|
Actin Filament
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but are modified by and interact with numerous other proteins in the cell. Microfilaments are usually about 7 nm in diameter and made up of two strands of actin. Microfilament functions include cytokinesis, amoeboid movement, cell motility, changes in cell shape, endocytosis and exocytosis, cell contractility, and mechanical stability. Microfilaments are flexible and relatively strong, resisting buckling by multi-piconewton compressive forces and filament fracture by nanonewton tensile forces. In inducing cell motility, one end of the actin filament elongates while the other end contracts, presumably by myosin II molecular motors. Additionally, they function as part of actomyosin-driven contractile molecular motors, wherein the thin filaments serve as tensile platforms for myosin's ATP-depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEF Microfilaments
MEF may stand for: Military * Malaita Eagle Force, a militant organization originating in the island of Malaita in the Solomon Islands * Marine Expeditionary Force (MEF), one of the major deployable subdivisions of the United States Marine Corps; see 1st Marine Expeditionary Force, 2nd Marine Expeditionary Force, 3rd Marine Expeditionary Force * Mediterranean Expeditionary Force * Mesopotamian Expeditionary Force during the First World War Organizations * Mahratta Education Fund, Indian non-profit organisation * Major Economies Forum on Energy and Climate Change * Media Education Foundation * MEF International School Istanbul * Middle East Forum, an American conservative think tank * Ministerio de Economía y Finanzas, the Uruguayan ministry of economics and finance * Ministero dell’Economia e delle Finanze, the Italian ministry of economics and finance * Ministry of Environment and Forests, India Science/technology * Managed Extensibility Framework, a software plugin f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
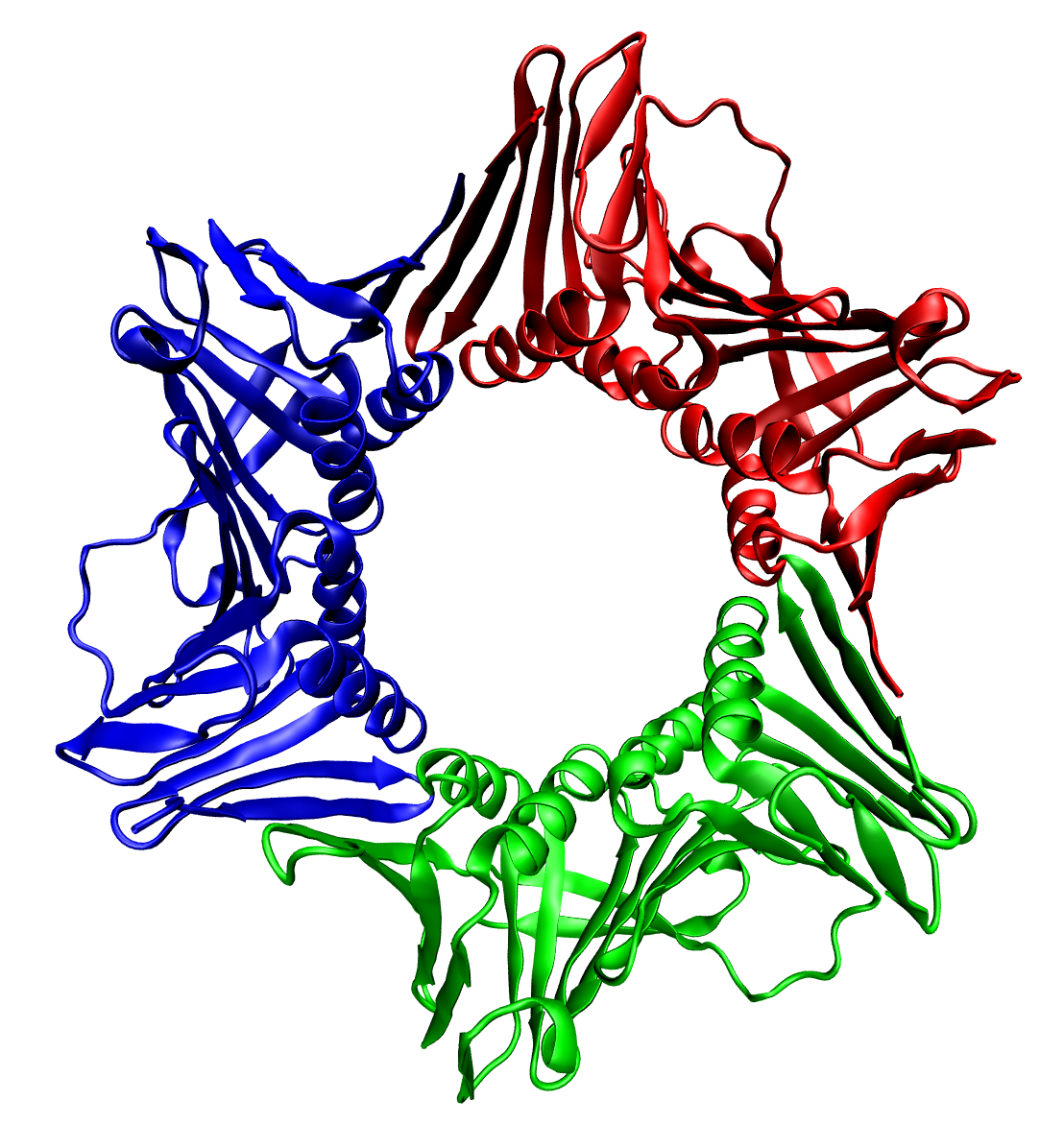
Trimer (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a protein trimer is a macromolecular complex formed by three, usually non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids. A homotrimer would be formed by three identical molecules. A heterotrimer would be formed by three different macromolecules. Type II Collagen is an example of homotrimeric protein. Porins usually arrange themselves in membranes as trimers. Bacteriophage T4 tail fiber Multiple copies of a polypeptide encoded by a gene often can form an aggregate referred to as a multimer. When a multimer is formed from polypeptides produced by two different mutant alleles of a particular gene, the mixed multimer may exhibit greater functional activity than the unmixed multimers formed by each of the mutants alone. When a mixed multimer displays increased functionality relative to the unmixed multimers, the phenomenon is referred to as intragenic complementation. The distal portion of each of the bacteriophage T4 tail fibers is encoded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleation
In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that determines how long an observer has to wait before the new phase or self-organized structure appears. For example, if a volume of water is cooled (at atmospheric pressure) below 0°C, it will tend to freeze into ice, but volumes of water cooled only a few degrees below 0°C often stay completely free of ice for long periods (supercooling). At these conditions, nucleation of ice is either slow or does not occur at all. However, at lower temperatures nucleation is fast, and ice crystals appear after little or no delay. Nucleation is a common mechanism which generates first-order phase transitions, and it is the start of the process of forming a new thermodynamic phase. In contrast, new phases at continuous phase transitions start to form immedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Quaternary Structure
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth (and highest) classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains (also referred to as subunits). Protein quaternary structure describes the number and arrangement of multiple protein folding, folded protein subunits in a Multiprotein complex, multi-subunit complex. It includes organizations from simple protein dimer, dimers to large homooligomers and multiprotein complex, complexes with defined or variable numbers of subunits. In contrast to the first three levels of protein structure, not all proteins will have a quaternary structure since some proteins function as single units. Protein quaternary structure can also refer to biomolecular complexes of proteins with nucleic acids and other Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors. Description and examples Many proteins are actually assemblies of multiple polypeptide c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding (molecular)
Molecular binding is an attractive interaction between two molecules that results in a stable association in which the molecules are in close proximity to each other. It is formed when atoms or molecules bind together by sharing of electrons. It often, but not always, involves some chemical bonding. In some cases, the associations can be quite strong—for example, the protein streptavidin and the vitamin biotin have a dissociation constant (reflecting the ratio between bound and free biotin) on the order of 10−14—and so the reactions are effectively irreversible. The result of molecular binding is sometimes the formation of a molecular complex in which the attractive forces holding the components together are generally non-covalent, and thus are normally energetically weaker than covalent bonds. Molecular binding occurs in biological complexes (e.g., between pairs or sets of proteins, or between a protein and a small molecule ligand it binds) and also in abiologic chemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a dimer of two globular proteins, alpha and beta tubulin into protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including the movement of secretory vesicles, organell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helix
A helix () is a shape like a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices. The word ''helix'' comes from the Greek word ''ἕλιξ'', "twisted, curved". A "filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is a surface called ''helicoid''. Properties and types The ''pitch'' of a helix is the height of one complete helix turn, measured parallel to the axis of the helix. A double helix consists of two (typically congruent) helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. A circular helix (i.e. one with constant radius) has constant band curvature and constant torsion. A ''conic helix'', also known as a ''conic spiral'', may be defined as a spiral on a conic surface, with the distance to the apex an expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymers
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'', meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid for the diameter of a sphere. In more modern usage, the length d of a diameter is also called the diameter. In this sense one speaks of diameter rather than diameter (which refers to the line segment itself), because all diameters of a circle or sphere have the same length, this being twice the radius r. :d = 2r \qquad\text\qquad r = \frac. For a convex shape in the plane, the diameter is defined to be the largest distance that can be formed between two opposite parallel lines tangent to its boundary, and the is often defined to be the smallest such distance. Both quantities can be calculated efficiently using rotating calipers. For a curve of constant width such as the Reuleaux triangle, the width and diameter are the same because all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, American spelling) is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth (short scale) of a metre () and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as , and as metres. History The nanometre was formerly known as the millimicrometre – or, more commonly, the millimicron for short – since it is of a micron (micrometre), and was often denoted by the symbol mμ or (more rarely and confusingly, since it logically should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron) as μμ. Etymology The name combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the parent unit name ''metre'' (from Greek , ', "unit of measurement"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |