|
ARA Bahía San Blas (B-4)
ARA ''Bahía San Blas'' is an amphibious cargo ship of the Argentine Navy, capable of unloading landing craft, troops, vehicles and cargo. She is the first Argentine Navy ship to bear the name of San Blas Bay of in the south of Buenos Aires Province. Design ''Bahía San Blas'' (B-4) is one of three The other ships in the class are the ARA ''Canal Beagle'' and ARA ''Cabo de Hornos''. cargo ships ordered by the Argentine Navy in 1975, designed and built by the Argentine Príncipe, Menghi y Penco shipyard, at Buenos Aires, Argentina. The design is optimised for Patagonic coastal service. ''Bahía San Blas'' has a steel hull and the superstructure at the stern, with a single mast and a single funnel atop, behind the bridge; the cargo area is located in the middle of the ship and three Liebherr cranes serve the three holds, one each.One 5-ton crane servers hold 1, and two 12.5-ton cranes serve holds 2 and 3; these can be used simultaneously to provide a 25-ton lifting capacity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
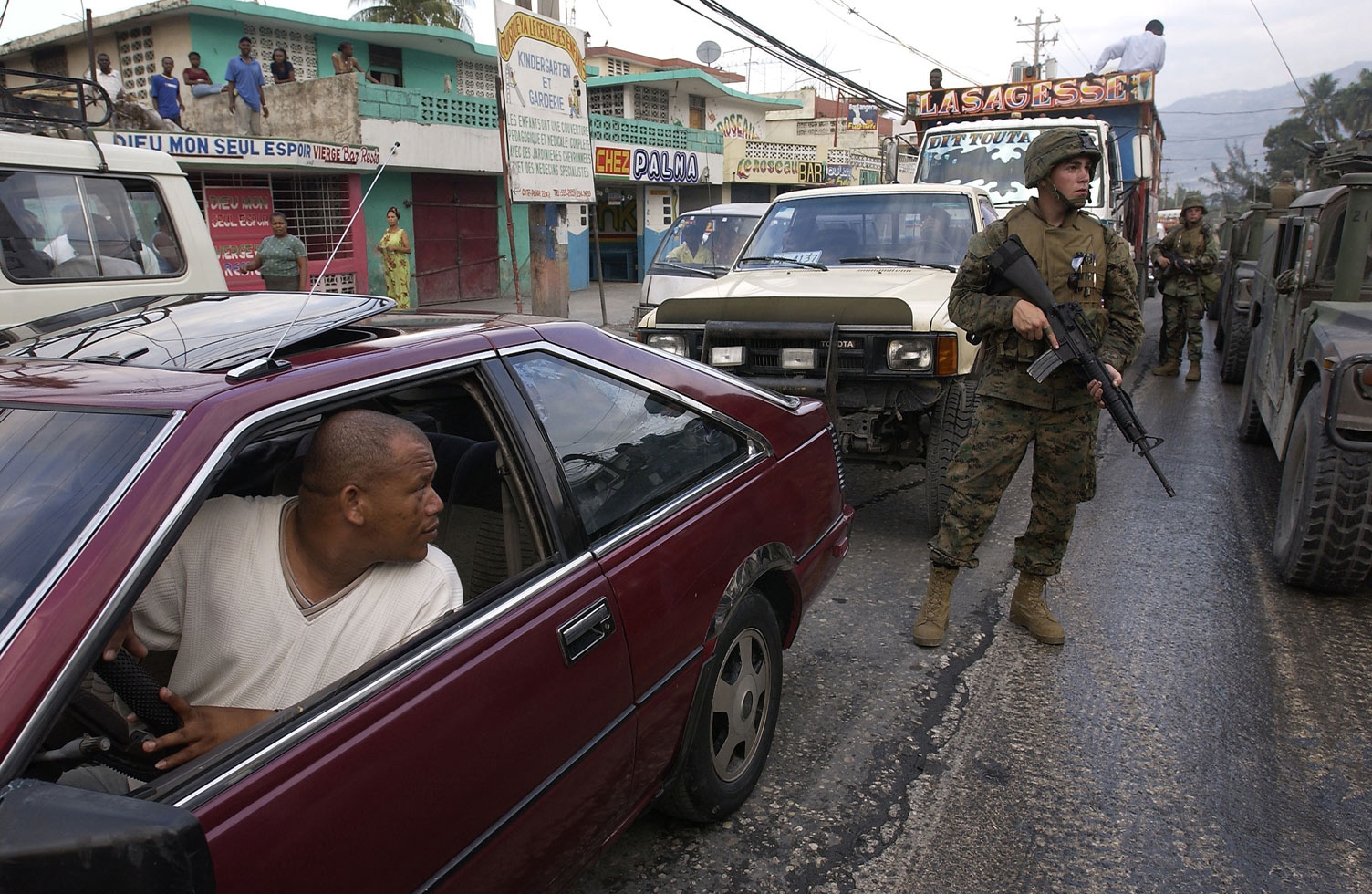
Gonaïves
Gonaïves (; ht, Gonayiv, ) is a commune in northern Haiti, and the capital of the Artibonite department of Haiti. It has a population of about 300,000 people, but current statistics are unclear, as there has been no census since 2003. History The city of Gonaïves was founded around 1422 by a group of Taíno, who named it ''Gonaibo'' (to designate a locality of cacicat of the Jaragua). The Gulf of Gonâve is named after the town. In 1802, an important battle of the Haitian Revolution, the Battle of Ravine-à-Couleuvres was fought near Gonaïves. Gonaïves is also known as Haiti's city of independence, because it was the location of Jean-Jacques Dessalines declaring Haiti independent from France on January 1, 1804, by reading the Act of Independence, drafted by Boisrond Tonnerre, on the Place d'Armes of the town. Marie-Claire Heureuse Félicité, the wife of Jean-Jacques Dessalines, died here in August 1858. In the early 2000s, Gonaïves was the scene of substantial riot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulzer (manufacturer)
Sulzer Ltd. is a Swiss industrial engineering and manufacturing firm, founded by Salomon Sulzer-Bernet in 1775 and established as Sulzer Brothers Ltd. (Gebrüder Sulzer) in 1834 in Winterthur, Switzerland. Today it is a publicly traded company with about 180 manufacturing facilities and service centers around the world. The company's shares are listed on the Swiss Stock Exchange. Sulzer is a global leader in fluid engineering. The company specializes in pumping, agitation, mixing, separation and purification technologies for fluids of all types. Sulzer provides new equipment for large infrastructure across various markets, among others water and wastewater, energy, chemicals, renewables and industrial processes. The service business makes up half of the company's sales. A growing part of the business are renewable applications such as biopolymers, recycling and low-carbon solutions. In its almost 200-year history, the company has gained international recognition with invention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa Sur Class Cargo Ships
Costa may refer to: Biology * Rib (Latin: ''costa''), in vertebrate anatomy * Costa (botany), the central strand of a plant leaf or thallus * Costa (coral), a stony rib, part of the skeleton of a coral * Costa (entomology), the leading edge of the forewing of winged insects, as well as a part of the male clasper Organisations * Costa Coffee, a British coffee shop chain, sponsor of the book award * Costa Cruises, a leading cruise company in Europe * Costa Del Mar, an American manufacturer of polarized sunglasses * Costa Group, Australian food supplier Places * Costa, Haute-Corse, a commune on the island of Corsica * Costa Head, prominent headland on the Orkney Islands * Costa Rica, a country in Central America * Costa Mesa, California, a city in Orange County * Costa, Lajas, Puerto Rico, a barrio Other uses * Costa (surname), including origin of the name and people sharing the surname * ''Costa!'', a 2001 Dutch film from BNN * Costa Book Awards, formerly the Whitbread Book A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MINUSTAH
) , leader_title = Head , leader_name = Sandra Honoré (Special Representative of the Secretary-General) , status = Replaced by MINUJUSTH , formation = 1 June 2004 , websiteUN Peacekeeping: MINUSTAH , parent_organization = UN , , subsidiaries = , footnotes = The United Nations Stabilisation Mission in Haiti (french: Mission des Nations Unies pour la stabilisation en Haïti), also known as MINUSTAH, an |
Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island which it shares with the Dominican Republic. To its south-west lies the small Navassa Island, which is claimed by Haiti but is disputed as a United States territory under federal administration."Haiti" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Haiti is in size, the third largest country in the Caribbean by area, and has an estimated population of 11.4 million, making it the most populous country in the Caribb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Marines
The Naval Infantry Command ( es, Comando de la Infantería de Marina, COIM), also known as the Naval Infantry of the Navy of the Argentine Republic ( es, Infantería de Marina de la Armada de la República Argentina, IMARA) and generally referred to in English as the Argentine marines are the amphibious warfare branch of the Argentine Navy and one of its four operational commands. The Argentine marines trace their origins to the Spanish Naval Infantry, which took part in conflicts in South America in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Argentine marines took part in various conflicts of the nineteenth and twentieth century, notably the War of the Triple Alliance and the Falklands War. The marines (represented by the 5th Naval Infantry Battalion) are considered to have been among the best Argentine combat units present in the Falklands. The most recent war in which Argentine naval infantry took part was the Gulf War of 1990. Today Argentine naval infantry are frequently dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ONUCA
ONUCA and ONUSAL were two United Nations peacekeeping missions deployed in Central America during the late 1980s and early 1990s. ONUCA The United Nations Security Council formally created ONUCA ("United Nations Observer Group in Central America") when it approved Resolution 644 on 7 November 1989. The 625-person group, located in 33 regional bases, was responsible for halting cross-border infiltration and cutting support for rebels in the Central American region, and consisted of 260 unarmed military observers along with supporting technicians. Hemisphere countries involved in ONUCA included Spain, Sweden, Ireland, India, Venezuela, Canada, Argentina, Brazil, Ecuador and Colombia. ONUCA's initial mandate, composition and operational concept reflected the UN reluctance to get involved in internal conflicts. It was to be a verification and peace-observing mission, not a full-scale peacekeeping interposition mission, and certainly not peace-enforcement, although as events unfolde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. It is the world's largest and most familiar international organization. The UN is headquarters of the United Nations, headquartered on extraterritoriality, international territory in New York City, and has other main offices in United Nations Office at Geneva, Geneva, United Nations Office at Nairobi, Nairobi, United Nations Office at Vienna, Vienna, and Peace Palace, The Hague (home to the International Court of Justice). The UN was established after World War II with Dumbarton Oaks Conference, the aim of preventing future world wars, succeeding the League of Nations, which was characterized as ineffective. On 25 April 1945, 50 governments met in San Francisco for United Nations Conference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Fonseca
The Gulf of Fonseca ( es, Golfo de Fonseca; ), a part of the Pacific Ocean, is a gulf in Central America, bordering El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua. History Fonseca Bay was discovered for Europeans in 1522 by Gil González de Ávila, and named by him after his patron, Archbishop Juan Fonseca, the implacable enemy of Columbus. In 1849, E. G. Squier negotiated a treaty for the United States to build a canal across Honduras from the Caribbean Sea to the Gulf. Frederick Chatfield, the British commander in Central America, was afraid the American presence in Honduras would destabilize the British Mosquito Coast, and sent his fleet to occupy El Tigre Island at the entrance to the Gulf. Shortly thereafter, however, Squier demanded the British leave, since he had anticipated the occupation and negotiated the island's temporary cession to the United States. Chatfield could only comply. All three countries—Honduras, El Salvador, and Nicaragua—with coastline along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert Storm
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases: Operation Desert Shield, which marked the military buildup from August 1990 to January 1991; and Operation Desert Storm, which began with the aerial bombing campaign against Iraq on 17 January 1991 and came to a close with the American-led Liberation of Kuwait on 28 February 1991. On 2 August 1990, Iraq invaded the neighbouring State of Kuwait and had fully occupied the country within two days. Initially, Iraq ran the occupied territory under a puppet government known as the " Republic of Kuwait" before proceeding with an outright annexation in which Kuwaiti sovereign territory was split, with the " Saddamiyat al-Mitla' District" being carved out of the country's northern portion and the " Kuwait Governorate" covering the rest. Varying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Desert Shield (Gulf War)
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases: Operation Desert Shield, which marked the military buildup from August 1990 to January 1991; and Operation Desert Storm, which began with the aerial bombing campaign against Iraq on 17 January 1991 and came to a close with the American-led Liberation of Kuwait on 28 February 1991. On 2 August 1990, Iraq invaded the neighbouring State of Kuwait and had fully occupied the country within two days. Initially, Iraq ran the occupied territory under a puppet government known as the "Republic of Kuwait" before proceeding with an outright annexation in which Kuwaiti sovereign territory was split, with the "Saddamiyat al-Mitla' District" being carved out of the country's northern portion and the "Kuwait Governorate" covering the rest. Varying specu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
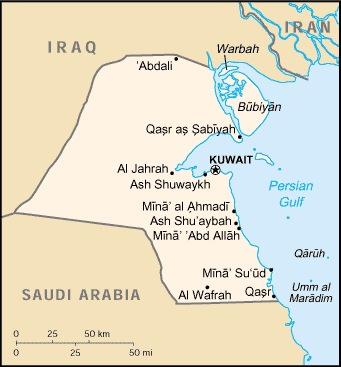
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Persis, Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical NameWorking Paper No. 61, 23rd Session, Vienna, 28 March – 4 April 2006. accessed October 9, 2010 It is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz. The Shatt al-Arab river delta forms the northwest shoreline. The Persian Gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive reefs (mostly rocky, but also Coral reef, coral), and abundant pearl oysters, however its ecology has been damaged by industrialization and oil spills. The Persian Gulf is in the Persian Gulf Basin, which is of Cenozoic origin and related to the subduction of the Arabian Plate u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |