|
ANKRD12
Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 1, or Cardiac ankyrin repeat protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ANKRD1'' gene also known as ''CARP''. CARP is highly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle, and is a transcription factor involved in development and under conditions of stress. CARP has been implicated in several diseases, including dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and several skeletal muscle myopathies. Structure Human cardiac ankyrin repeat protein is a 36.2kDa protein composed of 319 amino acids., though in cardiomyocytes, CARP can exist as multiple alternatively spliced forms. CARP contains five tandem ankyrin repeats. Studies have shown that CARP can homodimerize. Studies have also shown that CARP is N-terminally, post-translationally cleaved by calpain-3 in skeletal muscle, suggesting alternate bioactive forms of CARP exist. CARP has been localized to nuclei and Z-discs in animal and human muscle cells, and at in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Muscle Cell
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracycline
Anthracyclines are a class of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy that are extracted from ''Streptomyces'' bacterium. These compounds are used to treat many cancers, including leukemias, lymphomas, breast, stomach, uterine, ovarian, bladder cancer, and lung cancers. The first anthracycline discovered was daunorubicin (trade name Daunomycin), which is produced naturally by ''Streptomyces peucetius'', a species of Actinomycetota. Clinically the most important anthracyclines are doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin and idarubicin. The anthracyclines are among the most effective anticancer treatments ever developed and are effective against more types of cancer than any other class of chemotherapeutic agents. Their main adverse effect is cardiotoxicity, which considerably limits their usefulness. Use of anthracyclines has also been shown to be significantly associated with cycle 1 severe or febrile neutropenia. Other adverse effects include vomiting. The drugs act mainly by interc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used together with other chemotherapy agents. Doxorubicin is given by injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, vomiting, rash, and inflammation of the mouth. Other serious side effects may include allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis, heart damage, tissue damage at the site of injection, radiation recall, and treatment-related leukemia. People often experience red discoloration of the urine for a few days. Doxorubicin is in the anthracycline and antitumor antibiotic family of medications. It works in part by interfering with the function of DNA. Doxorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1974. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Versions th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischemic Injury
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue i.e. hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction (such as vasoconstriction, thrombosis, or embolism). Ischemia causes not only insufficiency of oxygen, but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial (poor perfusion) or total blockage. The inadequate delivery of oxygenated blood to the organs must be resolved either by treating the cause of the inadequate delivery or reducing the oxygen demand of the system that needs it. For example, patients with myocardial ischemia have a decreased blood flow to the heart and are prescribed with medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriogenesis
Arteriogenesis refers to an increase in the diameter of existing arterial vessels. Mechanical Stimulation Mechanically, arteriogenesis is linked to elevated pressure, which increases radial wall stress, and elevated flow, which increases endothelial surface stress. The vessel increases in diameter until the stress is normalized (Prior ''et al.'', 2004). Arteriogenesis does not occur every time there is an increase in flow, however. Most vessel networks can handle increased flow without increasing diameter because flow is related to vessel diameter by a power of four. Initial experiments demonstrated this phenomenon in that mature vessels are unlikely to respond to increased flow by increasing diameter, but will respond to decreased flow by decreasing diameter (Brownlee & Langille, 1991). Another experiment showed that increasing shear stress caused an immediate increase in vessel expansion followed by a rapid decrease, as well as demonstrating that the mature vessels do indeed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotendinous Junction
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in a proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
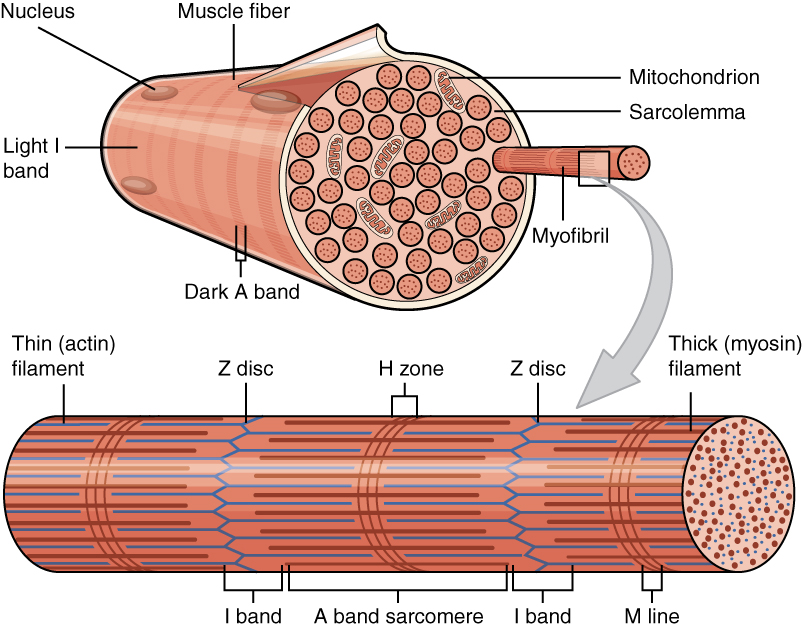
Myofibril
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2 micrometres. They are created during embryonic development in a process known as myogenesis. Myofibrils are composed of long proteins including actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together. These proteins are organized into thick, thin, and elastic myofilaments, which repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections or units of contraction called sarcomeres. Muscles contract by sliding the thick myosin, and thin actin myofilaments along each other. Structure Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2 micrometres (μm). The filaments of myofibrils, myofilaments, consist of three types, thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thin filaments consist primarily of the protein acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelial Cells
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells form the barrier between vessels and tissue and control the flow of substances and fluid into and out of a tissue. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contractility
Contractility refers to the ability for self-contraction, especially of the muscles or similar active biological tissue *Contractile ring in cytokinesis *Contractile vacuole *Muscle contraction **Myocardial contractility *See contractile cell for an overview of cell types in humans. See also *motility Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy. Definitions Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ... {{SIA Cell movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAMK
CAMK, also written as CaMK or CCaMK, is an abbreviation for the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase class of enzymes. CAMKs are activated by increases in the concentration of intracellular calcium ions (Ca2+) and calmodulin. When activated, the enzymes transfer phosphates from Adenosine triphosphate, ATP to defined serine or threonine residues in other proteins, so they are serine/threonine-specific protein kinases. Activated CAMK is involved in the phosphorylation of transcription factors and therefore, in the regulation of expression of responding genes. CAMK also works to regulate the cell life cycle (i.e. programmed cell death), rearrangement of the cell's cytoskeletal network, and mechanisms involved in the learning and memory of an organism. Types There are 2 common types of CAM Kinase proteins: specialized and multi-functional CAM kinases. ;Substrate-specific CAM Kinases: only have one target that they can phosphorylate, such as myosin light chain kinases. This group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |