|
Accelerated Life Testing
Accelerated life testing is the process of testing a product by subjecting it to conditions (stress, strain, temperatures, voltage, vibration rate, pressure etc.) in excess of its normal service parameters in an effort to uncover faults and potential modes of failure in a short amount of time. By analyzing the product's response to such tests, engineers can make predictions about the service life and maintenance intervals of a product. In polymers, testing may be done at elevated temperatures to produce a result in a shorter amount of time than it could be produced at ambient temperatures. Many mechanical properties of polymers have an Arrhenius type relationship with respect to time and temperature (for example, creep, stress relaxation, and tensile properties). If one conducts short tests at elevated temperatures, that data can be used to extrapolate the behavior of the polymer at room temperature, avoiding the need to do lengthy, and hence expensive tests. Purpose ALT is pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (mechanics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity. It is a quantity that describes the magnitude of forces that cause deformation. Stress is defined as ''force per unit area''. When an object is pulled apart by a force it will cause elongation which is also known as deformation, like the stretching of an elastic band, it is called tensile stress. But, when the forces result in the compression of an object, it is called compressive stress. It results when forces like tension or compression act on a body. The greater this force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Therefore, stress is measured in newton per square meter (N/m2) or pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting an overhead weight, each particle in the bar pushe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weibull Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Weibull distribution is a continuous probability distribution. It is named after Swedish mathematician Waloddi Weibull, who described it in detail in 1951, although it was first identified by Maurice René Fréchet and first applied by to describe a particle size distribution. Definition Standard parameterization The probability density function of a Weibull random variable is : f(x;\lambda,k) = \begin \frac\left(\frac\right)^e^, & x\geq0 ,\\ 0, & x 0 is the ''shape parameter'' and λ > 0 is the ''scale parameter'' of the distribution. Its complementary cumulative distribution function is a stretched exponential function. The Weibull distribution is related to a number of other probability distributions; in particular, it interpolates between the exponential distribution (''k'' = 1) and the Rayleigh distribution (''k'' = 2 and \lambda = \sqrt\sigma ). If the quantity ''X'' is a "time-to-failure", the Weibull distribution gives a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue Testing
Fatigue testing is a specialised form of mechanical testing that is performed by applying cyclic loading to a ''coupon'' or structure. These tests are used either to generate fatigue life and crack growth data, identify critical locations or demonstrate the safety of a structure that may be susceptible to fatigue. Fatigue tests are used on a range of components from coupons through to full size test articles such as automobiles and aircraft. Fatigue tests on coupons are typically conducted using servo hydraulic test machines which are capable of applying large ''variable amplitude'' cyclic loads. ''Constant amplitude'' testing can also be applied by simpler oscillating machines. The ''fatigue life'' of a coupon is the number of cycles it takes to break the coupon. This data can be used for creating stress-life or strain-life curves. The rate of crack growth in a coupon can also be measured, either during the test or afterward using fractography. Testing of coupons can also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cox Model
Proportional hazards models are a class of survival models in statistics. Survival models relate the time that passes, before some event occurs, to one or more covariates that may be associated with that quantity of time. In a proportional hazards model, the unique effect of a unit increase in a covariate is multiplicative with respect to the hazard rate. For example, taking a drug may halve one's hazard rate for a stroke occurring, or, changing the material from which a manufactured component is constructed may double its hazard rate for failure. Other types of survival models such as accelerated failure time models do not exhibit proportional hazards. The accelerated failure time model describes a situation where the biological or mechanical life history of an event is accelerated (or decelerated). Background Survival models can be viewed as consisting of two parts: the underlying baseline hazard function, often denoted \lambda_0(t), describing how the risk of event per tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AFT Model
"Aft", in nautical terminology, is an adjective or adverb meaning towards the stern (rear) of the ship, aircraft or spacecraft, when the frame of reference is within the ship, headed at the fore. For example, "Able Seaman Smith; lie aft!" or "What's happening aft?". The corresponding adjective in distinguishing one feature of the vessel from another is "after". Its antonym is "forward". The corresponding preposition is "abaft". For example, the mizzenmast is abaft the mainmast. Its antonym is "before" or, in a more clumsy form, "forward of". The difference between "aft" and "stern" is that aft is the (on board) rearmost part of the vessel, while stern refers to the (offboard) rearmost part of the vessel. The stern is opposite the bow, the outside (offboard) of the front of the boat. The term derives from the Old English Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerated Aging
Accelerated aging is testing that uses aggravated conditions of heat, humidity, oxygen, sunlight, vibration, etc. to speed up the normal aging processes of items. It is used to help determine the long-term effects of expected levels of stress within a shorter time, usually in a laboratory by controlled standard test methods. It is used to estimate the useful lifespan of a product or its shelf life when actual lifespan data is unavailable. This occurs with products that have not existed long enough to have gone through their useful lifespan: for example, a new type of car engine or a new polymer for replacement joints. Physical testing or chemical testing is carried out by subjecting the product to * representative levels of stress for long time periods, * unusually high levels of stress used to accelerate the effects of natural aging, or * levels of stress that intentionally force failures (for further analysis). Mechanical parts are run at very high speed, far in excess o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highly Accelerated Life Test
A highly accelerated life test (HALT) is a stress testing methodology for enhancing product reliability in which prototypes are stressed to a much higher degree than expected from actual use in order to identify weaknesses in the design or manufacture of the product. Manufacturing and research and development organizations in the electronics, computer, medical, and military industries use HALT to improve product reliability. HALT can be effectively used multiple times over a product's life time. During product development, it can find design weakness earlier in the product lifecycle when changes are much less costly to make. By finding weaknesses and making changes early, HALT can lower product development costs and compress time to market. When HALT is used at the time a product is being introduced into the market, it can expose problems caused by new manufacturing processes. When used after a product has been introduced into the market, HALT can be used to audit product reliabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability (engineering)
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The reliability function is theoretically defined as the probability of success at time t, which is denoted R(t). This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets or through reliability testing and reliability modelling. Availability, testability, maintainability and maintenance are often defined as a part of "reliability engineering" in reliability programs. Reliability often plays the key role in the cost-effectiveness of systems. Reliability engineering deals with the prediction, prevention and manageme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service Life
A product's service life is its period of use in service. Several related terms describe more precisely a product's life, from the point of manufacture, storage, and distribution, and eventual use. Service life has been defined as "a product's total life in use from the point of sale to the point of discard" and distinguished from replacement life, "the period after which the initial purchaser returns to the shop for a replacement". Determining a product's expected service life as part of business policy (product life cycle management) involves using tools and calculations from maintainability and reliability analysis. Service life represents a commitment made by the item's manufacturer and is usually specified as a median. It is the time that any manufactured item can be expected to be "serviceable" or supported by its manufacturer. Service life is not to be confused with ''shelf life'', which deals with storage time, or with technical life, which is the maximum period during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Management
Product management is the business process of planning, developing, launching, and managing a product or service. It includes the entire lifecycle of a product, from ideation to development to go to market. Product managers are responsible for ensuring that a product meets the needs of its target market and contributes to the business strategy, while managing a product or products at all stages of the product lifecycle. Software product management adapts the fundamentals of product management for digital products. History The concept of product management originates from a 1931 memo by Procter & Gamble President Neil H. McElroy. McElroy, requesting additional employees focused on brand management, needed "Brand Men" who would take on the role of managing products, packaging, positioning, distribution, and sales performance. The memo defined a Brand Man's work as: * Study carefully shipments of his brands by units. * Where brand development is heavy ... examine carefully t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research And Development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in Europe as research and technological development (RTD), is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products, and improving existing ones. Research and development constitutes the first stage of development of a potential new service or the production process. R&D activities differ from institution to institution, with two primary models of an R&D department either staffed by engineers and tasked with directly developing new products, or staffed with industrial scientists and tasked with applied research in scientific or technological fields, which may facilitate future product development. R&D differs from the vast majority of corporate activities in that it is not intended to yield immediate profit, and generally carries greater risk and an uncertain return on investment. However R&D is crucial for acquiring larger shares of the market through the marketisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
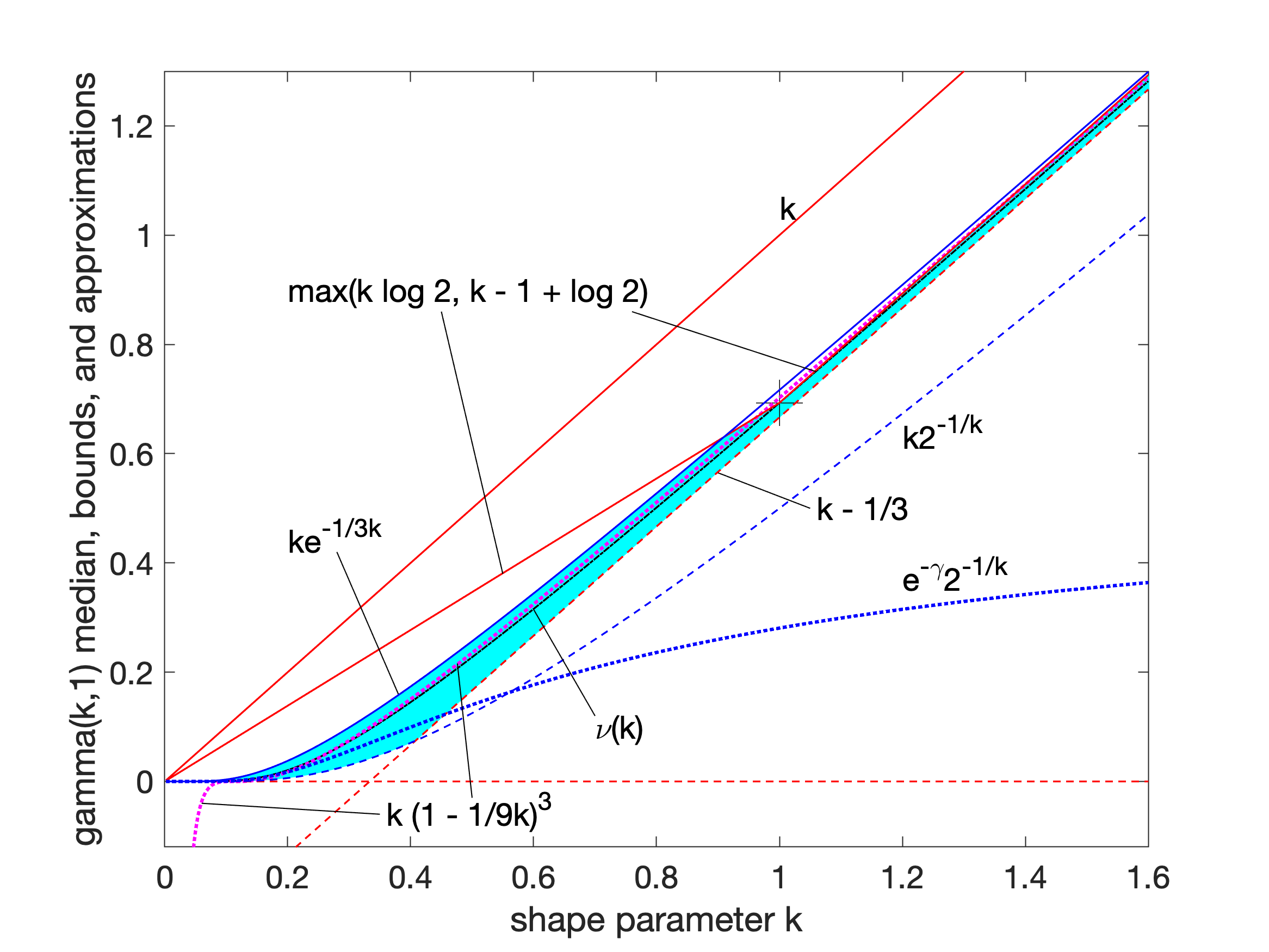
Gamma Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-square distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use: #With a shape parameter k and a scale parameter \theta. #With a shape parameter \alpha = k and an inverse scale parameter \beta = 1/ \theta , called a rate parameter. In each of these forms, both parameters are positive real numbers. The gamma distribution is the maximum entropy probability distribution (both with respect to a uniform base measure and a 1/x base measure) for a random variable X for which E 'X''= ''kθ'' = ''α''/''β'' is fixed and greater than zero, and E n(''X'')= ''ψ''(''k'') + ln(''θ'') = ''ψ''(''α'') − ln(''β'') is fixed (''ψ'' is the digamma function). Definitions The parameterization with ''k'' and ''θ'' appears to be more common in econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |