|
Active Networking
Active networking is a communication pattern that allows packets flowing through a telecommunications network to dynamically modify the operation of the network. Active network architecture is composed of execution environments (similar to a unix shell that can execute active packets), a node operating system capable of supporting one or more execution environments. It also consists of active hardware, capable of routing or switching as well as executing code within active packets. This differs from the traditional network architecture which seeks robustness and stability by attempting to remove complexity and the ability to change its fundamental operation from underlying network components. Network processors are one means of implementing active networking concepts. Active networks have also been implemented as overlay networks. What does it offer? Active networking allows the possibility of highly tailored and rapid "real-time" changes to the underlying network operation. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Network
A telecommunications network is a group of Node (networking), nodes interconnected by telecommunications links that are used to exchange messages between the nodes. The links may use a variety of technologies based on the methodologies of circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching, to pass messages and signals. Multiple nodes may cooperate to pass the message from an originating node to the destination node, via multiple network hops. For this routing function, each node in the network is assigned a network address for identification and locating it on the network. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space of the network. Examples of telecommunications networks include computer networks, the Internet, the public switched telephone network (PSTN), the global Telex network, the aeronautical ACARS network, and the wireless radio networks of cell phone telecommunication providers. Network structure this is the structure of network genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Architecture
Network architecture is the design of a computer network. It is a framework for the specification of a network's physical components and their functional organization and configuration, its operational principles and procedures, as well as communication protocols used. In telecommunications, the specification of a network architecture may also include a detailed description of products and services delivered via a communications network, as well as detailed rate and billing structures under which services are compensated. The network architecture of the Internet is predominantly expressed by its use of the Internet protocol suite, rather than a specific model for interconnecting networks or nodes in the network, or the usage of specific types of hardware links. OSI model The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) defines and codifies the concept of layered network architecture. Abstraction layers are used to subdivide a communications system further into smaller man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David L
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the Kings of Israel and Judah, third king of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as "Davidic line, House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the ''Seder Olam Rabbah'', ''Seder Olam Zutta'', and ''Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, Historicity of the Bible, the historicit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Complexity
In theoretical computer science, communication complexity studies the amount of communication required to solve a problem when the input to the problem is distributed among two or more parties. The study of communication complexity was first introduced by Andrew Yao in 1979, while studying the problem of computation distributed among several machines. The problem is usually stated as follows: two parties (traditionally called Alice and Bob) each receive a (potentially different) n- bit string x and y. The goal is for Alice to compute the value of a certain function, f(x, y), that depends on both x and y, with the least amount of communication between them. While Alice and Bob can always succeed by having Bob send his whole n-bit string to Alice (who then computes the function f), the idea here is to find clever ways of calculating ''f'' with fewer than n bits of communication. Note that, unlike in computational complexity theory, communication complexity is not concerned with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Processing
A network processor is an integrated circuit which has a feature set specifically targeted at the networking application domain. Network processors are typically software programmable devices and would have generic characteristics similar to general purpose central processing units that are commonly used in many different types of equipment and products. History of development In modern telecommunications networks, information (voice, video, data) is transferred as packet data (termed packet switching) which is in contrast to older telecommunications networks that carried information as analog signals such as in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or analog TV/Radio networks. The processing of these packets has resulted in the creation of integrated circuits (IC) that are optimised to deal with this form of packet data. Network processors have specific features or architectures that are provided to enhance and optimise packet processing within these networks. Network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoscale Networking
A nanonetwork or nanoscale network is a set of interconnected nanomachines (devices a few hundred nanometers or a few micrometers at most in size) which are able to perform only very simple tasks such as computing, data storing, sensing and actuation. Nanonetworks are expected to expand the capabilities of single nanomachines both in terms of complexity and range of operation by allowing them to coordinate, share and fuse information. Nanonetworks enable new applications of nanotechnology in the biomedical field, environmental research, military technology and industrial and consumer goods applications. Nanoscale communication is defined in IEEE P1906.1. Communication approaches Classical communication paradigms need to be revised for the nanoscale. The two main alternatives for communication in the nanoscale are based either on electromagnetic communication or on molecular communication. Electromagnetic This is defined as the transmission and reception of electromagnetic rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE P1906
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines. The IEEE has a corporate office in New York City and an operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The IEEE was formed in 1963 as an amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers. History The IEEE traces its founding to 1884 and the American Institute of Electrical Engineers. In 1912, the rival Institute of Radio Engineers was formed. Although the AIEE was initially larger, the IRE attracted more students and was larger by the mid-1950s. The AIEE and IRE merged in 1963. The IEEE is headquartered in New York City, but most business is done at the IEEE Operations Center in Piscataway, New Jersey, opened in 1975. The Australian Section of the IEEE existed between 1972 and 1985, after which it split into state- and te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix Shell
A Unix shell is a Command-line_interface#Command-line_interpreter, command-line interpreter or shell (computing), shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to control the execution of the system using shell scripts. Users typically interact with a Unix shell using a terminal emulator; however, direct operation via serial hardware connections or Secure Shell are common for server systems. All Unix shells provide filename Wildcard character, wildcarding, Pipeline (Unix), piping, here documents, command substitution, Variable (programming), variables and control flow, control structures for Conditional (programming), condition-testing and iteration. Concept Generally, a ''shell'' is a program that executes other programs in response to text commands. A sophisticated shell can also change the environment in which other programs exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
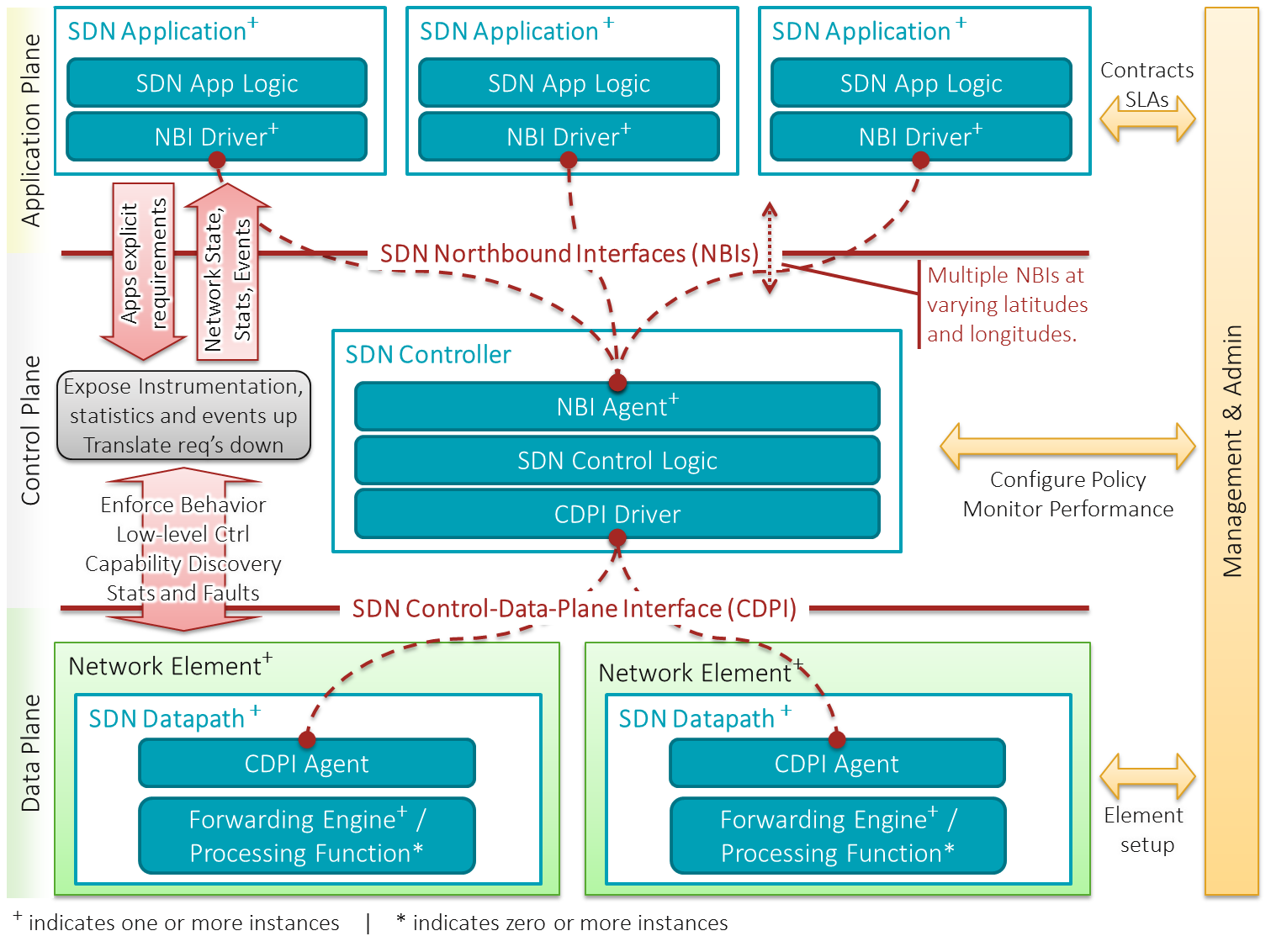
Software-defined Networking
Software-defined networking (SDN) is an approach to network management that uses abstraction to enable dynamic and programmatically efficient network configuration to create grouping and segmentation while improving network performance and monitoring in a manner more akin to cloud computing than to traditional network management. SDN is meant to improve the static architecture of traditional networks and may be employed to centralize network intelligence in one network component by disassociating the forwarding process of network packets ( data plane) from the routing process ( control plane). The control plane consists of one or more controllers, which are considered the brains of the SDN network, where the whole intelligence is incorporated. However, centralization has certain drawbacks related to security, scalability and elasticity. SDN was commonly associated with the OpenFlow protocol for remote communication with network plane elements to determine the path of network pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to generate high-quality solutions to optimization and search problems via biologically inspired operators such as selection, crossover, and mutation. Some examples of GA applications include optimizing decision trees for better performance, solving sudoku puzzles, hyperparameter optimization, and causal inference. Methodology Optimization problems In a genetic algorithm, a population of candidate solutions (called individuals, creatures, organisms, or phenotypes) to an optimization problem is evolved toward better solutions. Each candidate solution has a set of properties (its chromosomes or genotype) which can be mutated and altered; traditionally, solutions are represented in binary as strings of 0s and 1s, but other encod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |