|
Adactylidium
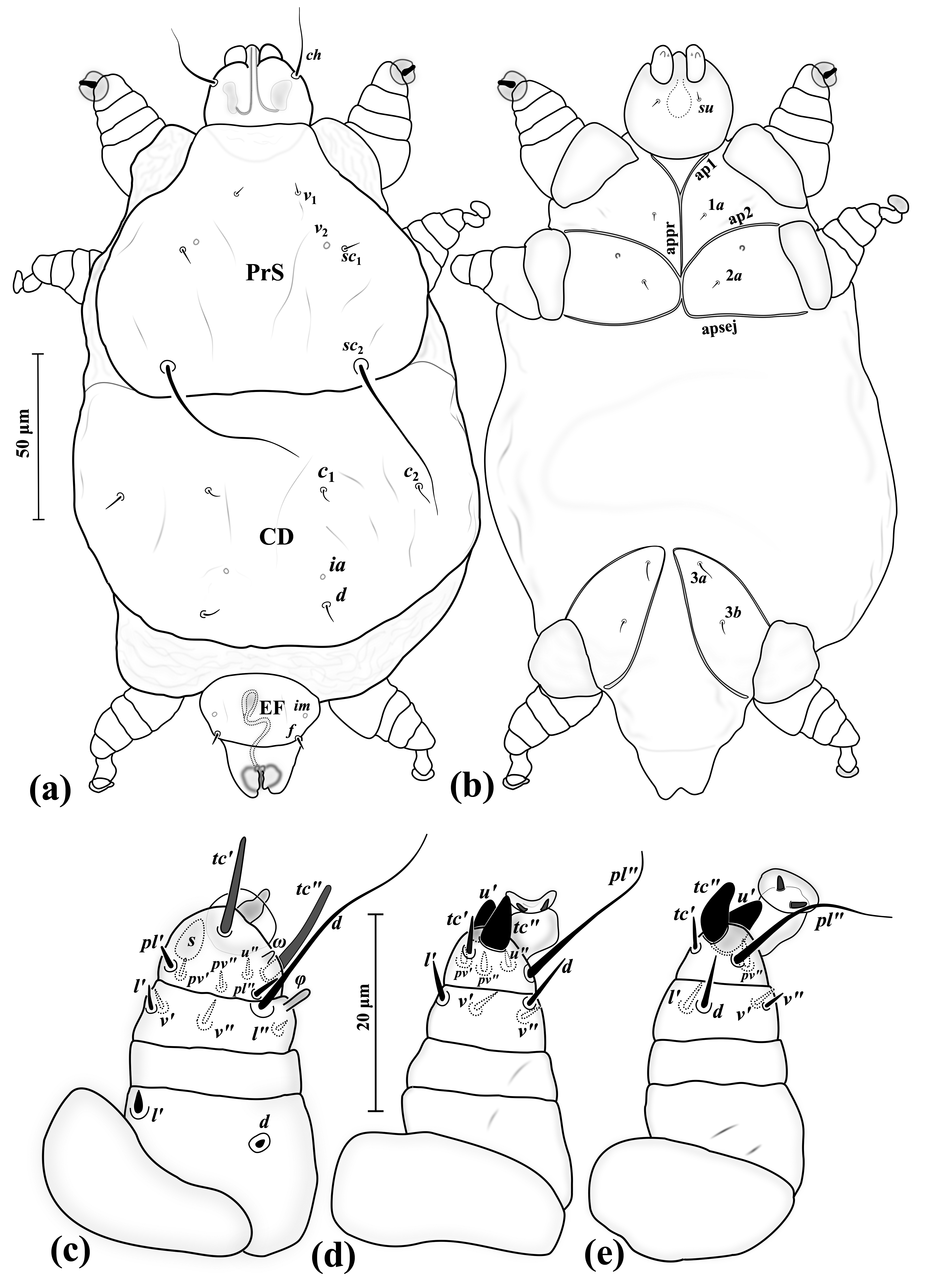
''Adactylidium'' is a genus of mites known for its unusual life cycle. An impregnated female mite feeds upon a single egg of a thrips, rapidly growing five to eight female offspring and one male in her body. The single male mite mates with all the daughters when they are still inside their mother. The new females, now impregnated, eat their way out of their mother's body so that they can emerge to find new thrips eggs, killing their mother in the process (though the mother may be only 4 days old at the time), starting the cycle again. The male emerges as well, but does not look for food or new mates, and dies after a few hours. See also * Telescoping generations Telescoping generations can occur in parthenogenetic species, such as aphids or other life forms that have the ability to reproduce without ovum fertilization. This occurrence is characterized by a viviparous female having a daughter growing inside ... References Trombidiformes genera Parasites of insects Ince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acarophenacidae
Acarophenacidae is a family of mites in the order Trombidiformes that are egg parasitoids and ectoparasites of beetles or thrips. It contains eight genera and around 40 species. Morphology Acarophenacidae are <200 μm in length and elongate to oval in shape. Distinguishing features are the gnathosoma (mouthparts) partially/completely fused into the propodosoma, indistinct palps and the first leg pair being thickest. Life cycle Acarophenacidae have a reduced , in which the larvae complete their development within their mother; the entire life cycle can take only 4–5 days. # A mated female rides on an adult insect to disperse to new areas. In genus ''Adactylidium'', she also feeds on the insect's body fluids. # When the insect begins laying eggs, the female drops of ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescoping Generations
Telescoping generations can occur in parthenogenetic species, such as aphids or other life forms that have the ability to reproduce without ovum fertilization. This occurrence is characterized by a viviparous female having a daughter growing inside her that is also parthenogenetically pregnant with a daughter cell. This pattern of reproduction can also occur in certain mites that are not parthenogenetic, e.g. ''Adactylidium ''Adactylidium'' is a genus of mites known for its unusual life cycle. An impregnated female mite feeds upon a single egg of a thrips, rapidly growing five to eight female offspring and one male in her body. The single male mite mates with all t ...'', in which the young hatch and mate within the mother, eating her from the inside and then escaping; in some species the males never escape, and in others they die shortly afterwards. However, the resulting inbreeding has consequences much like those of parthenogenesis, and the females are not actually pregnant o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods such as insects, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the mother. At and up to , the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombidiformes Genera
The Trombidiformes are a large, diverse order of mites. Taxonomy In 1998, Trombidiformes was divided into the Sphaerolichida and the Prostigmata. The group has few synapomorphies by which it can be defined, unlike the other major group of acariform mites, Sarcoptiformes. Its members include medically important mites (such as ''Demodex'', the chiggers, and scrub-itch mites) and many agriculturally important species, including the spider mites (Tetranychidae). The superfamily Eriophyoidea, traditionally considered members of the Trombidiformes, have been found to be basal mites in genomic analyses, sister to the clade containing Sarcoptiformes and Trombidiformes. The 2004 classification retained the two suborders, comprising around 125 families and more than 22,000 described species. In the 2011 revised classification, the order now contains 151 families, 2235 genera and 25,821 species, and there were another 10 species with 24 species that present only as fossils. These 151 fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearson Education, Inc
Pearson Education is a British-owned education publishing and assessment service to schools and corporations, as well for students directly. Pearson owns educational media brands including Addison–Wesley, Peachpit, Prentice Hall, eCollege, Longman, Scott Foresman, and others. Pearson is part of Pearson plc, which formerly owned the ''Financial Times''. It claims to have been formed in 1840, with the current incarnation of the company created when Pearson plc purchased the education division of Simon & Schuster (including Prentice Hall and Allyn & Bacon) from Viacom and merged it with its own education division, Addison-Wesley Longman, to form Pearson Education. Pearson Education was rebranded to Pearson in 2011 and split into an International and a North American division. Although Pearson generates approximately 60 percent of its sales in North America, it operates in more than 70 countries. Pearson International is headquartered in London, and maintains offices across Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genetics (journal)
''Human Genetics'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering all aspects of human genetics, including legal and social issues. It was established in 1964 by Arno Motulsky and Friedrich Vogel as the German-language ''Humangenetik'', obtaining its current title in 1976. It is published by Springer Science+Business Media. Its editors-in-chief are David N. Cooper (Cardiff University) and Thomas J. Hudson (Ontario Institute for Cancer Research). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2018 impact factor of 5.20. Ethics scandal The journal published findings exploring the DNA of physical appearance traits of Uighur men from Tumxuk TumxukThe official spelling according to , (Beijing, ''SinoMaps Press'' 1997); is a sub-prefecture-level city in the western part of Xinjiang, China. The eastern part of Tumxuk is surrounded by Maralbexi County, Kashgar Prefecture. The smaller ... in 2019. One of the authors of the paper on DNA phenotyping said he had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matriphagy
Matriphagy is the consumption of the mother by her offspring. The behavior generally takes place within the first few weeks of life and has been documented in some species of insects, nematode worms, pseudoscorpions, and other arachnids as well as in caecilian amphibians. The specifics of how matriphagy occurs varies among different species, but the process is best described in the Desert spider, '' Stegodyphus lineatus'', where the mother harbors nutritional resources for her young through food consumption. The mother is able to regurgitate small portions of food for her growing offspring, but between 1–2 weeks after hatching the progeny capitalize on this food source by eating her alive. Typically, offspring only feed on their biological mother as opposed to other females in the population. In other arachnid species, matriphagy occurs after the ingestion of nutritional eggs known as trophic eggs (e.g. Black lace-weaver ''Amaurobius ferox'', Crab spider ''Australomisidia ergandr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrips
Thrips ( order Thysanoptera) are minute (mostly long or less), slender insects with fringed wings and unique asymmetrical mouthparts. Different thrips species feed mostly on plants by puncturing and sucking up the contents, although a few are predators. Entomologists have described approximately 6,000 species. They fly only weakly and their feathery wings are unsuitable for conventional flight; instead, thrips exploit an unusual mechanism, clap and fling, to create lift using an unsteady circulation pattern with transient vortices near the wings. Many thrips species are pests of commercially important crops. A few species serve as vectors for over 20 viruses that cause plant disease, especially the Tospoviruses. Some species of thrips are beneficial as pollinators or as predators of other insects or mites. In the right conditions, such as in greenhouses, many species can exponentially increase in population size and form large swarms because of a lack of natural predators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
More Reflections In Natural History
More or Mores may refer to: Computing * MORE (application), outline software for Mac OS * more (command), a shell command * MORE protocol, a routing protocol * Missouri Research and Education Network Music Albums * ''More!'' (album), by Booka Shade, 2010 * ''More'' (soundtrack), by Pink Floyd with music from the 1969 film * ''More...'' (Trace Adkins album), or the title song, 1999 * ''More'' (Mary Alessi album), 2005 * ''More'' (Beyoncé EP), 2014 * ''More'' (Michael Bublé EP), 2005 * ''More'' (Clarke-Boland Big Band album), 1968 * ''More'' (Double Dagger album), 2009 * ''More...'' (Montell Jordan album), 1996 * ''More'' (Crystal Lewis album), 2001 * ''More'' (Giuseppi Logan album), 1966 * ''More'' (No Trend album), 2001 * ''More'' (Jeremy Riddle album), or the title song, 2017 * ''More'' (Symphony Number One album), 2016 * ''More'' (Tamia album), or the title song, 2004 * ''More'' (Vitamin C album), 2001 * ''More'', by Mylon LeFevre, 1983 * ''More'', by Resin Dog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Life Cycle
In biology, a biological life cycle (or just life cycle or lifecycle when the biological context is clear) is a series of changes in form that an organism undergoes, returning to the starting state. "The concept is closely related to those of the life history, development and ontogeny, but differs from them in stressing renewal." Transitions of form may involve growth, asexual reproduction, or sexual reproduction. In some organisms, different "generations" of the species succeed each other during the life cycle. For plants and many algae, there are two multicellular stages, and the life cycle is referred to as alternation of generations. The term life history is often used, particularly for organisms such as the red algae which have three multicellular stages (or more), rather than two.Dixon, P.S. 1973. ''Biology of the Rhodophyta.'' Oliver & Boyd. Life cycles that include sexual reproduction involve alternating haploid (''n'') and diploid (2''n'') stages, i.e., a change of pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |