|
AURKC
Aurora kinase C, also Serine/threonine-protein kinase 13 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''AURKC'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the highly conserved Aurora subfamily of serine/threonine protein kinases with two other members, Aurora A and Aurora B. The encoded protein is a chromosomal passenger protein that forms complexes with Aurora-B and inner centromere proteins and may play a role in organizing microtubules in relation to centrosome/spindle function during mitosis. This gene is overexpressed in several cancer cell lines, suggesting an involvement in oncogenic signal transduction. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Function Temporal expression patterns and subcellular localization of Aurora kinases in mitotic cells from G2 to cytokinesis indicate association with mitotic and meiotic structure. Although yeast contain only one Aurora kinase and C. elegans and Drosophila contain only two, mammals have three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurora Kinase
Aurora kinases are serine/threonine kinases that are essential for cell proliferation. They are phosphotransferase enzymes that help the dividing cell dispense its genetic materials to its daughter cells. More specifically, Aurora kinases play a crucial role in cellular division by controlling chromatid segregation. Defects in this segregation can cause genetic instability, a condition which is highly associated with tumorigenesis.Bolanos-Garcia V M. Aurora kinases. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 37 (2005) 1572–1577. The first aurora kinases were identified in ''Drosophila melanogaster'', where mutations led to failure of centrosome separation with the monopolar spindles reminiscent of the North Pole, suggesting the name aurora. Three Aurora kinases have been identified in mammalian cells to date. Besides being implicated as mitotic regulators, these three kinases have generated significant interest in the cancer research field due to their elevated exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurora A
Aurora kinase A also known as serine/threonine-protein kinase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''AURKA'' gene. Aurora A is a member of a family of mitotic serine/threonine kinases. It is implicated with important processes during mitosis and meiosis whose proper function is integral for healthy cell proliferation. Aurora A is activated by one or more phosphorylations and its activity peaks during the G2 phase to M phase transition in the cell cycle. Discovery The aurora kinases were first identified in 1990 during a cDNA screen of ''Xenopus'' eggs. The kinase discovered, Eg2, is now referred to as Aurora A. It was not until 1998, however, that Aurora A's meiotic and mitotic importance was realized. Aurora kinase family The human genome contains three members of the aurora kinase family: Aurora kinase A, Aurora kinase B and Aurora C kinase. The ''Xenopus'', ''Drosophila'', and ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' genomes, on the other hand, contain orthologues on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of Transcription (biology), transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as Translation (biology), translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. This is not to be confused with experiments done ''in vitro'' ("within the glass"), i.e., in a laboratory environment using test tubes, Petri dishes, etc. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multinucleate
Multinucleate cells (also known as multinucleated or polynuclear cells) are eukaryotic cells that have more than one nucleus per cell, i.e., multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. Mitosis in multinucleate cells can occur either in a coordinated, synchronous manner where all nuclei divide simultaneously or asynchronously where individual nuclei divide independently in time and space. Certain organisms may have a multinuclear stage of their life cycle. For example, slime molds have a vegetative, multinucleate life stage called a plasmodium. Although not normally viewed as a case of multinucleation, plant cells share a common cytoplasm by plasmodesmata, and most cells in animal tissues are in communication with their neighbors via gap junctions. Multinucleate cells, depending on the mechanism by which they are formed, can be divided into "syncytia" (formed by cell fusion) or "coenocytes" (formed by nuclear division not being followed by cytokinesis). A number of dinoflagellat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
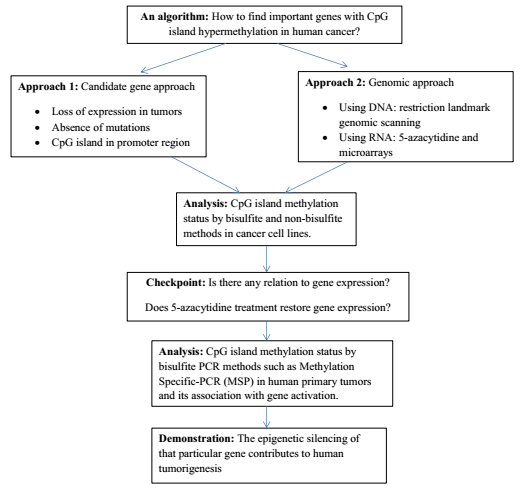
CpG Island Hypermethylation
CpG island hypermethylation is a phenomenon that is important for the regulation of gene expression in cancer cells, as an epigenetic control aberration responsible for gene inactivation. Hypermethylation of CpG islands has been described in almost every type of tumor. Many important cellular pathways, such as DNA repair ( hMLH1, for example), cell cycle (p14ARF), apoptosis ( DAPK), and cell adherence ( CDH1, CDH13), are inactivated by it. Hypermethylation is linked to methyl-binding proteins, DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylase, but the degree to which this process selectively silences tumor suppressor genes remains a research area. The list for hypermethylated genes is growing. History The first discovery of methylation in a CpG island of a tumor suppressor gene in humans was that of the Retinoblastoma (Rb) gene in 1989. This was just a few years after the first oncogene mutation was discovered in a human primary tumor. The discovery of the methylation-associate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repressor
In molecular genetics, a repressor is a DNA- or RNA-binding protein that inhibits the expression of one or more genes by binding to the operator or associated silencers. A DNA-binding repressor blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter, thus preventing transcription of the genes into messenger RNA. An RNA-binding repressor binds to the mRNA and prevents translation of the mRNA into protein. This blocking or reducing of expression is called repression. Function If an inducer, a molecule that initiates the gene expression, is present, then it can interact with the repressor protein and detach it from the operator. RNA polymerase then can transcribe the message (expressing the gene). A co-repressor is a molecule that can bind to the repressor and make it bind to the operator tightly, which decreases transcription. A repressor that binds with a co-repressor is termed an ''aporepressor'' or ''inactive repressor''. One type of aporepressor is the trp repressor, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLZF
Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ZBTB16'' gene. Function This gene is a member of the Krueppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family and encodes a zinc finger transcription factor that contains nine Kruppel-type zinc finger domains at the carboxyl terminus. This protein is located in the nucleus, is involved in cell cycle progression, and interacts with a histone deacetylase. Specific instances of aberrant gene rearrangement at this locus have been associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) and physiological roles have been identified in mouse Natural Killer T cells and gamma-delta T cells. Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized in human. Interactions Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 has been shown to interact with: * Angiotensin II receptor type 1, * BCL6, * BMI1, * Calcitriol receptor, * FHL2, * GATA1, * GATA2, * HDAC1, * HDAC4, * HDAC5, * HDAC6, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any number of complete chromosome sets is called a ''euploid'' cell. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of some genetic disorders. Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. About 68% of human solid tumors are aneuploid. Aneuploidy originates during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate properly between the two cells (nondisjunction). Most cases of aneuploidy in the autosomes result in miscarriage, and the most common extra autosomal chromosomes among live births are 21, 18 and 13. Chromosome abnormalities are detected in 1 of 160 live human births. Autosomal aneuploidy is more dangerous than sex chromosome aneuploidy, as autosomal aneuploidy is almost always lethal to embryos that cease develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Spindle
The central spindle is a microtubule based structure, which forms in between segregating chromosomes during anaphase where the two sets of microtubules, emanating from opposite halves of the cell, overlap, and become arranged into antiparallel bundles by various microtubule associated proteins (MAPs) and motor proteins. The central spindle is widely regarded as a key regulating center for cytokinesis, recruiting proteins for successful cleavage furrow positioning and membrane abscission. For these important roles to be achieved successfully the central spindle has to be carefully regulated to control the size of the overlap region, the alignment of those overlaps and the overall length and symmetry of the structure. Without this regulation, signaling faults in cytokinesis can occur, resulting in unequal chromosome segregation or polyploid cells, greatly increasing the risk of cancer Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spindle Assembly Checkpoint
The spindle checkpoint, also known as the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), the metaphase checkpoint, or the mitotic checkpoint, is a cell cycle checkpoint during mitosis or meiosis that prevents the separation of the duplicated chromosomes (anaphase) until each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle. To achieve proper segregation, the two kinetochores on the sister chromatids must be attached to opposite spindle poles (bipolar orientation). Only this pattern of attachment will ensure that each daughter cell receives one copy of the chromosome. The defining biochemical feature of this checkpoint is the stimulation of the anaphase-promoting complex by M-phase cyclin-CDK complexes, which in turn causes the proteolytic destruction of cyclins and proteins that hold the sister chromatids together. Overview and importance The beginning of metaphase is characterized by the connection of the microtubules to the kinetochores of the chromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |