|
ANGPTL3
Angiopoietin-like 3, also known as ANGPTL3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ANGPTL3'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the angiopoietin-like family of secreted factors. It is expressed predominantly in the liver, and has the characteristic structure of angiopoietins, consisting of a signal peptide, N-terminal coiled-coil domain, and the C-terminal fibrinogen (FBN)-like domain. The FBN-like domain in angiopoietin-like 3 protein was shown to bind alpha-5/beta-3 integrins, and this binding induced endothelial cell adhesion and migration. This protein may also play a role in the regulation of angiogenesis. Angptl3 also acts as dual inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and endothelial lipase (EL), thereby increasing plasma triglyceride, LDL cholesterol and HDL cholesterol in mice and humans. ANGPTL3 inhibits endothelial lipase hydrolysis Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoprotein Lipase
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) (EC 3.1.1.34, systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase (lipoprotein-dependent)) is a member of the lipase gene family, which includes pancreatic lipase, hepatic lipase, and endothelial lipase. It is a water-soluble enzyme that hydrolyzes triglycerides in lipoproteins, such as those found in chylomicrons and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), into two free fatty acids and one monoacylglycerol molecule: :triacylglycerol + H2O = diacylglycerol + a carboxylate It is also involved in promoting the cellular uptake of chylomicron remnants, cholesterol-rich lipoproteins, and free fatty acids. LPL requires ApoC-II as a cofactor. LPL is attached to the luminal surface of endothelial cells in capillaries by the protein glycosylphosphatidylinositol HDL-binding protein 1 (GPIHBP1) and by heparan sulfated peptidoglycans. It is most widely distributed in adipose, heart, and skeletal muscle tissue, as well as in lactating mammary glands. Synthesis In brief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiopoietin
Angiopoietin is part of a family of vascular growth factors that play a role in embryonic and postnatal angiogenesis. Angiopoietin signaling most directly corresponds with angiogenesis, the process by which new arteries and veins form from preexisting blood vessels. Angiogenesis proceeds through sprouting, endothelial cell migration, proliferation, and vessel destabilization and stabilization. They are responsible for assembling and disassembling the endothelial lining of blood vessels. Angiopoietin cytokines are involved with controlling microvascular permeability, vasodilation, and vasoconstriction by signaling smooth muscle cells surrounding vessels. There are now four identified angiopoietins: ANGPT1, ANGPT2, ANGPTL3, ANGPT4. In addition, there are a number of proteins that are closely related to ('like') angiopoietins (Angiopoietin-related protein 1, , , , , , , ). Angiopoietin-1 is critical for vessel maturation, adhesion, migration, and survival. Angiopoietin-2, on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Peptide
A signal peptide (sometimes referred to as signal sequence, targeting signal, localization signal, localization sequence, transit peptide, leader sequence or leader peptide) is a short peptide (usually 16-30 amino acids long) present at the N-terminus (or occasionally nonclassically at the C-terminus or internally) of most newly synthesized proteins that are destined toward the secretory pathway. These proteins include those that reside either inside certain organelles (the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi or endosomes), secreted from the cell, or inserted into most cellular membranes. Although most type I membrane-bound proteins have signal peptides, the majority of type II and multi-spanning membrane-bound proteins are targeted to the secretory pathway by their first transmembrane domain, which biochemically resembles a signal sequence except that it is not cleaved. They are a kind of target peptide. Function (translocation) Signal peptides function to prompt a cell to translo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coiled-coil
A coiled coil is a structural motif in proteins in which 2–7 alpha helix, alpha-helices are coiled together like the strands of a rope. (Protein dimer, Dimers and Protein trimer, trimers are the most common types.) Many coiled coil-type proteins are involved in important biological functions, such as the regulation of gene expression — e.g., transcription factors. Notable examples are the oncoproteins c-Fos and c-Jun, as well as the muscle protein tropomyosin. Discovery The possibility of coiled coils for α-keratin was initially somewhat controversial. Linus Pauling and Francis Crick independently came to the conclusion that this was possible at about the same time. In the summer of 1952, Pauling visited the laboratory in England where Crick worked. Pauling and Crick met and spoke about various topics; at one point, Crick asked whether Pauling had considered "coiled coils" (Crick came up with the term), to which Pauling said he had. Upon returning to the United States, Paul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (factor I) is a glycoprotein complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and then to a fibrin-based blood clot. Fibrin clots function primarily to occlude blood vessels to stop bleeding. Fibrin also binds and reduces the activity of thrombin. This activity, sometimes referred to as antithrombin I, limits clotting. Fibrin also mediates blood platelet and endothelial cell spreading, tissue fibroblast proliferation, capillary tube formation, and angiogenesis and thereby promotes revascularization and wound healing. Reduced and/or dysfunctional fibrinogens occur in various congenital and acquired human fibrinogen-related disorders. These disorders represent a group of rare conditions in which individuals may present with severe episodes of pathological bleeding and thrombosis; these conditions are treated by supplementing blood fibrinogen levels an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
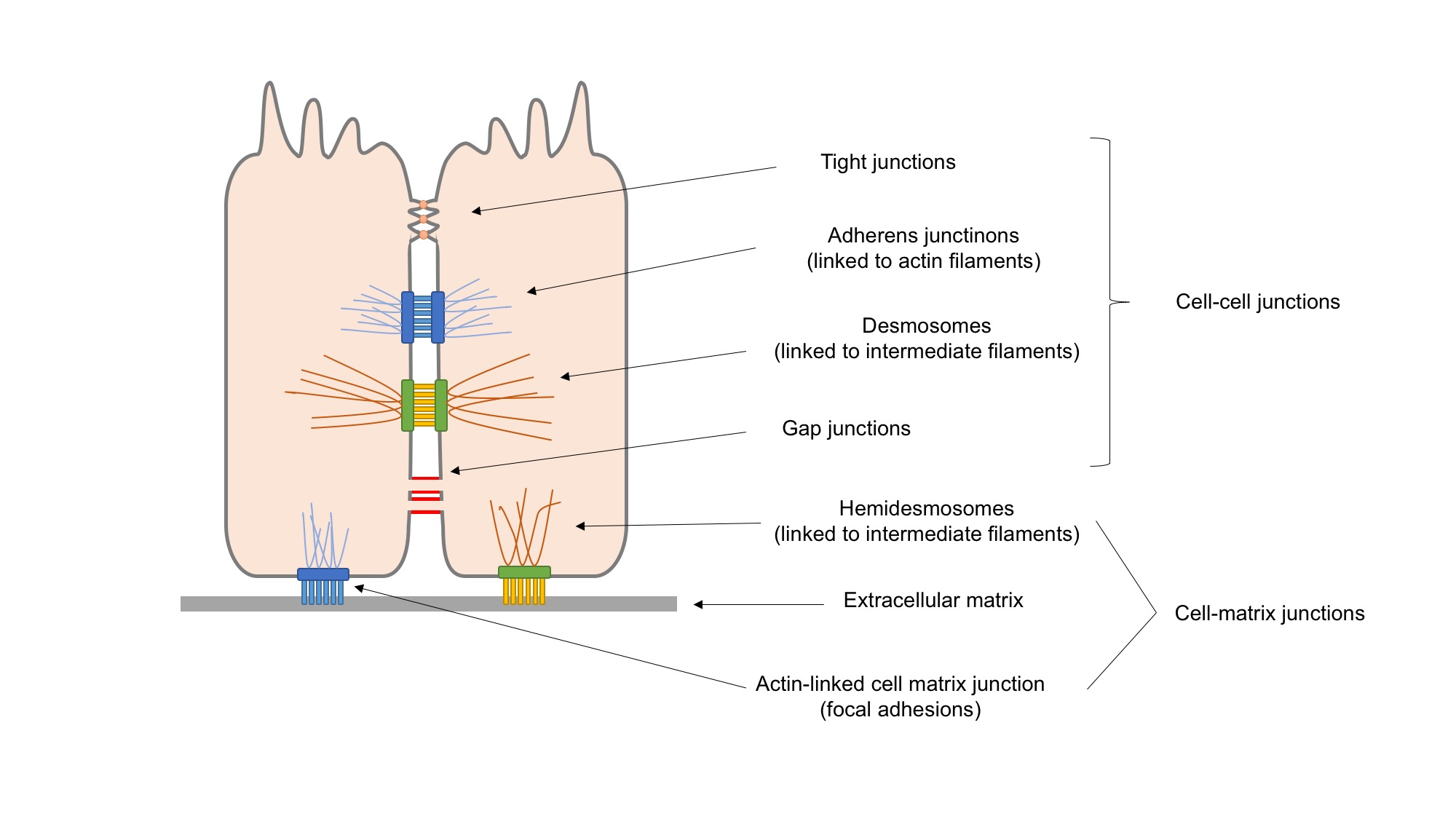
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Migration
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryonic development, wound healing and immune responses all require the orchestrated movement of cells in particular directions to specific locations. Cells often migrate in response to specific external signals, including chemical signals and mechanical signals. Errors during this process have serious consequences, including intellectual disability, vascular disease, tumor formation and metastasis. An understanding of the mechanism by which cells migrate may lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for controlling, for example, invasive tumour cells. Due to the highly viscous environment (low Reynolds number), cells need to continuously produce forces in order to move. Cells achieve active movement by very different mechanisms. Many less complex prokaryotic organisms (and sperm cells) use flagella or cilia to propel themselves. Eukaryot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |