|
Actinolepidae
Actinolepidae is an extinct family of placoderm fishes which lived during the Early Devonian period. They are considered to be among the most primitive of the arthrodires, and are widely accepted to be phylogenetically basal to the group. Description The bodies of Actinolepids are wide and flat, suggesting that most members of this family were benthic fish. Their jaws were comparatively underdeveloped in comparison to the more robust-jawed arthrodires that would come after them, such as ''Dunkleosteus ''Dunkleosteus'' is an extinct genus of large armored, jawed fishes that existed during the Late Devonian period, about 382–358 million years ago. It consists of ten species, some of which are among the largest placoderms to have ever lived: ...'' and '' Coccosteus'', indicating that it likely subsisted primarily on smaller, softer-bodied animals such as mollusks or worms instead of larger, tougher prey animals. References External links * Devonian placoderms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
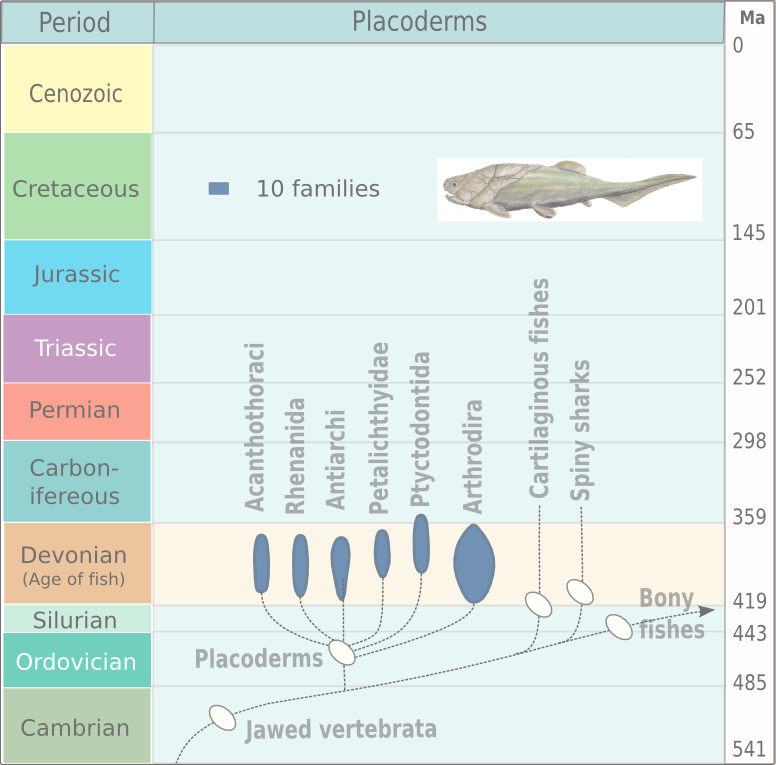
Arthrodira
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus ''Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, ''Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed ''Rolfosteus'' measured just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrodires
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus ''Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, ''Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed ''Rolfosteus'' measured just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinolepis (placoderm)
''Actinolepis'' is an extinct genus of actinolepidH. G. Johnson, D. K. Elliott, and J. H. Wittke. 2000. A new actinolepid arthrodire (Class Placodermi) from the Lower Devonian Sevy Dolomite, east-central Nevada. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 129(2):241-266 . Wagner/P. Wagner/P. Wagner/ref> placoderm from the Early Devonian. Four species are known: ''A. magna'' from Estonia,R. Denison. 1978. Placodermi. In H.-P. Schultze (ed.), Handbook of Palaeoichthyology 2:1-128 . Dahdul/B. Frable /G. Lloyd/ref> ''A. spinosa'' from Latvia ( Sevy Dolomite), the type species ''A. tuberculata'' from New Zealand ( Adam Mudstone Formation) and ''A. zaikai'' from Belarus ( Lepel Beds). Gallery Estonian Museum of Natural History Specimen No 203503 photo (g204 g204-1 jpg).jpg, Fragmentary dorsal armour of ''A. magna'' (specimen EMNH 203503); housed at the Estonian Museum of Natural History The Estonian Museum of Natural History (abbreviated EMNH; Estonian language, Estonian: ''Ees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lehmanosteus
''Lehmanosteus'' is an extinct arthrodire placoderm fish. Its fossils have been found in Early Devonian strate. It was first referred to as Actinolepidae Actinolepidae is an extinct family of placoderm fishes which lived during the Early Devonian period. They are considered to be among the most primitive of the arthrodires, and are widely accepted to be phylogenetically basal to the group. Des ... sp. References Arthrodire genera Emsian life Fossil taxa described in 1984 {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aethapsis
''Aethapsis'' is an actinolepid placoderm known from two species, ''A. major'' and ''A. utahensis''. Placoderms of North America Placoderms Paleontology in Utah Paleontology in Ohio {{placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleosteus
''Aleosteus eganensis'' is an extinct arthrodire placoderm fish. Its fossils have been found in the Late Emsian The Emsian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 407.6 ± 2.6 million years ago to 393.3 ± 1.2 million years ago. It was preceded by the Pragian Stage and followed by the Eifelian Stage. It is named after the ... strate of the Sevy Dolomite Formation, in the Egan Range of east-central Nevada, USA. Almost complete fossils belong to juvenile and adult specimens and show a short and broad skull, posteriorly concave. References Arthrodire genera Placoderms of North America Emsian life Fossil taxa described in 2000 Fossils of Nevada {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heightingtonaspis
''Heightingtonaspis'' is an extinct genus of primitive arthrodire placoderm with two species previously allied with the genus '' Kujdanowiaspis''. The fossils of ''H. anglica'' were first discovered on the surface at Besom Farm Quarry, Shropshire, England and the fossils were radiocarbon dated ''in situ ''In situ'' (; often not italicized in English) is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position." It can mean "locally", "on site", "on the premises", or "in place" to describe where an event takes place and is used in ...'' to 416 million years old.White, E.I. (1969). The deepest vertebrate fossil and other arctolepid fishes. ''Biological Journal of the Linnean Society'' 1(3): 293-310 References Placoderms of Europe Placoderms Fossil taxa described in 1969 {{placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kujdanowiaspis
''Kujdanowiaspis'' is an extinct genus of actinolepid placoderm from the Early Devonian of Nyrkiv, Ukraine and Poland. As an actinolepid, it is among the most basal of all placoderms. ''Kujdanowiaspis'' is only known from many well-preserved fragmentary head shield and skull fossils. After revising the genus in 2010, Dupret left three species within the genus: ''K. buczacziensis'', ''K. podolica'' and possibly also ''K. zychi''. Description Because of the consistently poor preservation of ''Kujdanowiaspis'' fossils, little is known about its physiology. What is known about it is typical of Actinolepid placoderms, and it could be compared to the better known primitive arthrodires such as '' Dicksonosteus'' or '' Actinolepis''. It had a very pronounced, serrated spinal plate, giving it an almost lunate dorsal silhouette. Its body is wide and flat, suggesting a benthic lifestyle. Its jaws were comparatively underdeveloped in comparison to the more robust-jawed arthrodires that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simblaspis
''Simblaspis'' is an extinct arthrodire placoderm fish. Its fossils have been found in Pragian strate of the Qasr Limestone in Saudi Arabia Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A .... References Arthrodire genera Pragian life Fossil taxa described in 1958 {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian Placoderms
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |