|
ATC Code N01
N01A Anesthetics, general N01AA Ethers :N01AA01 Diethyl ether :N01AA02 Vinyl ether N01AB Halogenated hydrocarbons :N01AB01 Halothane :N01AB02 Chloroform :N01AB04 Enflurane :N01AB05 Trichloroethylene :N01AB06 Isoflurane :N01AB07 Desflurane :N01AB08 Sevoflurane N01AF Barbiturates, plain :N01AF01 Methohexital :N01AF02 Hexobarbital :N01AF03 Thiopental :QN01AF90 Thiamylal N01AG Barbiturates in combination with other drugs :N01AG01 Narcobarbital N01AH Opioid anesthetics :N01AH01 Fentanyl :N01AH02 Alfentanil :N01AH03 Sufentanil :N01AH04 Phenoperidine :N01AH05 Anileridine :N01AH06 Remifentanil :N01AH51 Fentanyl, combinations N01AX Other general anesthetics :N01AX03 Ketamine :N01AX04 Propanidid :N01AX05 Alfaxalone :N01AX07 Etomidate :N01AX10 Propofol :N01AX11 Sodium oxybate :N01AX13 Nitrous oxide :N01AX14 Esketamine :N01AX15 Xenon :N01AX63 Nitrous oxide, combinations :QN01AX91 Azaperone :QN01AX92 Benzocaine :QN01AX93 Tricaine mesilate :QN01AX94 Isoeugenol :QN01AX99 Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness. A wide variety of drugs are used in modern anesthetic practice. Many are rarely used outside anesthesiology, but others are used commonly in various fields of healthcare. Combinations of anesthetics are sometimes used for their synergistic and additive therapeutic effects. Adverse effects, however, may also be increased. Anesthetics are distinct from analgesics, which block only sensation of painful stimuli. Local anesthetics Local anesthetic agents prevent the transmission of nerve impulses without causi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiamylal
Thiamylal (Surital) is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1950s. It has sedative, anticonvulsant, and hypnotic effects, and is used as a strong but short acting sedative. Thiamylal is still in current use, primarily for induction in surgical anaesthesia or as an anticonvulsant to counteract side effects from other anaesthetics. It is the thiobarbiturate analogue of secobarbital Secobarbital (as the sodium salt, originally marketed by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of insomnia, and subsequently by other companies as described below, under the brand name Seconal) is a short-acting barbiturate derivative drug that .... References Thiobarbiturates GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Allyl compounds {{sedative-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
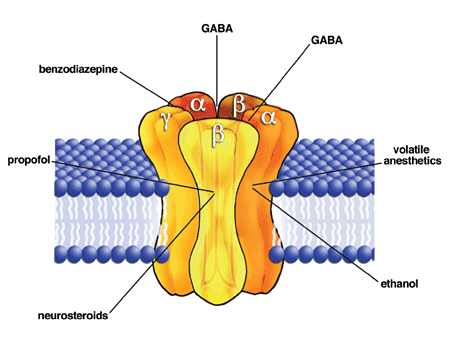
Propofol
Propofol, marketed as Diprivan, among other names, is a short-acting medication that results in a decreased level of consciousness and a lack of memory for events. Its uses include the starting and maintenance of general anesthesia, sedation for mechanically ventilated adults, and procedural sedation. It is also used for status epilepticus if other medications have not worked. It is given by injection into a vein, and the maximum effect takes about two minutes to occur and typically lasts five to ten minutes. Propofol is also used for medical assistance in dying in Canada. The medication appears to be safe for use during pregnancy but has not been well studied for use in this case. It is not recommended for use during a cesarean section. It is not a pain medication, so opioids such as morphine may also be used; however, whether or not they are always needed is not clear. Propofol is believed to work at least partly via a receptor for GABA. Propofol was discovered in 1977 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etomidate
Etomidate (USAN, INN, BAN; marketed as Amidate) is a short-acting intravenous anaesthetic agent used for the induction of general anaesthesia and sedation for short procedures such as reduction of dislocated joints, tracheal intubation, cardioversion and electroconvulsive therapy. It was developed at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1964 and was introduced as an intravenous agent in 1972 in Europe and in 1983 in the United States. The most common side effects include venous pain on injection and skeletal muscle movements. Medical uses Sedation and anesthesia In emergency settings, etomidate can be used as a sedative hypnotic agent. It is used for conscious sedation and as a part of a rapid sequence induction to induce anaesthesia. It is used as an anaesthetic agent since it has a rapid onset of action and a safe cardiovascular risk profile, and therefore is less likely to cause a significant drop in blood pressure than other induction agents. In addition, etomidate is often used becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfaxalone
Alfaxalone, also known as alphaxalone or alphaxolone and sold under the brand name Alfaxan, is a neuroactive steroid and general anesthetic which is used currently in veterinary practice as an induction agent for anesthesia and as an injectable anesthetic. Though it is more expensive than other induction agents, it often preferred due to the lack of depressive effects on the cardiovascular system. The most common side effect seen in current veterinary practice is respiratory depression when Alfaxan is administered concurrently with other sedative and anesthetic drugs; when premedications aren't given, veterinary patients also become agitated and hypersensitive when waking up. Alfaxalone works as a positive allosteric modulator on GABAA receptors and, at high concentrations, as a direct agonist of the GABAA receptor. It is cleared quickly by the liver, giving it a relatively short terminal half-life and preventing it from accumulating in the body, lowering the chance of ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propanidid
Propanidid is an ultra short-acting phenylacetate general anesthetic. It was originally introduced by Bayer in 1963 but anaphylactic reaction Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the follo ...s caused it to be withdrawn shortly afterwards. Even though Cremophor EL has been shown to cause anaphylactic reactions in humans in several cases (both when given intravenously and orally), it is still debated whether propanidid itself may have contributed to the reactions. It has been argued that the toxic effects or reactions to propanidid (and Althesin) were due to the drugs themselves. Several cases of negative reactions have been recorded for different drugs using Cremophor EL as solubilizer, suggesting that the negative reactions were mainly caused by Cremophor and not by the drug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a recreational drug. It is one of the safest anesthetics, as, in contrast with opiates, ether, and propofol, it suppresses neither respiration nor heart rate. Ketamine is also simple to administer and highly tolerable compared to drugs with similar effects which are flammable, irritating, or even explosive. Ketamine is a novel compound, derived from PCP, created in pursuit of a safer anesthetic with similar characteristics. Ketamine is also used for acute pain management. At anesthetic doses, ketamine induces a state of "dissociative anesthesia", a trance-like state providing pain relief, sedation, and amnesia. The distinguishing features of ketamine anesthesia are preserved breathing and airway reflexes, stimulated heart function with increased blood pressure, and moderate bronchodilation. At lower, sub-anesthetic doses, ketamine is a promising agent for pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remifentanil
Remifentanil is a potent, short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug. It is given to patients during surgery to relieve pain and as an adjunct to an anaesthetic. Remifentanil is used for sedation as well as combined with other medications for use in general anesthesia. The use of remifentanil has made possible the use of high-dose opioid and low-dose hypnotic anesthesia, due to synergism between remifentanil and various hypnotic drugs and volatile anesthetics. Clinical use Remifentanil is used as an opioid analgesic that has a rapid onset and rapid recovery time. It has been used effectively during craniotomies, spinal surgery, cardiac surgery, and gastric bypass surgery. While opiates function similarly, with respect to analgesia, the pharmacokinetics of remifentanil allows for quicker post-operative recovery. Administration It is administered in the form ''remifentanil hydrochloride'' and in adults is given as an intravenous infusion in doses ranging from 0.1 microgram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anileridine
Anileridine (trade name: Leritine) is a synthetic analgesic drug and is a member of the piperidine class of analgesic agents developed by Merck & Co. in the 1950s. It differs from pethidine (meperidine) in that the ''N''-methyl group of meperidine is replaced by an ''N''-aminophenethyl group, which increases its analgesic activity. Anileridine is no longer manufactured in the US or Canada. Anileridine is in Schedule II of the Controlled Substances Act 1970 of the United States as ACSCN 9020 with a zero aggregate manufacturing quota as of 2014. The free base conversion ratio for salts includes 0.83 for the dihydrochloride and 0.73 for the phosphate. It is also under international control per UN treaties. Administration As tablets or injection. Pharmacokinetics Anileridine usually takes effect within 15 minutes of either oral or intravenous administration, and lasts 2–3 hours. It is mostly metabolized by the liver The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenoperidine
Phenoperidine(Operidine or Lealgin), is an opioid analgesic which is structurally related to pethidine and is used clinically as a general anesthetic. Medical use Phenoperidine is an opioid pain killer -- narcotic analgesic. Pharmacology It is a derivative of isonipecotic acid, like pethidine, and is metabolized in part to norpethidine. Its potency range is due to method of ingestion. figure 20-80 times as potent as pethidine as an analgesic. The greatly increased potency essentially eliminates the toxic effects of norpethidine accumulation which are seen when pethidine is administered in high doses or for long periods of time. History and Synthesis Phenoperidine was first synthesized in 1957 by Paul Janssen, of the company now known as Janssen Pharmaceutica, who was seeking better opioid pain-killers. His two prototype drugs were methadone and pethidine, each which had been invented in 1930s by Otto Eisleb, who worked for IG Farben. His initial work starting with methado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufentanil
Sufentanil, sold under the brand names Dsuvia and Sufenta, is a synthetic opioid analgesic drug approximately 5 to 10 times as potent as its parent drug, fentanyl, and 500 times as potent as morphine. Structurally, sufentanil differs from fentanyl through the addition of a methoxymethyl group on the piperidine ring (which increases potency but is believed to reduce duration of action), and the replacement of the phenyl ring by thiophene. Sufentanil first was synthesized at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1974. Sufentanil is marketed for use by specialist centers under different trade names, such as Sufenta and Sufentil. Sufentanil with and without lidocaine or mepivacaine is available as a transdermal patch similar to Duragesic in Europe under trade names such as Chronogesic. It is available as a sublingual tablet under the trade name Dsuvia. Medical uses The main use of this medication is in operating suites and critical care where pain relief is required for a short period of time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfentanil
Alfentanil (R-39209, trade name Alfenta, Rapifen in Australia) is a potent but short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic medication, drug, used for anaesthesia in surgery. It is an analogue of fentanyl with around one-fourth to one-tenth the potency, one-third the duration of action, and an onset of action four times faster than that of fentanyl. Alfentanil has a pKa of approximately 6.5, which leads to a very high proportion of the drug being uncharged at physiologic pH, a characteristic responsible for its rapid onset. It is an agonist at mu opioid receptors. While alfentanil tends to cause fewer cardiovascular complications than other similar drugs such as fentanyl and remifentanil, it tends to give stronger respiratory depression and so requires careful monitoring of breathing and vital signs. Almost exclusively used by anesthesia providers during portions of a case where quick, fast-acting (though not long-lasting) pain control is needed (as, for example, during nerve blocks), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)