|
Accessory Muscle
An accessory muscle is a relatively rare anatomical variation where duplication of a muscle may appear anywhere in the muscular system. Treatment is not indicated unless the accessory muscle interferes with normal function. Examples are the sternalis muscle, accessory soleus muscle, extensor digitorum brevis manus and epitrochleoanconeus muscle. An accessory muscle can also refer to a muscle that is not primarily responsible for movement but does provide assistance. Examples of such muscles are the accessory muscles of respiration where the sternocleidomastoid and the scalene muscles (anterior, middle and posterior scalene) are typically considered accessory muscles of respiration.Netter FH. Atlas of Human Anatomy 3rd ed. Icon Learning Systems. Teterboro, New Jersey 2003 - plate 191 See also * Accessory bone An accessory bone or supernumerary bone is a bone that is not normally present in the body, but can be found as a variant in a significant number of people. It poses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Variation
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomical variations are categorized into three types including morphometric (size or shape), consistency (present or absent), and spatial (proximal/distal or right/left). Variations are seen as normal in the sense that they are found consistently among different individuals, are mostly without symptoms, and are termed anatomical variations rather than abnormalities. Anatomical variations are mainly caused by genetics and may vary considerably between different populations. The rate of variation considerably differs between single organs, particularly in muscles. Knowledge of anatomical variations is important in order to distinguish them from pathological conditions. A very early paper published in 1898, presented anatomic variations to have a wide range and sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
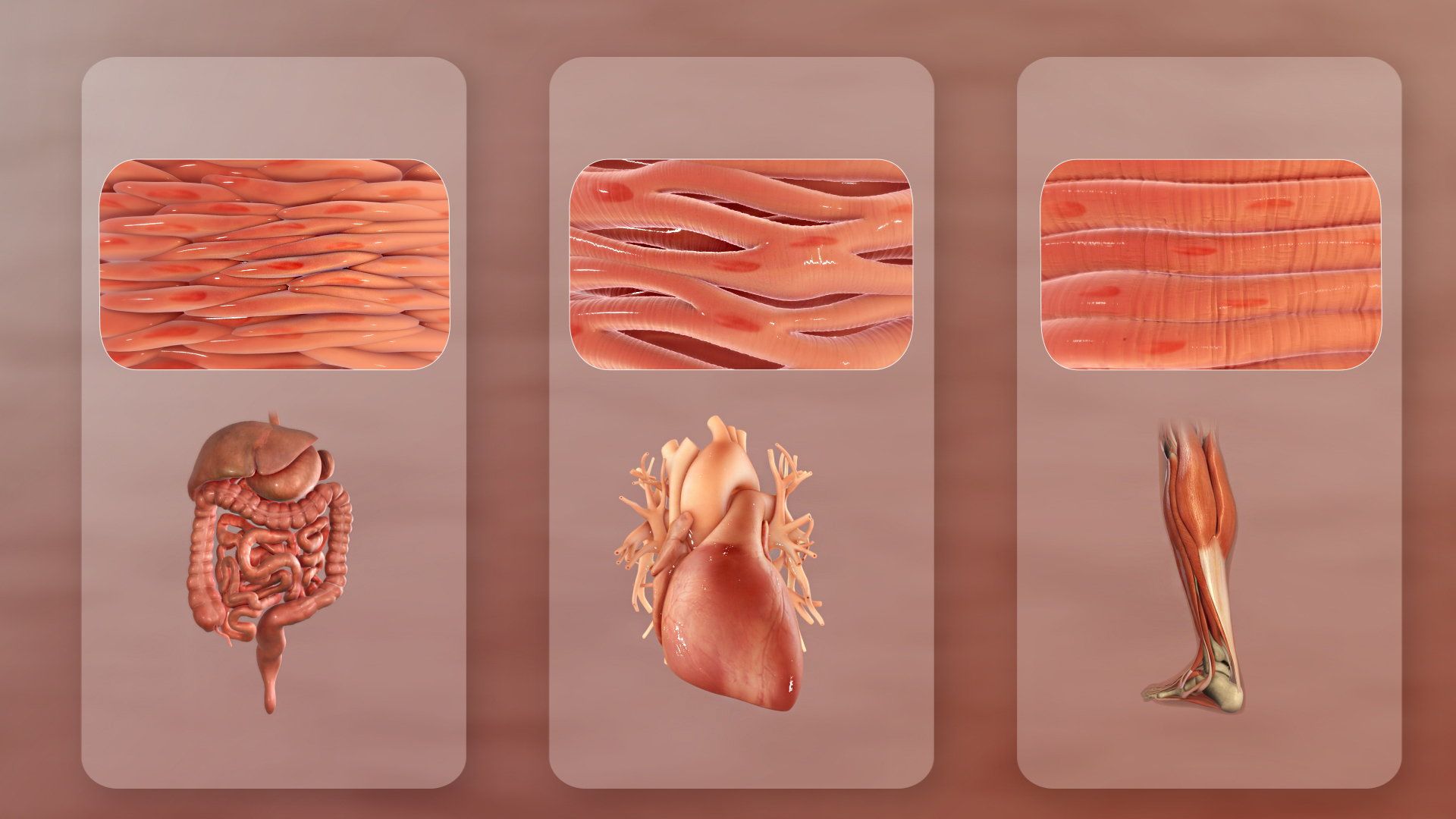
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular System
The muscular system is an organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates blood throughout the body. The muscular systems in vertebrates are controlled through the nervous system although some muscles (such as the cardiac muscle) can be completely autonomous. Together with the skeletal system in the human, it forms the musculoskeletal system, which is responsible for the movement of the body. Types There are three distinct types of muscle: skeletal muscle, cardiac or heart muscle, and smooth (non-striated) muscle. Muscles provide strength, balance, posture, movement, and heat for the body to keep warm. There are over 650 muscles in the human body. A kind of elastic tissue makes up each muscle, which consists of thousands, or tens of thousands, of small muscle fibers. Each fiber comprises many tiny strands called fibrils, impulses from nerve cells control the contraction of each muscle fib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
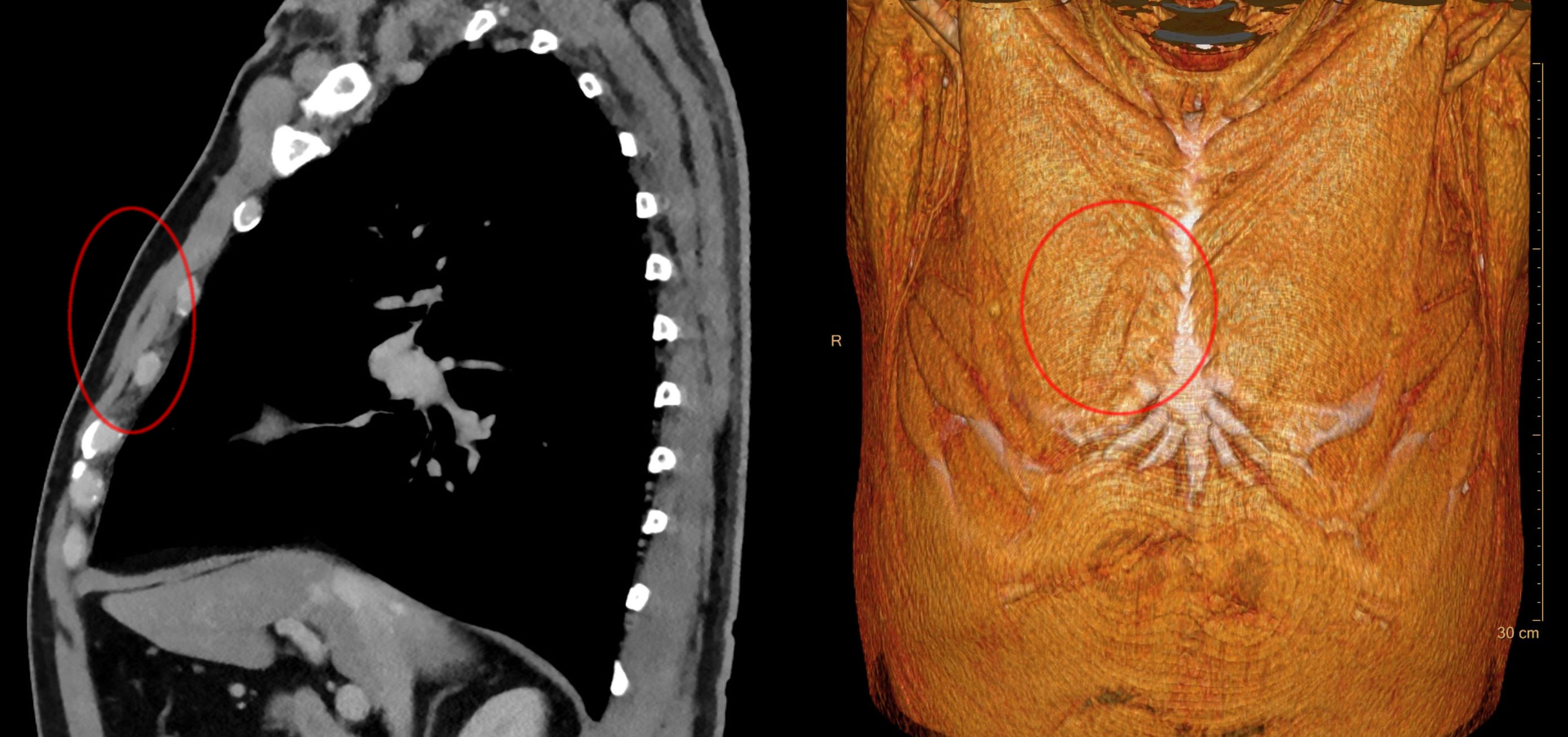
Sternalis Muscle
The sternalis muscle is an anatomical variation that lies in front of the sternal end of the pectoralis major parallel to the margin of the sternum. The sternalis muscle may be a variation of the pectoralis major or of the rectus abdominis. Structure The sternalis is a muscle that runs along the anterior aspect of the body of the sternum. It lies superficially and parallel to the sternum. Its origin and insertion are variable. The sternalis muscle often originates from the upper part of the sternum and can display varying insertions such as the pectoral fascia, lower ribs, costal cartilages, rectus sheath, aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle. There is still a great deal of disagreement about its innervation and its embryonic origin. In a review, it was reported that the muscle was innervated by the external or internal thoracic nerves in 55% of the cases, by the intercostal nerves in 43% of the cases, while the remaining cases were supplied by both nerves. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Soleus Muscle
The accessory soleus muscle is an accessory muscle of the calf which is rarely present in humans; it is, however, the most common accessory muscle of the ankle. The muscle inserts on the anterior aspect of the soleus muscle or on the posterior aspect of the tibia or the muscles of the deep posterior compartment. It lies anterior to the calcaneal tendon and terminates on the calcaneal tendon or the superior or medial aspect of the calcaneus via fleshy fibers or a distinct tendon. Present in approximately 3% (or 10%)Kouvalchouk JF, et al. 2018. of people, this muscle usually appears as a distant belly, medial to the Achilles tendon The Achilles tendon or heel cord, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is a tendon at the back of the lower leg, and is the thickest in the human body. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius (calf) and soleus muscles to the calcaneus ( .... Clinically, the accessory soleus may be associated with pain and edema during periods of prolonged ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Digitorum Brevis Manus
Extensor digitorum brevis manus is an extra or accessory muscle on the backside (dorsum) of the hand. It was first described by Albinus in 1758. The muscles lies in the fourth extensor compartment of the wrist, and is relatively rare. It has a prevalence of 4% in the general population according to a meta-analysis. This muscle is commonly misdiagnosed as a ganglion cysta, synovial nodule or cyst. Structure The extensor digitorum brevis manus usually originates from the dorsal aspect (backside) of the wrist, either from the joint capsule, the distal end (the most distant end) of the radius, the metacarpal, or from the radiocarpal ligament in the area of the fourth extensor compartment. Many variations of the muscle have been described in the literature. It could have up to four tendons with a single tendon inserting to the index or the middle finger being the two most common variations. At the insertion the tendon of the extensor digitorum brevis manus often joins the extensor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epitrochleoanconeus Muscle
The epitrochleoanconeus muscle (anconeous epitrochlearis muscle, anconeus-epitrochlearis or anconeus sextus) is a small accessory muscle of the arm which runs from the back of the inner condyle of the humerus over the ulnar nerve to the olecranon. The average prevalence of this muscle is 14.2% in healthy individuals. Structure The epitrochleoanconeus is a short striated muscle which originates on the posterior surface of the medial epicondyle of the humerus. The muscle runs over the ulnar nerve, forms an arch over the cubital tunnel and inserts on the olecranon. It is innervated by the ulnar nerve. Variation There are cases where there is no structure at all bridging the space occupied by the epitrochleoanconeus. The muscle tends to be hypertrophied when associated with cubital tunnel syndrome. Clinical significance The presence of the epitrochleoanconeus muscle can lead to ulnar neuropathy, or cubital tunnel syndrome, due to compression of the ulnar nerve. The absence of epit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscles Of Respiration
The muscles of respiration are the muscles that contribute to inhalation and exhalation, by aiding in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm and, to a lesser extent, the intercostal muscles drive respiration during quiet breathing. The elasticity of these muscles is crucial to the health of the respiratory system and to maximize its functional capabilities. Diaphragm The diaphragm is the major muscle responsible for breathing. It is a thin, dome-shaped muscle that separates the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts, so that its center moves caudally (downward) and its edges move cranially (upward). This compresses the abdominal cavity, raises the ribs upward and outward and thus expands the thoracic cavity. This expansion draws air into the lungs. When the diaphragm relaxes, elastic recoil of the lungs causes the thoracic cavity to contract, forcing air out of the lungs, and returning to its dome-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
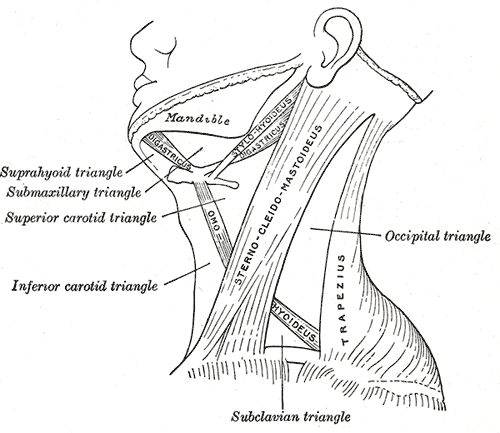
Sternocleidomastoid
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its centre, and broader and thinner at either end. The sternal head is a round fasciculus, tendinous in front, fleshy behind, arising from the upper part of the front of the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
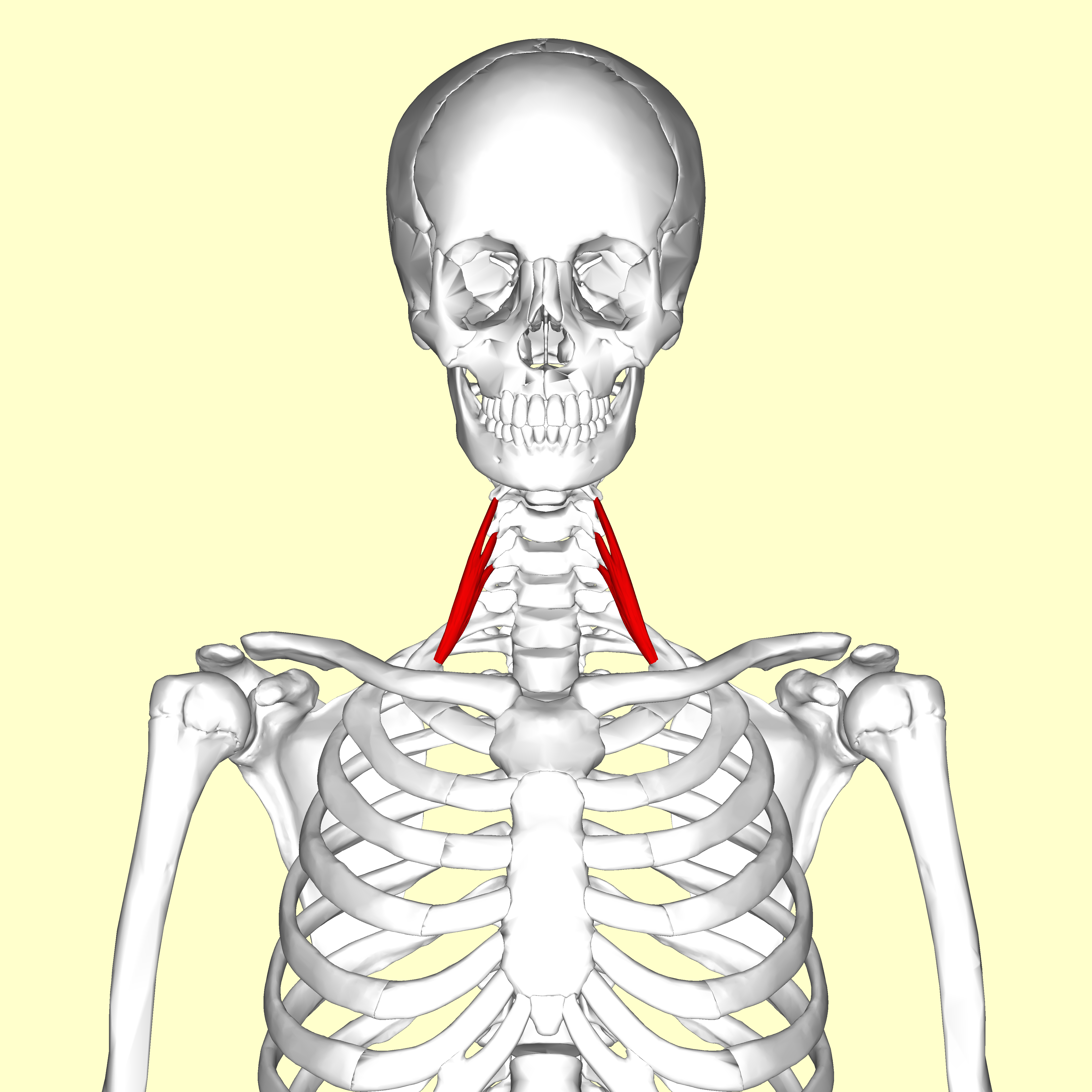
Scalene Muscles
The scalene muscles are a group of three pairs of muscles in the lateral neck, namely the anterior scalene, middle scalene, and posterior scalene. They are innervated by the third to the eight cervical spinal nerves (C3-C8). The anterior and middle scalene muscles lift the first rib and bend the neck to the same side; the posterior scalene lifts the second rib and tilts the neck to the same side. The muscles are named . Structure The scalene muscles originate from the transverse processes from the cervical vertebrae of C2 to C7 and insert onto the first and second ribs. Anterior scalene The anterior scalene muscle ( la, scalenus anterior), lies deeply at the side of the neck, behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It arises from the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebrae, and descending, almost vertically, is inserted by a narrow, flat tendon into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first rib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalenus Anterior
The scalene muscles are a group of three pairs of muscles in the lateral neck, namely the anterior scalene, middle scalene, and posterior scalene. They are innervated by the third to the eight cervical spinal nerves (C3-C8). The anterior and middle scalene muscles lift the first rib and bend the neck to the same side; the posterior scalene lifts the second rib and tilts the neck to the same side. The muscles are named . Structure The scalene muscles originate from the transverse processes from the cervical vertebrae of C2 to C7 and insert onto the first and second ribs. Anterior scalene The anterior scalene muscle ( la, scalenus anterior), lies deeply at the side of the neck, behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It arises from the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebrae, and descending, almost vertically, is inserted by a narrow, flat tendon into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first rib, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalenus Medius
The scalene muscles are a group of three pairs of muscles in the lateral neck, namely the anterior scalene, middle scalene, and posterior scalene. They are innervated by the third to the eight cervical spinal nerves (C3-C8). The anterior and middle scalene muscles lift the first rib and bend the neck to the same side; the posterior scalene lifts the second rib and tilts the neck to the same side. The muscles are named . Structure The scalene muscles originate from the transverse processes from the cervical vertebrae of C2 to C7 and insert onto the first and second ribs. Anterior scalene The anterior scalene muscle ( la, scalenus anterior), lies deeply at the side of the neck, behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It arises from the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebrae, and descending, almost vertically, is inserted by a narrow, flat tendon into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |