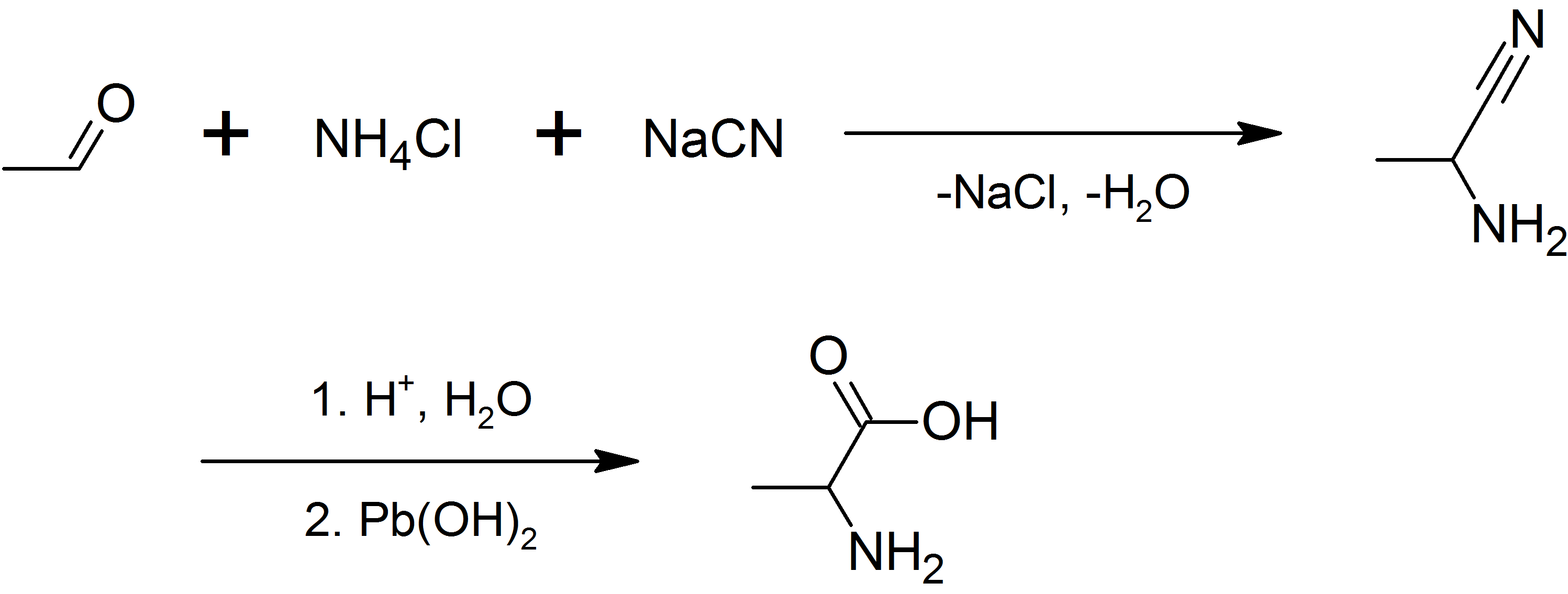
|
Acaricomes
''Acaricomes phytoseiuli'' is a bacterium which is thought to be a pathogen of the mite ''Phytoseiulus persimilis''. ''A. phytoseiuli'' causes a set of symptoms in the mite, known as nonresponding syndrome or NR syndrome. Dramatic changes in longevity, fecundity, and behavior are characteristic with this disease. The bacteria accumulate in the lumen of the mite's digestive tract and cause extreme degeneration of its epithelium. Infection with ''A. phytoseiuli'' greatly reduces the mite's attraction to herbivore-induced plant volatiles, and the mite is more prone to leave patches with ample prey. The disease is transmitted horizontally by means of feces and debris. The strain that was isolated was “CSC” (=DSM 14247T=CCUG 49701T). Differences between strain CSC compared to its closest phylogenetic neighbors are as follows: CSC uses glucose-1-phosphate and L-glutamic acid, and its colonies are more yellow in appearance as compared to its phylogenetic neighbors which are more cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrococcaceae
The family ''Micrococcaceae'' includes bacterial genera of Gram positive cocci that inhabit the air and skin, such as ''Micrococcus luteus''. Genera The family ''Micrococcaceae'' comprises the following genera: * '' Acaricomes'' Pukall ''et al''. 2006 * '' Arthrobacter'' Conn and Dimmick 1947 (Approved Lists 1980) * '' Auritidibacter'' Yassin ''et al''. 2011 * '' Citricoccus'' Altenburger ''et al''. 2002 * '' Enteractinococcus'' Cao ''et al''. 2012 * '' Falsarthrobacter'' Busse and Moore 2018 * '' Galactobacter'' Hahne ''et al''. 2019 * '' Garicola'' Lo ''et al''. 2015 * '' Glutamicibacter'' Busse 2016 * '' Haematomicrobium'' Schumann and Busse 2017 * ''Kocuria'' Stackebrandt ''et al''. 1995 * '' Micrococcoides'' Tóth ''et al''. 2017 * ''Micrococcus'' Cohn 1872 (Approved Lists 1980) * '' Neomicrococcus'' Prakash ''et al''. 2015 * '' Nesterenkonia'' Stackebrandt ''et al''. 1995 * '' Paenarthrobacter'' Busse 2016 * '' Paeniglutamicibacter'' Busse 2016 * '' Pseudarthrobacter'' B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DSC05872 British Spiders, Phytoseiulus Persimilis
DSC may refer to: Academia * Doctor of Science (D.Sc.) * District Selection Committee, an entrance exam in India * Doctor of Surgical Chiropody, superseded in the 1960s by Doctor of Podiatric Medicine Educational institutions * Dalton State College, Georgia, United States * Daytona State College, Florida, United States * Deep Springs College, California, United States * Dixie State College, now Utah Tech University, Utah, United States * Dyal Singh College, Delhi, India * DSC International School, Hong Kong, China Science and technology * DECT Standard Cipher, an encryption algorithm used by wireless telephone systems * Dice similarity coefficient, a statistical measure * Differential scanning calorimetry, or the differential scanning calorimeter * Digital selective calling in marine telecommunications * Digital setting circles on telescopes * Digital signal controller, a hybrid microcontroller and digital signal processor * Digital still camera, a type of camera * Display Strea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evidence of a close relationship. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others again are Predation, predators or Parasitism, parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive ''Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoseiulus Persimilis
''Phytoseiulus'' is a genus of mites in the Phytoseiidae family. A predatory mite, this is the mite predator most frequently used to control two-spotted spider mites in greenhouses and outdoor crops grown in mild environments. This mite was accidentally introduced into Germany from Chile Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ... in 1958; it was subsequently shipped to other parts of the world, including California and Florida, from Germany. A ''Phytoseiulus'' mite can consume up to seven adult spider mites or several dozen of their eggs in a day. Adult females are reddish, pear-shaped, about long, and active at room temperature. Immatures and males are smaller and lighter in color. Eggs are oblong. About 80% are females. At optimum temperatures, Phytoseiidae can develop f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidase Test
The oxidase test is used to determine if an organism possesses the cytochrome c oxidase enzyme. The test is used as an aid for the differentiation of ''Neisseria'', ''Moraxella'', '' Campylobacter'' and ''Pasteurella'' species (oxidase positive). It is also used to differentiate pseudomonads from related species.MacFaddin JF, editor. Biochemical Tests for Identification of Medical Bacteria. 3rd ed. Philadelphia:Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2000. p. 363-7 Classification Strains may be either oxidase-positive (OX+) or oxidase-negative (OX-). OX+ OX+ normally means the bacterium contains cytochrome c oxidase (also known as Complex IV) and can therefore use oxygen for energy production by converting O2 to H2O2 or H2O with an electron transfer chain. The Pseudomonadaceae are typically OX+. The Gram-negative diplococci Neisseria and Moraxella are oxidase-positive. Many Gram-negative, spiral curved rods are also oxidase-positive, which includes ''Helicobacter pylori'', ''Vibrio cho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypticase Soy Agar
Trypticase soy agar or tryptone soya agar (TSA) and Trypticase soy broth or tryptone soya broth (TSB) with agar are growth media for the culturing of bacteria. They are general-purpose, nonselective media providing enough nutrients to allow for a wide variety of microorganisms to grow. They are used for a wide range of applications, including culture storage, enumeration of cells (counting), isolation of pure cultures, or simply general culture. TSA contains enzymatic digests of casein and soybean meal, which provide amino acids and other nitrogenous substances, making it a nutritious medium for a variety of organisms. Glucose is the energy source. Sodium chloride maintains the osmotic equilibrium, while dipotassium phosphate acts as buffer to maintain pH. Agar extracted from any number of organisms is used as a gelling agent. The medium may be supplemented with blood to facilitate the growth of more fastidious bacteria or antimicrobial agents to permit the selection of vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most bacteria (domain ''Bacteria''). The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked ''N''-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and ''N''-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the ''N''-acetylmuramic acid is a oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. This repetitive linking results in a dense peptidoglycan layer which is critical for maintaining cell form and withstanding high osmotic pressures, and it is regularly replaced by peptidoglycan production. Pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain lysyl ((CH2)4NH2), classifying it as a basic, charged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is encoded by the codons AAA and AAG. Like almost all other amino acids, the α-carbon is chiral and lysine may refer to either enantiomer or a racemic mixture of both. For the purpose of this article, lysine will refer to the biologically active enantiomer L-lysine, where the α-carbon is in the ''S'' configuration. The human body cannot synthesize lysine. It is essential in humans and must therefore be obtained from the diet. In organisms that synthesise lysine, two main biosynthetic pathways exist, the diaminopimelate and α-aminoadipate pathways, which employ distinct e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side chain. Consequently, its IUPAC systematic name is 2-aminopropanoic acid, and it is classified as a nonpolar, aliphatic α-amino acid. Under biological conditions, it exists in its zwitterionic form with its amine group protonated (as −NH3+) and its carboxyl group deprotonated (as −CO2−). It is non-essential to humans as it can be synthesised metabolically and does not need to be present in the diet. It is encoded by all codons starting with GC (GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG). The L-isomer of alanine (left-handed) is the one that is incorporated into proteins. L-alanine is second only to leucine in rate of occurrence, accounting for 7.8% of the primary structure in a sample of 1,150 proteins. The right-handed form, D-alanine, occurs in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABA-ergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in three optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water solutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactose
Galactose (, '' galacto-'' + '' -ose'', "milk sugar"), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweet as glucose, and about 65% as sweet as sucrose. It is an aldohexose and a C-4 epimer of glucose. A galactose molecule linked with a glucose molecule forms a lactose molecule. Galactan is a polymeric form of galactose found in hemicellulose, and forming the core of the galactans, a class of natural polymeric carbohydrates. D-Galactose is also known as brain sugar since it is a component of glycoproteins (oligosaccharide-protein compounds) found in Nerve tissue, nerve tissue. Etymology The word ''galactose'' was coined by Charles Weissman in the mid-19th century and is derived from Greek ''galaktos'' (of milk) and the generic chemical suffix for sugars ''-ose''. The etymology is comparable to that of the word '' lactose'' in that both contain roots meaning "milk sugar". Lactose is a disaccharide of galactose plus glucose. Structure and isomerism Gal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Lorryia_formosa_2_edit.jpg)