|
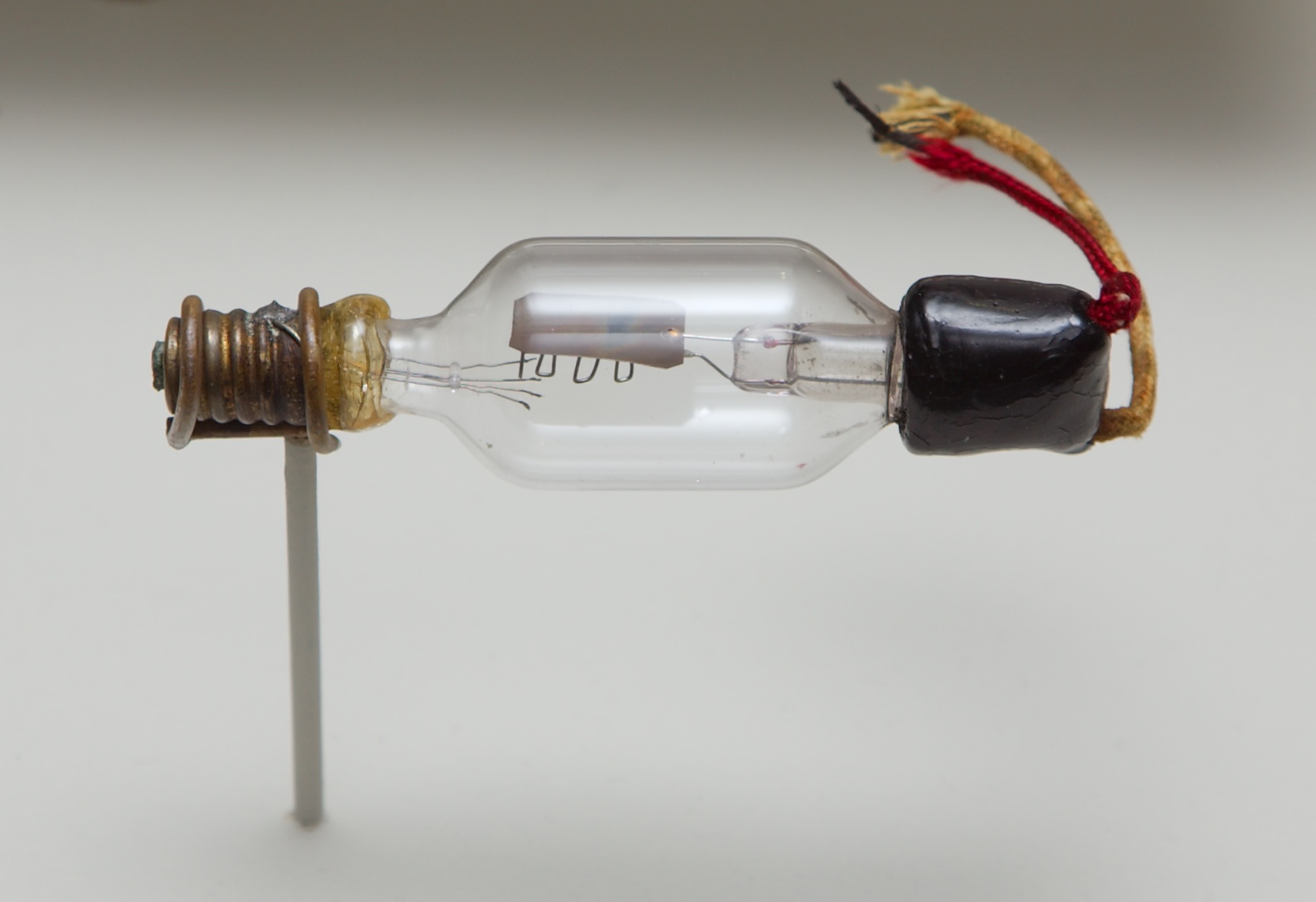
Acorn Tube
The 955 is typical of the acorn designs, named for the glass cap holding the terminals with the main part of the tube extending from it. An acorn tube, or acorn valve, refers to any member of a family of VHF/ UHF vacuum tubes starting just before World War II. They were named after their resemblance to the acorn, specifically due to the glass cap at one end of the tube that looked similar to the cap on an acorn. The acorn tubes found widespread use in radios and radar systems. High-frequency performance is limited by (1) parasitic lead inductance and capacitance and skin effect, and (2) electron transit time (the time required to travel from cathode to anode). Transit time effects are complicated, but one simple effect is the phase margin; another one is input conductance, also known as grid loading. At extremely high frequencies, electrons arriving at the grid may become out of phase with those departing towards the anode. This imbalance of charge causes the grid to exhibit a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuvistor
The nuvistor is a type of vacuum tube announced by RCA in 1959. Nuvistors were made to compete with the then-new bipolar junction transistors, and were much smaller than conventional tubes of the day, almost approaching the compactness of early discrete transistor casings. Due to their small size, there was no space to include a vacuum fitting to evacuate the tube; instead, nuvistors were assembled and processed in a vacuum chamber with simple robotic devices. The tube is made entirely of metal with a ceramic base. Triodes and a few tetrodes were made; Nuvistor tetrodes were taller than their triode counterparts. Nuvistors are among the highest performing small signal receiving tubes. They feature excellent VHF and UHF performance plus low noise figures, and were widely used throughout the 1960s in television sets (beginning with RCA's "New Vista" line of color sets in 1961 with the CTC-11 chassis), radio and high-fidelity equipment primarily in RF sections, and oscilloscope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EF50
In the field of electronics, the EF50 is an early all-glass wideband remote cutoff pentode designed in 1938 by Philips. It was a landmark in the development of vacuum tube technology, departing from construction ideas of the time essentially unchanged from light bulb designs. Initially used in television receivers, it quickly gained a vital role in British radar and great efforts were made to secure a continuing supply of the device as Holland fell in World War II. The EF50 tube is a 9-pin Loctal-socket device with short internal wires to nine short chromium-iron pins, making it suitable for Very High Frequency (VHF) use. History The EF50 was preceded by RCA's acorn design and several other attempts, such as the "Stahlröhre" (~steel tube) from Telefunken, to reduce inductance in the wire leads, all with some disadvantages. Philips had been working since 1934–1935 on an alternative that would solve the problems of the other bases, and a design that could be produced cheaply a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Tube Designations
Vacuum tubes produced in the former Soviet Union and in present-day Russia carry their own unique designations. Some confusion has been created in "translating" these designations, as they use Cyrillic rather than Latin characters. 1929 system The first system was introduced in 1929. It consisted of one or two letters and a number with up to 3 digits denoting the production number First letter: System type: *B (Russian: Б) – Power oscillator tube or barretter *V (Russian: В) – Rectifier *G (Russian: Г) – Transmitting tube ("генераторная" "generator") * J (Russian: Ж) – Low-power oscillator tube *M (Russian: M) – Modulator *N (Russian: Н) – AF amplifier *P (Russian: П) – Receiver tube *S (Russian: С) – Special tube, such as a tetrode, a pentode or a CRT *T (Russian: Т) – Carrier frequency tube *U (Russian: У) – Amplifier tube Second letter (optional): Type of cathode: *B (Russian: Б) – Barium-coated *K (Russian: К) – Carburized * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
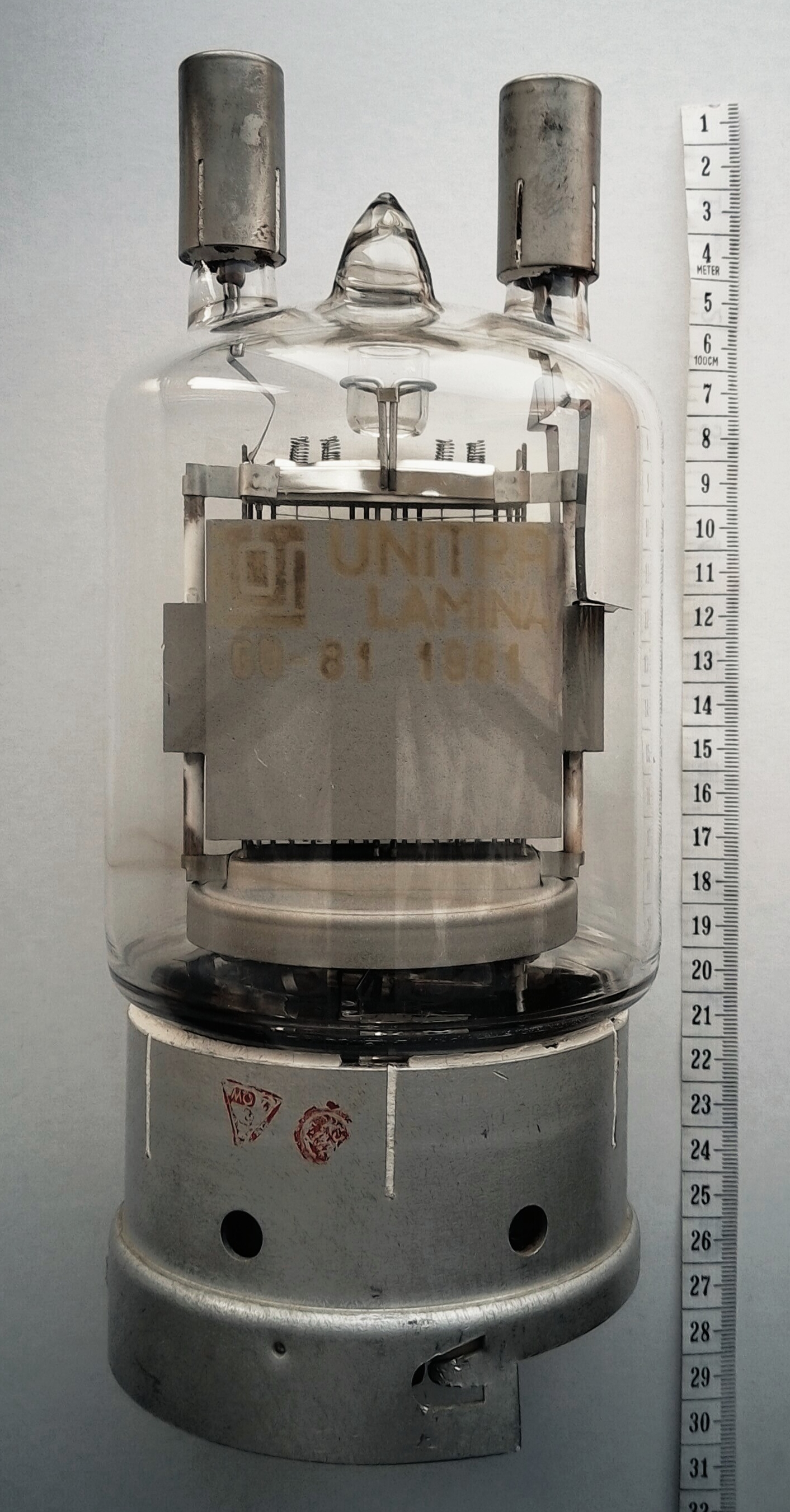
Mullard–Philips Tube Designation
In Europe, the principal method of numbering vacuum tubes ("thermionic valves") was the nomenclature used by the Philips company and its subsidiaries Mullard in the UK, Valvo( de, it) in Germany, Radiotechnique (''Miniwatt-Dario'' brand) in France, and Amperex in the United States, from 1934 on. Adhering manufacturers include AEG (de), CdL (1921, ''French Mazda'' brand), CIFTE (fr, ''Mazda-Belvu'' brand), EdiSwan (''British Mazda'' brand), Lorenz (de), MBLE( fr, nl) (be, ''Adzam'' brand), RCA (us), RFT( de, sv) (de), Siemens (de), Telefunken (de), Tesla (cz), Toshiba (ja), Tungsram (hu), and Unitra (pl; ''Dolam'', ''Polam'', ''Telam'' brands). This system allocated meaningful codes to tubes based on their function and became the starting point for the Pro Electron naming scheme for active devices (including tubes and transistors). Nomenclature systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RETMA Tube Designation
The Radio Electronics Television Manufacturers' Association was formed in 1953, as a result of mergers with other trade standards organisations, such as the RMA. It was principally responsible for the standardised nomenclature for American vacuum tubes - however the standard itself had already been in use for a long time before 1953; for example, the 6L6 was introduced in July 1936. American-made tubes bear a RETMA designation to allow for easy cross-referencing. The RETMA tube designation does not incorporate the purpose of each tube in the designation. The Anglo-European Mullard–Philips tube designation does include tube use information in the designation. *First figure group: indicates heater/filament voltage; 0 means a cold-cathode tube. * Letter group: letter(s) indicate the serial order of assignment of the designation; combinations like AB, AC, AD, AE... were used, avoiding same-letter repetitions, after the single letters were exhausted. Wherever possible, the 12V equiva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of EIA Standards
Here is a list of American Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) Standards. The EIA ceased operations on February 11, 2011, but the former sectors continue to serve the constituencies of EIA. EIA designated ECA to continue to develop standards for interconnect, passive and electro-mechanical (IP&E) electronic components under the ANSI-designation of EIA standards. All other electronic components standards are managed by their respective sectors. ECA is expected to merge with the National Electronic Distributors Association (NEDA) to form the Electronic Components Industry Association (ECIA). However, the EIA standards brand will continue for IP&E standards within ECIA. As currently authorized, any ANSI standard designated at ANSI EIA-xxx is developed and/or managed by ECA (and, in the future, ECIA). 1–199 * TIA/EIA-41 Cellular Radiocommunications Intersystem Operations. * EIA/TIA/IS-55 Recommended Minimum Performance Standards of 800 MHz Dual Mode Mobile Stations * EIA/TIA/IS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel–cadmium Battery
The nickel–cadmium battery (Ni–Cd battery or NiCad battery) is a type of rechargeable battery using nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes. The abbreviation ''Ni-Cd'' is derived from the chemical symbols of nickel (Ni) and cadmium (Cd): the abbreviation ''NiCad'' is a registered trademark of SAFT Corporation, although this brand name is commonly used to describe all Ni–Cd batteries. Wet-cell nickel-cadmium batteries were invented in 1899. A Ni-Cd battery has a terminal voltage during discharge of around 1.2 volts which decreases little until nearly the end of discharge. The maximum electromotive force offered by a Ni-Cd cell is 1.3V. Ni-Cd batteries are made in a wide range of sizes and capacities, from portable sealed types interchangeable with carbon-zinc dry cells, to large ventilated cells used for standby power and motive power. Compared with other types of rechargeable cells they offer good cycle life and performance at low temperatures with a fai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentode
A pentode is an electronic device having five electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a three-grid amplifying vacuum tube or thermionic valve that was invented by Gilles Holst and Bernhard D.H. Tellegen in 1926. The pentode (called a ''triple-grid amplifier'' in some literature) was developed from the ''screen-grid tube'' or ''shield-grid tube'' (a type of tetrode tube) by the addition of a grid between the screen grid and the plate. The screen-grid tube was limited in performance as an amplifier due to secondary emission of electrons from the plate. The additional grid is called the ''suppressor grid''. The suppressor grid is usually operated at or near the potential of the cathode and prevents secondary emission electrons from the plate from reaching the screen grid. The addition of the suppressor grid permits much greater output signal amplitude to be obtained from the plate of the pentode in amplifier operation than from the plate of the screen-grid tube at the same plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or ''valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Developed from Lee De Forest's 1906 Audion, a partial vacuum tube that added a grid electrode to the thermionic diode (Fleming valve), the triode was the first practical electronic amplifier and the ancestor of other types of vacuum tubes such as the tetrode and pentode. Its invention founded the electronics age, making possible amplified radio technology and long-distance telephony. Triodes were widely used in consumer electronics devices such as radios and televisions until the 1970s, when transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. In recent years there has been a resurgence in demand for low power triodes due to renewed interest in tube-type audio systems by audiophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or ''valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Developed from Lee De Forest's 1906 Audion, a partial vacuum tube that added a grid electrode to the thermionic diode (Fleming valve), the triode was the first practical electronic amplifier and the ancestor of other types of vacuum tubes such as the tetrode and pentode. Its invention founded the electronics age, making possible amplified radio technology and long-distance telephony. Triodes were widely used in consumer electronics devices such as radios and televisions until the 1970s, when transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. In recent years there has been a resurgence in demand for low power triodes due to renewed interest in tube-type audio systems by audiophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very High Frequency
Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves ( radio waves) from 30 to 300 megahertz (MHz), with corresponding wavelengths of ten meters to one meter. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted high frequency (HF), and the next higher frequencies are known as ultra high frequency (UHF). VHF radio waves propagate mainly by line-of-sight, so they are blocked by hills and mountains, although due to refraction they can travel somewhat beyond the visual horizon out to about 160 km (100 miles). Common uses for radio waves in the VHF band are Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) and FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, two-way land mobile radio systems (emergency, business, private use and military), long range data communication up to several tens of kilometers with radio modems, amateur radio, and marine communications. Air traffic control communications and air navigation systems (e.g. VOR and ILS) wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |