|
Adiabatic MRI Pulses
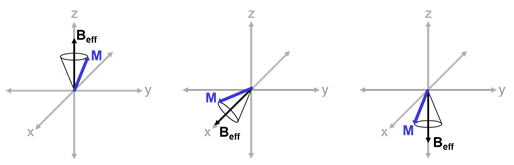
Adiabatic radio frequency (RF) pulses are used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to achieve excitation that is insensitive to spatial inhomogeneities in the excitation field or off-resonances in the sampled object. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments are often performed with surface transceiver coils that have desirable sensitivity, but have the disadvantage of producing an inhomogeneous excitation field. This inhomogeneous field causes spatial variations in spin flip angles, which, in turn, causes errors and degrades the receiver’s sensitivity. RF pulses can be designed to create low-variation flip-angles or uniform magnetization inversion across a sample, even in the presence of inhomogeneities such as B1-variation and off-resonance. Analysis - Adiabatic Excitation Principles Traditional RF Excitation In traditional MRI RF excitation, an RF pulse, B1, is applied with a frequency that is resonant with the nutation frequency of the spins of interest. In the frame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |