|
ATC Code H03
H03A Thyroid preparations H03AA Thyroid hormones :H03AA01 Levothyroxine sodium :H03AA02 Liothyronine sodium :H03AA03 Combinations of levothyroxine and liothyronine :H03AA04 Tiratricol :H03AA05 Thyroid gland preparations H03B Antithyroid preparations H03BA Thiouracils :H03BA01 Methylthiouracil :H03BA02 Propylthiouracil :H03BA03 Benzylthiouracil H03BB Sulphur-containing imidazole derivatives :H03BB01 Carbimazole :H03BB02 Thiamazole :H03BB52 Thiamazole, combinations H03BC Perchlorates :H03BC01 Potassium perchlorate H03BX Other antithyroid preparations :H03BX01 Diiodotyrosine Diiodotyrosine (DIT) is a precursor in the production of thyroid hormone, and results from iodization of monoiodotyrosine at the other meta- position on the phenol ring. Function DIT is a modulator of the enzyme thyroid peroxidase (which is invo ... :H03BX02 Dibromotyrosine H03C Iodine therapy H03CA Iodine therapy References {{Thyroid therapy H03 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are any hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), whose half-life of around one week is longer th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzylthiouracil
Benzylthiouracil (BTU) is an antithyroid preparation. It is a thioamide, closely related to propylthiouracil. Adverse effects Benzylthiouracil has been associated with severe adverse effects, notably vasculitis and subsequent ANCA-positive glomerulonephritis, as well as isolated reports A report is a document that presents information in an organized format for a specific audience and purpose. Although summaries of reports may be delivered orally, complete reports are almost always in the form of written documents. Usage In ... of lung damage. References Antithyroid drugs Pyrimidines Thioureas Nucleobases {{systemic-hormonal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibromotyrosine
Dibromotyrosine is an antithyroid preparation and a derivative of the natural amino acid tyrosine. It is formed by eosinophil peroxidase Eosinophil peroxidase is an enzyme found within the eosinophil granulocytes, innate immune cells of humans and mammals. This oxidoreductase protein is encoded by the gene ''EPX'', expressed within these myeloid cells. EPO shares many similarities .... References Amino acid derivatives Bromoarenes {{systemic-hormonal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
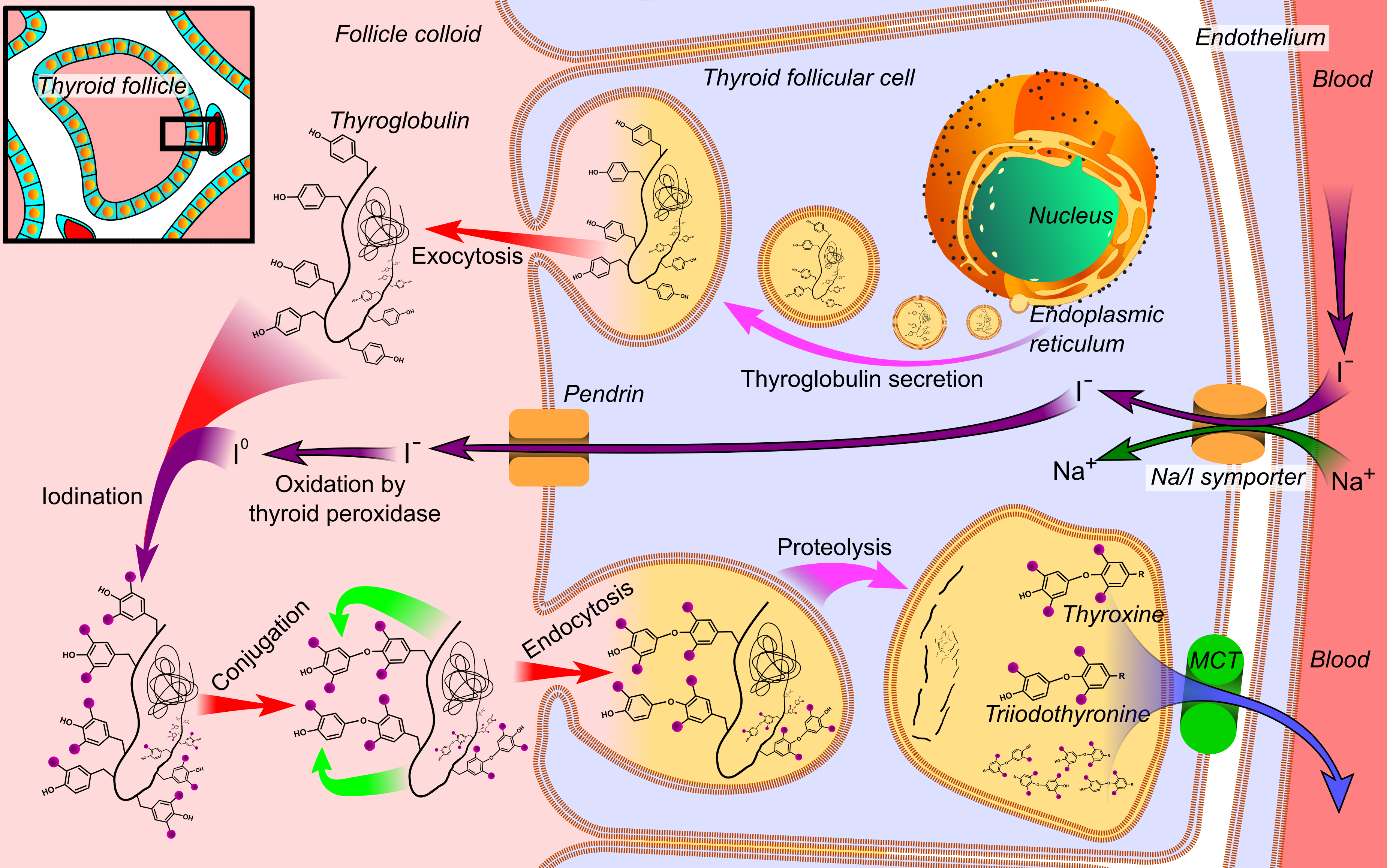
Diiodotyrosine
Diiodotyrosine (DIT) is a precursor in the production of thyroid hormone, and results from iodization of monoiodotyrosine at the other meta- position on the phenol ring. Function DIT is a modulator of the enzyme thyroid peroxidase (which is involved in the production of thyroid hormones). Triiodothyronine is formed, when diiodotyrosine is combined with monoiodotyrosine (in the colloid of the thyroid follicle). Two molecules of DIT combine to make the thyroid hormone thyroxine File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 25 ... ('T4' and 'T3'). See also * Diiodotyrosine transaminase References External links * Iodinated tyrosine derivatives {{organohalide-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Perchlorate
Potassium perchlorate is the inorganic salt with the chemical formula K Cl O4. Like other perchlorates, this salt is a strong oxidizer although it usually reacts very slowly with organic substances. This, usually obtained as a colorless, crystalline solid, is a common oxidizer used in fireworks, ammunition percussion caps, explosive primers, and is used variously in propellants, flash compositions, stars, and sparklers. It has been used as a solid rocket propellant, although in that application it has mostly been replaced by the higher performance ammonium perchlorate. Production Potassium perchlorate is prepared industrially by treating an aqueous solution of sodium perchlorate with potassium chloride. This single precipitation reaction exploits the low solubility of KClO4, which is about 1/100 as much as the solubility of NaClO4 (209.6 g/100 mL at 25 °C). It can also be produced by bubbling chlorine gas through a solution of potassium chlorate and potassium hydroxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perchlorate
A perchlorate is a chemical compound containing the perchlorate ion, . The majority of perchlorates are commercially produced salts. They are mainly used as oxidizers for pyrotechnic devices and to control static electricity in food packaging. Perchlorate contamination in food, water, and other parts of the environment has been studied in the U.S. because of harmful effects on human health. Perchlorate ions are somewhat toxic to the thyroid gland. Most perchlorates are colorless solids that are soluble in water. Four perchlorates are of primary commercial interest: ammonium perchlorate , perchloric acid , potassium perchlorate and sodium perchlorate . Perchlorate is the anion resulting from the dissociation of perchloric acid and its salts upon their dissolution in water. Many perchlorate salts are soluble in non-aqueous solutions. Production Perchlorate salts are produced industrially by the oxidation of aqueous solutions of sodium chlorate by electrolysis. This method is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiamazole
Thiamazole, also known as methimazole, is a medication used to treat hyperthyroidism. This includes Graves disease, toxic multinodular goiter, and thyrotoxic crisis. It is taken by mouth. Full effects may take a few weeks to occur. Common side effects include itchiness, hair loss, nausea, muscle pain, swelling, and abdominal pain. Severe side effects may include low blood cell counts, liver failure, and vasculitis. Use is not recommended during the first trimester of pregnancy due to the risk of congenital anomalies, but it may be used in the second trimester or third trimester. It may be used during breastfeeding. Those who developed significant side effects may also have problems with propylthiouracil. Thiamazole is a thioamide and works by decreasing the production of thyroid hormones. Thiamazole was approved for medical use in the United States in 1950. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbimazole
Carbimazole (brand names Neo-Mercazole, Anti-Thyrox, etc.) is used to treat hyperthyroidism. Carbimazole is a pro-drug as after absorption it is converted to the active form, methimazole. Methimazole prevents thyroid peroxidase enzyme from iodinating and coupling the tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, hence reducing the production of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 (thyroxine). It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Medical therapy for hyperthyroidism typically involves either titrating the dose of carbimazole until the patient becomes euthyroid or maintaining a high dose of carbimazole to suppress endogenous thyroid production, and then replacing thyroid hormone with levothyroxine ("block and replace"). Treatment is usually given for 18–24 months followed by a trial withdraw. The onset of anti-thyroid effect is rapid but the onset of clinical effects on thyroid hormone levels in the blood is much slower. This is because the large s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylthiouracil
Propylthiouracil (PTU) is a medication used to treat hyperthyroidism. This includes hyperthyroidism due to Graves' disease and toxic multinodular goiter. In a thyrotoxic crisis it is generally more effective than methimazole. Otherwise it is typically only used when methimazole, surgery, and radioactive iodine is not possible. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include itchiness, hair loss, parotid swelling, vomiting, muscle pains, numbness, and headache. Other severe side effects include liver problems and low blood cell counts. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Propylthiouracil is in the antithyroid family of medications. It works by decreasing the amount of thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland and blocking the conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3). Propylthiouracil came into medical use in the 1940s. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Side effects Propylthiouracil is generally well tolerated, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levothyroxine Sodium
Levothyroxine, also known as -thyroxine, is a manufactured form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4). It is used to treat thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism), including a severe form known as myxedema coma. It may also be used to treat and prevent certain types of thyroid tumors. It is not indicated for weight loss. Levothyroxine is taken by mouth or given by intravenous injection. Maximum effect from a specific dose can take up to six weeks to occur. Side effects from excessive doses include weight loss, trouble tolerating heat, sweating, anxiety, trouble sleeping, tremor, and fast heart rate. Use is not recommended in people who have had a recent heart attack. Use during pregnancy has been found to be safe. Dosing should be based on regular measurements of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4 levels in the blood. Much of the effect of levothyroxine is following its conversion to triiodothyronine (T3). Levothyroxine was first made in 1927. It is on the Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylthiouracil
Methylthiouracil is an organosulfur compound that is used antithyroid preparation. It is a thioamide, closely related to propylthiouracil. Methylthiouracil is not used clinically in the United States, it has a similar mechanism of action and side effect to that of propylthiouricil. The drug acts to decrease the formation of stored thyroid hormone, as thyroglobulin in the thyroid gland. The clinical effects of the drug to treat the hyperthyroid state can have a lag period of up to two weeks, depending on the stores of thyroglobulin and other factors. Synthesis Methylthiouracil is prepared quite simply by condensation of ethyl acetoacetate with thiourea Thiourea () is an organosulfur compound with the formula and the structure . It is structurally similar to urea (), except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom (as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix); however, the properties of urea a .... Further work in this series shows that better activity was obtained by incorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Thiouracil
2-Thiouracil is a specific molecule consisting of a sulfated uracil. Medical use The substance is a historically relevant anti-thyroid preparation. Astwood E.B. used it in 1943 as therapy of Graves' disease for the first time. It remains in use. Thiouracil inhibits thyroid activity by blocking the enzyme thyroid peroxidase Thyroid peroxidase, also called thyroperoxidase (TPO) or iodide peroxidase, is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid. Thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine re .... Its use in recent times has been replaced by advent of more potent and safer antithyroid drugs. It occurs in seeds of Brassica and Crucifera species. Thiouracil has been used as antithyroid, coronary vasodilator, and in congestive heart failure although its use has been largely supplanted by other drugs. References Pyrimidines IARC Group 2B carcinogens Thioureas Nucleobases {{heterocyclic-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |