|
ASC-US
The Bethesda system (TBS), officially called The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology, is a system for reporting cervical or vaginal cytologic diagnoses, used for reporting Pap smear results. It was introduced in 1988 and revised in 1991, 2001, and 2014. The name comes from the location ( Bethesda, Maryland) of the conference, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, that established the system. Since 2010, there is also a Bethesda system used for cytopathology of thyroid nodules, which is called The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC or BSRTC). Like TBS, it was the result of a conference sponsored by the NIH and is published in book editions (currently by Springer). Mentions of "the Bethesda system" without further specification usually refer to the cervical system, unless the thyroid context of a discussion is implicit. Cervix Abnormal results include: * Atypical squamous cells ** Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
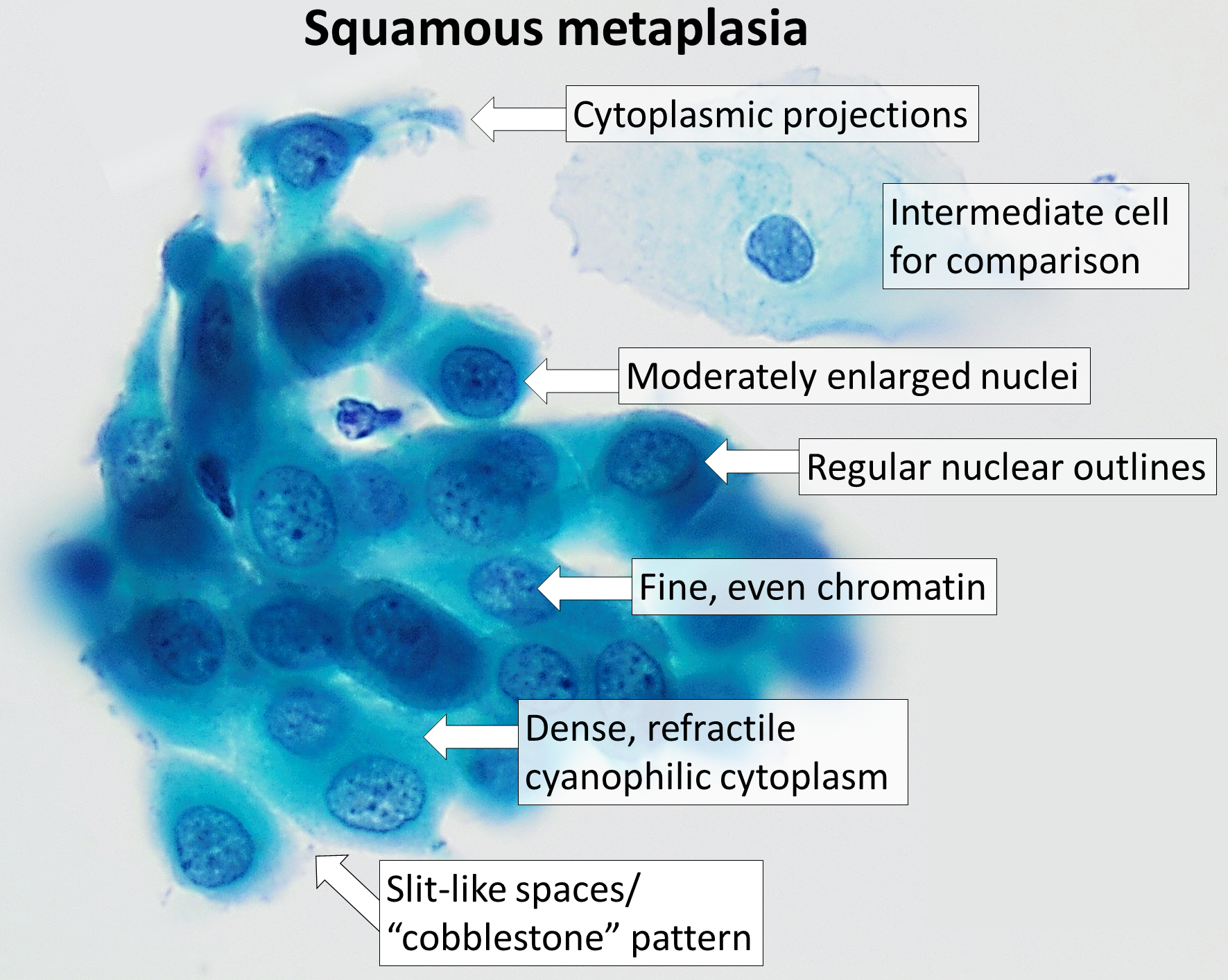
Pap Smear
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb) or Colon (organ), colon (in both men and women). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was independently invented in the 1920s by Georgios Papanikolaou and Aurel Babeș and named after Papanikolaou. A simplified version of the test was introduced by Anna Marion Hilliard in 1957. A Pap smear is performed by opening the vagina with a speculum (medical), speculum and collecting cell (biology), cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells), using an Ayre spatula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pap Test
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb) or colon (in both men and women). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was independently invented in the 1920s by Georgios Papanikolaou and Aurel Babeș and named after Papanikolaou. A simplified version of the test was introduced by Anna Marion Hilliard in 1957. A Pap smear is performed by opening the vagina with a speculum and collecting cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells), using an Ayre spatula or a cytobrush. A similar method is used to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
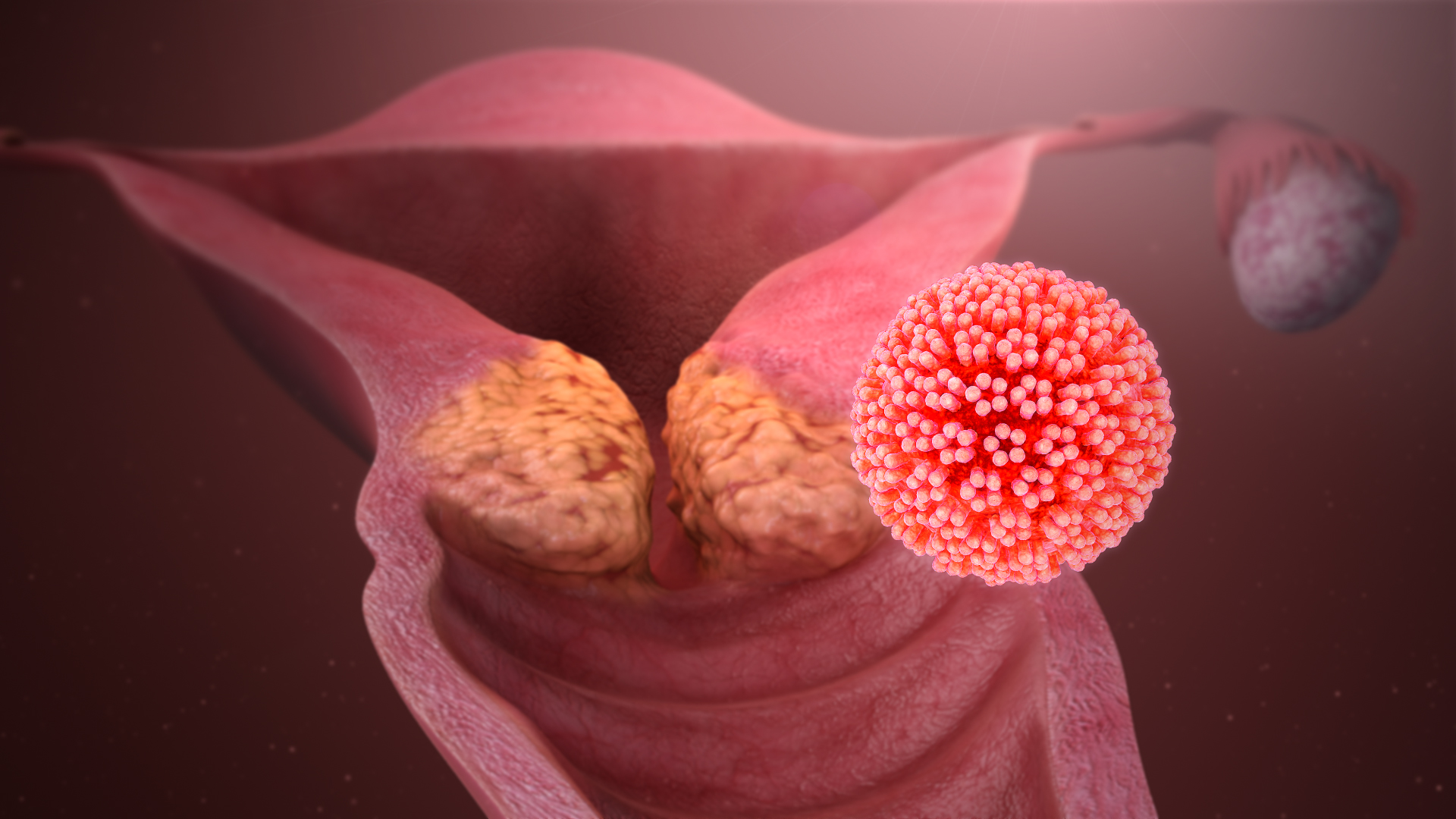
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
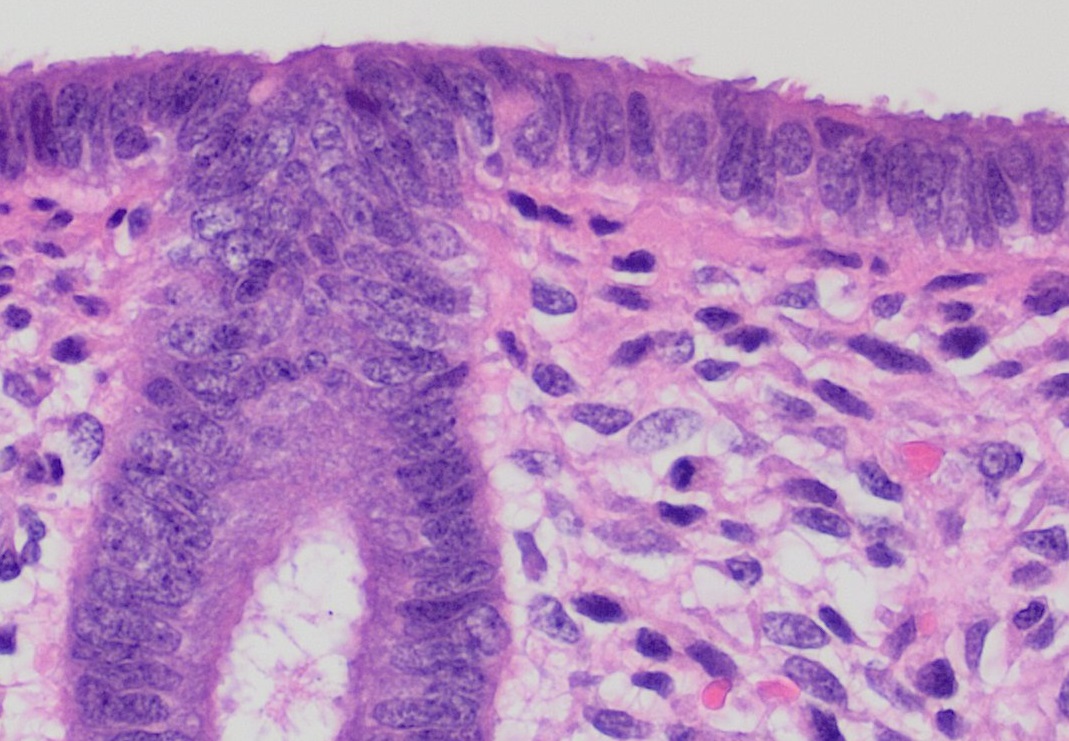
Cervix
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during pregnancy. The narrow, central cervical canal runs along its entire length, connecting the uterine cavity and the lumen of the vagina. The opening into the uterus is called the internal os, and the opening into the vagina is called the external os. The lower part of the cervix, known as the vaginal portion of the cervix (or ectocervix), bulges into the top of the vagina. The cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervical canal is a passage through which sperm must travel to fertilize an egg cell after sexual intercourse. Several methods of contraception, including cervical caps and cervical diaphragms, aim to block or prevent the passage of sperm through the cervical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoma In Situ
Carcinoma ''in situ'' (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells. While they are a form of neoplasm, there is disagreement over whether CIS should be classified as cancer. This controversy also depends on the exact CIS in question (i.e. cervical, skin, breast). Some authors do not classify them as cancer, however, recognizing that they can potentially become cancer. Others classify certain types as a non-invasive form of cancer. The term "pre-cancer" has also been used. These abnormal cells grow in their normal place, thus "''in situ''" (from Latin for "in its place"). For example, carcinoma ''in situ'' of the skin, also called Bowen's disease, is the accumulation of dysplastic epidermal cells within the epidermis only, that has failed to penetrate into the deeper dermis. For this reason, CIS will usually not form a tumor. Rather, the lesion is flat (in the skin, cervix, etc.) or follows the existing architecture of the organ (in the breast, lung, etc.). Exceptions include CIS of the colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
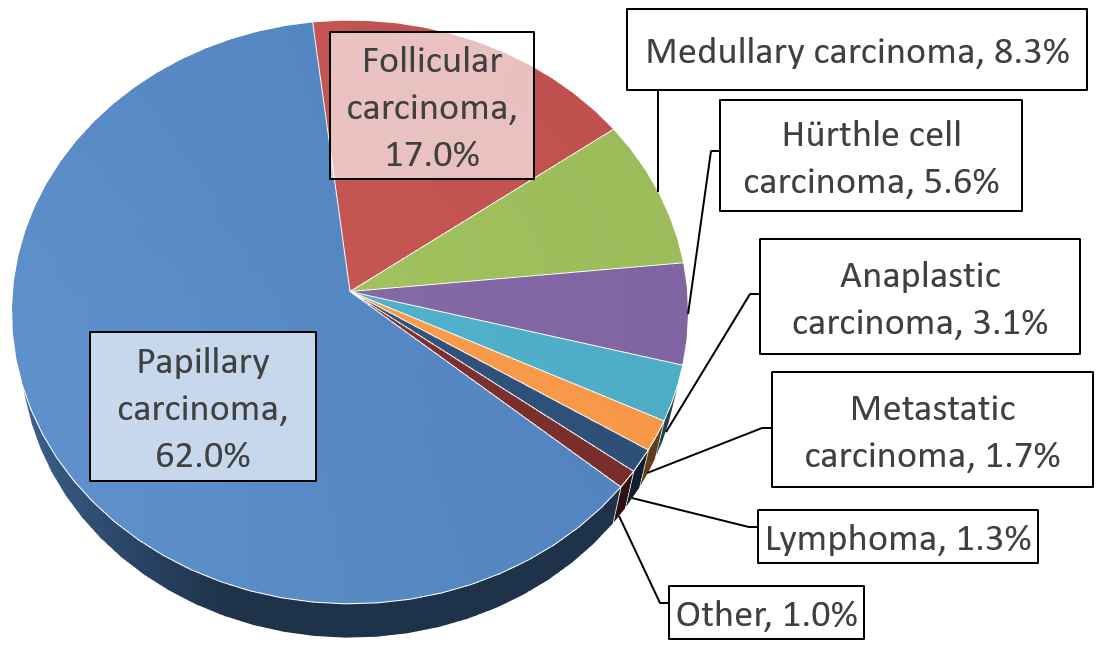
Hürthle Cell Neoplasm
Hürthle cell neoplasm is a rare tumor of the thyroid, typically seen in women between the ages of 70 and 80 years old. When benign, it is called a Hürthle cell adenoma, and when malignant it is called a Hürthle cell carcinoma. Hürthle cell adenoma is characterized by a mass of benign Hürthle cells (Askanazy cells). Typically such a mass is removed because it is not easy to predict whether it will transform into the malignant counterpart of Hürthle cell carcinoma, which is a subtype of follicular thyroid cancer. Histology Hürthle cells are characterized as enlarged epithelial cells. These cells, when stained with hematoxylin-eosin show as pink. This is due to the abundant mitochondria and granular eosinophilic matter within the cells' cytoplasm. These cells are often found in the thyroid. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped organ, responsible for producing various hormones for metabolism. These cells are often benign, but they can be malignant and metastasize. Hürthle c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroidectomy
A thyroidectomy is an operation that involves the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. In general surgery, endocrine or head and neck surgeons often perform a thyroidectomy when a patient has thyroid cancer or some other condition of the thyroid gland (such as hyperthyroidism) or goiter. Other indications for surgery include cosmetic (very enlarged thyroid), or symptomatic obstruction (causing difficulties in swallowing or breathing). Thyroidectomy is a common surgical procedure that has several potential complications or sequelae including: temporary or permanent change in voice, temporary or permanently low calcium, need for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement, bleeding, infection, and the remote possibility of airway obstruction due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis. Complications are uncommon when the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon. The thyroid produces several hormones, such as thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine-needle Aspiration Cytology
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, after being stained, are examined under a microscope (biopsy). The sampling and biopsy considered together are called fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) or fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) (the latter to emphasize that any aspiration biopsy involves cytopathology, not histopathology). Fine-needle aspiration biopsies are very safe minor surgical procedures. Often, a major surgical (excisional or open) biopsy can be avoided by performing a needle aspiration biopsy instead, eliminating the need for hospitalization. In 1981, the first fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the United States was done at Maimonides Medical Center. Today, this procedure is widely used in the diagnosis of cancer and inflammatory conditions. Aspiration is safer and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMedicine
eMedicine is an online clinical medical knowledge base founded in 1996 by doctors Scott Plantz and Jonathan Adler, and computer engineer Jeffrey Berezin. The eMedicine website consists of approximately 6,800 medical topic review articles, each of which is associated with a clinical subspecialty "textbook". The knowledge base includes over 25,000 clinically multimedia files. Each article is authored by board certified specialists in the subspecialty to which the article belongs and undergoes three levels of physician peer-review, plus review by a Doctor of Pharmacy. The article's authors are identified with their current faculty appointments. Each article is updated yearly, or more frequently as changes in practice occur, and the date is published on the article. eMedicine.com was sold to WebMD in January, 2006 and is available as the Medscape Reference. History Plantz, Adler and Berezin evolved the concept for eMedicine.com in 1996 and deployed the initial site via Boston Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenocarcinomas are part of the larger grouping of carcinomas, but are also sometimes called by more precise terms omitting the word, where these exist. Thus invasive ductal carcinoma, the most common form of breast cancer, is adenocarcinoma but does not use the term in its name—however, esophageal adenocarcinoma does to distinguish it from the other common type of esophageal cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Several of the most common forms of cancer are adenocarcinomas, and the various sorts of adenocarcinoma vary greatly in all their aspects, so that few useful generalizations can be made about them. In the most specific usage (narrowest sense), the glandular origin or traits are exocrine; endocrine gland tumors, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenocarcinoma On Pap Test 1
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenocarcinomas are part of the larger grouping of carcinomas, but are also sometimes called by more precise terms omitting the word, where these exist. Thus invasive ductal carcinoma, the most common form of breast cancer, is adenocarcinoma but does not use the term in its name—however, esophageal adenocarcinoma does to distinguish it from the other common type of esophageal cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Several of the most common forms of cancer are adenocarcinomas, and the various sorts of adenocarcinoma vary greatly in all their aspects, so that few useful generalizations can be made about them. In the most specific usage (narrowest sense), the glandular origin or traits are exocrine; endocrine gland tumors, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |