated in what is now southeastern Gansu and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangut People
The Tangut people ( Tangut: , ''mjɨ nja̱'' or , ''mji dzjwo''; ; ; mn, Тангуд) were a Tibeto-Burman tribal union that founded and inhabited the Western Xia dynasty. The group initially lived under Tuyuhun authority, but later submitted to the Tang dynasty, prior to their establishment of the Western Xia. They spoke the Tangut language, which was previously believed to be one of the Qiangic languages or Yi languages that belong to the Tibeto-Burman family. Phylogenetic and historical linguistic accounts, however, reveal that Tangut belonged to the Gyalrongic languages. Language The Tangut language, otherwise known as ''Fan'', belongs to the Tibeto-Burman branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Like many other Sino-Tibetan languages, it is a tonal language with predominantly mono-syllabic roots, but it shares certain grammatical traits central to the Tibeto-Burman branch. It is still debated as to whether Tangut belongs to the Yi or Qiangic subdivision of Tibeto-Burm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in 1954 but was later separated from Gansu in 1958 and reconstituted as an autonomous region for the Hui people, one of the 56 officially recognised nationalities of China. Twenty percent of China's Hui population lives in Ningxia. Ningxia is bounded by Shaanxi to the east, Gansu to the south and west and Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to the north and has an area of around . This sparsely settled, mostly desert region lies partially on the Loess Plateau and in the vast plain of the Yellow River and features the Great Wall of China along its northeastern boundary. Over about 2000 years an extensive system of canals (The total length about 1397 kilometers) has been built from Qin dynasty. Extensive land reclamation and irrigation projec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhangye
Zhangye (), formerly romanized as Changyeh or known as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Gansu Province in the People's Republic of China. It borders Inner Mongolia on the north and Qinghai on the south. Its central district is Ganzhou, formerly a city of the Western Xia and one of the most important outposts of western China. Name The city was formerly also known as Ganzhou, named after the sweet waters () of its oasis. An alternative theory states that "Gan" was from the Ganjun Hill () near the city. The name of province came from a contraction of Ganzhou and Suzhou (modern Jiuquan). The name appears in Marco Polo's '' Travels'' under the name Campichu. Zhangye Commandery was established by Western Han in 111 BC, with the seat at the site of modern Wuwei, Gansu. Etymology of Zhangye is unclear. A popular theory interprets the name Zhangye as "Extending Arm", excerpted from a phrase "to extend the arm of the country through to the Western Realm" () documented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gansu Province (Yuan Dynasty)
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan and Loess plateaus and borders Mongolia ( Govi-Altai Province), Inner Mongolia and Ningxia to the north, Xinjiang and Qinghai to the west, Sichuan to the south and Shaanxi to the east. The Yellow River passes through the southern part of the province. Part of Gansu's territory is located in the Gobi Desert. The Qilian mountains are located in the south of the Province. Gansu has a population of 26 million, ranking 22nd in China. Its population is mostly Han, along with Hui, Dongxiang and Tibetan minorities. The most common language is Mandarin. Gansu is among the poorest administrative divisions in China, ranking 31st, last place, in GDP per capita as of 2019. The State of Qin originated in what is now southeastern Gansu a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han Chinese, Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of The People's Republic Of China
Counties ( zh, t=縣, s=县, hp=Xiàn), formally county-level divisions, are found in the Administrative divisions of China#County level, third level of the administrative hierarchy in Provinces of China, Provinces and Autonomous regions of China, Autonomous regions and the second level in Direct-controlled municipality#People's Republic of China, municipalities and Hainan, a level that is known as "county level" and also contains autonomous county, autonomous counties, county-level city, county-level cities, Banners of Inner Mongolia, banners, Banners of Inner Mongolia#Autonomous banner, autonomous banners and District (China)#City districts, City districts. There are 1,355 counties in Mainland China out of a total of 2,851 county-level divisions. The term ''xian'' is sometimes translated as "district" or "prefecture" when put in the context of History of China, Chinese history. History ''Xian'' have existed since the Warring States period and were set up nationwide by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou (country Subdivision)
''Zhou'' () were historical administrative and political divisions of China. Formally established during the Han dynasty, ''zhou'' existed continuously in 1912—a period of over 2000 years. ''Zhou'' were also previously used in Korea (, ''ju''), Vietnam ( vi, châu), and . Overview ''Zhou'' is typically rendered by several terms in the English language: * The large ''zhou'' before the Tang dynasty and in countries other than China are called "provinces" * The smaller ''zhou'' during and after the Tang dynasty are called "prefectures" * The ''zhou'' of the Qing dynasty are also called either "independent" or "dependent departments", depending on their level. The Tang dynasty also established '' fǔ'' (, "prefectures"), ''zhou'' of special importance such as capitals and other major cities. By the Ming and Qing, became predominant divisions within Chinese provinces. In Ming and Qing, the word ''fǔ'' () was typically attached to the name of each prefecture's capital cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |