|
A Book To Burn
''A Book to Burn'' () is a late 16th-century philosophical work by the late-Ming Dynasty thinker and historian Li Zhi. A critique of the social, philosophical and cultural norms of his time, the book was highly controversial and cemented Li Zhi's reputation as a heretic at the time. History Li Zhi began compiling the book in 1588, while living in a Buddhist monastery. It was first published in 1590 in Macheng, with a foreword by Mei Guozhen. The title was chosen by Li Zhi, who was aware that the book would be highly controversial, and that calls for its burning would be inevitable. Indeed, soon after its publication, it incited a vitriolic response from the exponents of Cheng-Zhu orthodoxy, accusing Li of heresy and poisoning minds; this controversy, however, only served to heighten Li Zhi's reputation. In 1602, after the imprisonment and suicide of Li Zhi, the book was proscribed and all copies were burned; this ban proceeded even into the Qing Dynasty. Yet, while officially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han Chinese, Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Zhi (philosopher)
Li Zhi (1527–1602), often known by his pseudonym Zhuowu (which means, “I who am smart”), was a Chinese philosopher, historian and writer of the late Ming dynasty. A critic of the Neo-Confucianist views espoused by Zhu Xi, which was then the orthodoxy of the Ming government, he was persecuted and committed suicide in prison. Biography He was born in Jinjiang, Fujian province (in modern Quanzhou). His ancestor by seven generations was Lin Nu, the son of Li Lü, a maritime merchant. Lin Nu visited Hormuz in Persia in 1376, converted to Islam upon marriage to a Semu girl ("娶色目女") (who was most likely either Persian or Arab), and brought her back to Quanzhou. This was recorded in the Lin and Li genealogy《林李宗譜》. However, the new faith did not take root in his lineage and the family stopped practising Islam during the time of his grandfather. His father made a living by teaching, and Li Zhi was therefore educated from an early age. In 1551, he passed the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
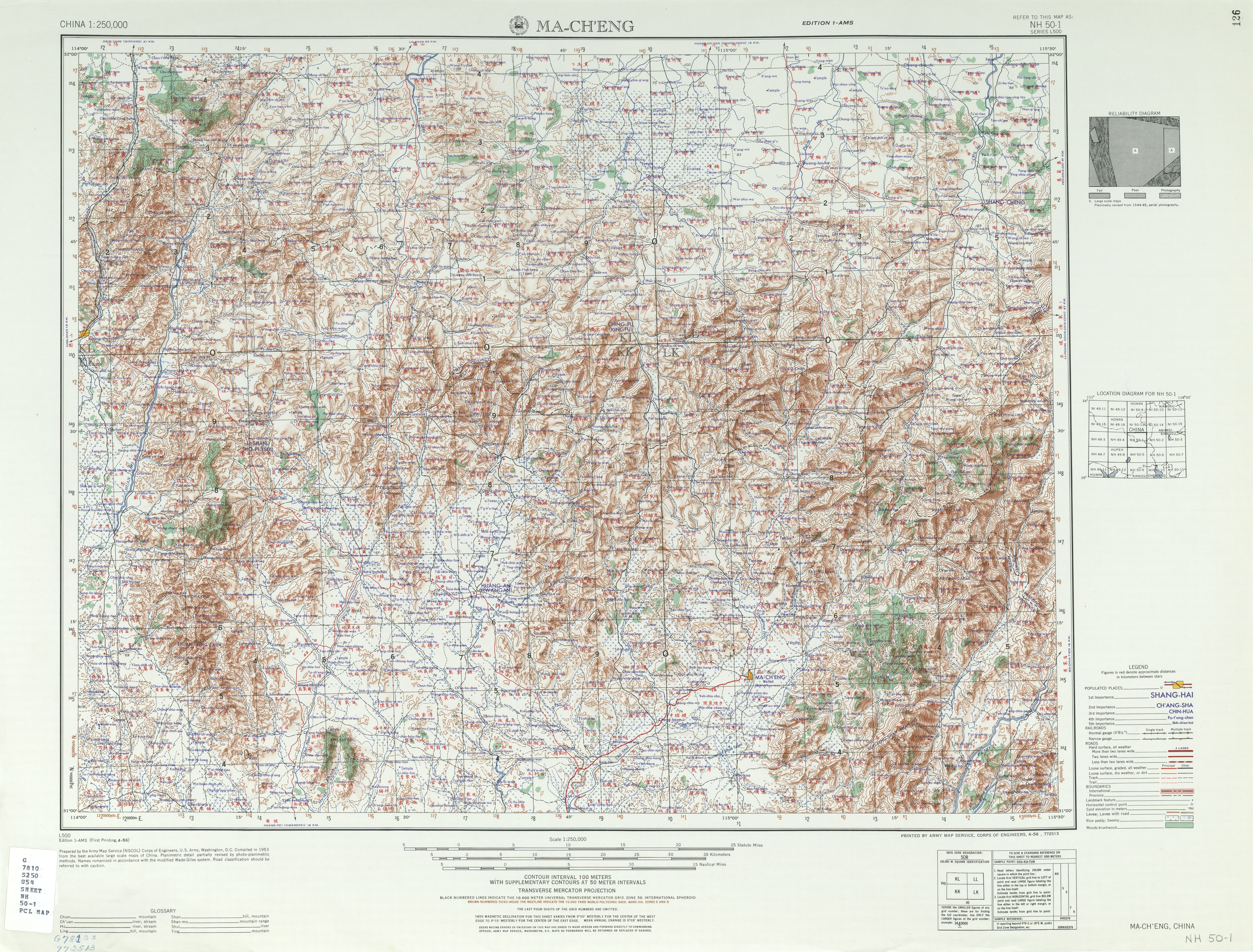
Macheng
Macheng () is a city in northeastern Hubei province, People's Republic of China, bordering the provinces of Henan to the north and Anhui to the northeast. It is a county-level city under the administration of Huanggang City and abuts the south side of the Dabie Mountains. The city's administrative area covers about , and includes some 704 villages and small towns. Total population was 849,092 at the 2010 census. History Macheng has a long history, dating back to the Spring and Autumn period as part of the state of Chu, and was the site of the historic Battle of Boju fought between Chu and Wu in 506 BC. It was named Macheng in 598 AD. In 1927, a major peasant revolt erupted in Macheng, creating a strong base for the ensuing Communist revolution in 1949. More than 100,000 people joined Mao's Red Army under local Generals, Wang Shusheng and Chen Zaidao. A guerilla base in Macheng was eliminated in the Campaign to Suppress Bandits in Dabieshan. Macheng played a key role during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mei Guozhen
Mei may refer to: Names * Mei (surname), a Chinese, Italian, Russian or Estonian family name * Mei (given name), a given name Places * Mei County, Guangdong, China, a county * Mei Pass, Guangdong, a strategic mountain pass * Mei River, Guangdong * Mei County, Shaanxi, China, a county * Mei, Arcos de Valdevez, a civil parish of Arcos de Valdevez Municipality, Portugal Art, entertainment, and media Characters * Mei (''Overwatch''), a playable character in ''Overwatch'' and ''Heroes of the Storm'' * Mei, a character in the anime series ''Endro!'' * Mei, a character in '' ER'' * Mei Fong (born 1972), female character who passes as a boy in ''Hell on Wheels'' * Mey-Rin, a character in the manga series ''Black Butler'' *Mei, a character from the movie My Neighbor Totoro * Mei Meido from the manga '' Kimi no koto ga Dai Dai Dai Dai Daisuki na 100-nin no Kanojo'' Films * ''Mei'' (film), 2019 Indian Tamil crime thriller film Music * ''Mei'' (album), a 2002 album by American ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangmingism
School of the Heart, or Yangmingism, known in Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin as (), lit. 'heart study' and in Japanese as (), is one of the major philosophical schools of Neo-Confucianism, based on the ideas of the Idealism (philosophy), idealist Neo-Confucian philosopher Wang Yangming, Wang Shouren (whose pseudonym was Yangming Zi and thus is often referred as Wang Yangming). Throughout the whole Yuan dynasty, as well as in the beginning of the Ming dynasty, the magistral philosophy in China was the Rationalistic School, another Neo-Confucianism school emphasizing the importance of observational science built by Cheng Yi (philosopher), Cheng Yi and especially Zhu Xi. Wang Yangming, on the other hand, developed his philosophy as the main intellectual opposition to the Cheng-Zhu School. Yangmingism is considered to be part of the School of Mind established by Lu Jiuyuan, upon whom Yangming drew inspirations. Yangming argued that one can learn the Li (neo-Confucianism), supreme principl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Yangming
Wang Shouren (, 26 October 1472 – 9 January 1529), courtesy name Bo'an (), art name Yangmingzi (), usually referred to as Wang Yangming (), was a Chinese calligrapher, general, philosopher, politician, and writer during the Ming dynasty. After Zhu Xi, he is commonly regarded as the most important Neo-Confucian thinker, for his interpretations of Confucianism that denied the rationalist dualism of the orthodox philosophy of Zhu Xi. Wang and Lu Xiangshan are regarded as the founders as the Lu–Wang school, or the School of the Mind. In China, Japan, and Western countries, he is known by his honorific name rather than his private name. Life and times Wang was born in Yuyao, Zhejiang Province, to a scholarly family with a tradition of bureaucratic service. His father, Wang Hua, was first (''Zhuangyuan'', 狀元) in the Imperial Examination of 1481, and rose to become the vice-minister of the Ministry of Rites, but was later demoted and subsequently expelled from gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=Kǒng Fūzǐ, "Master Kǒng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=Kǒngzǐ, labels=no; – ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Confucius's teachings and philosophy underpin East Asian culture and society, remaining influential across China and East Asia to this day. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, correctness of social relationships, justice, kindness, and sincerity. His followers competed with many other schools during the Hundred Schools of Thought era, only to be suppressed in favor of the Legalists during the Qin dynasty. After the collapse of Qin and the victory of Han over Chu, Confucius's thoughts received official sanction in the new government. During the Tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism (, often shortened to ''lǐxué'' 理學, literally "School of Principle") is a moral, ethical, and metaphysical Chinese philosophy Chinese philosophy originates in the Spring and Autumn period () and Warring States period (), during a period known as the " Hundred Schools of Thought", which was characterized by significant intellectual and cultural develop ... influenced by Confucianism, and originated with Han Yu (768–824) and Li Ao (philosopher), Li Ao (772–841) in the Tang Dynasty, and became prominent during the Song dynasty, Song and Ming dynasty, Ming dynasties under the formulations of Zhu Xi (1130–1200). After the Mongol conquest of China in the thirteenth century, Chinese scholars and officials restored and preserved neo-Confucianism as a way to safeguard the cultural heritage of China. Neo-Confucianism could have been an attempt to create a more rationalist and secular form of Confucianism by rejecting superstitious and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty Literature
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han Chinese, Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |