|
AMOS-6 (satellite)
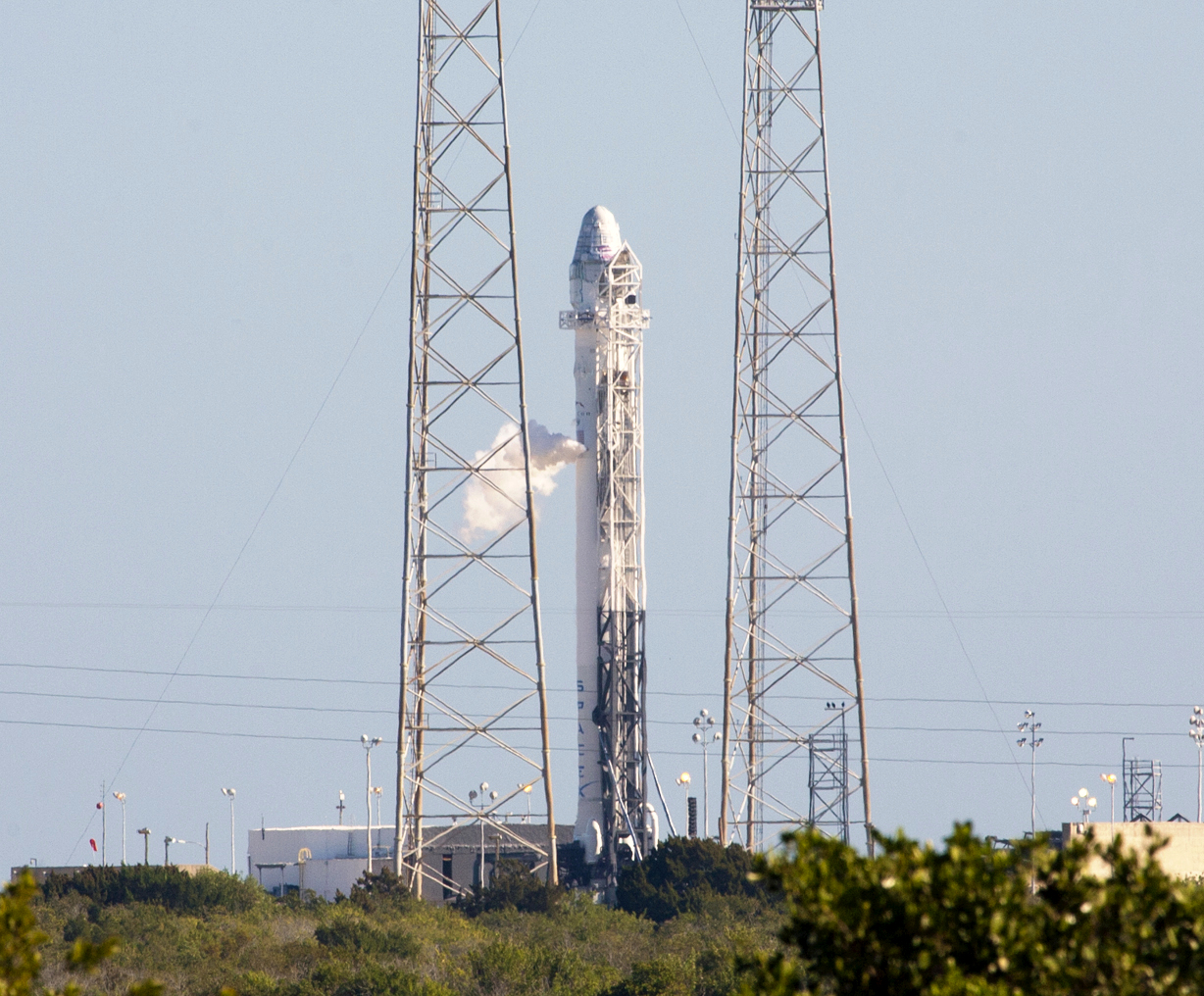
AMOS-6 was an Israeli communications satellite, one of the Spacecom AMOS series, that was built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), a defense and aerospace company. AMOS-6 was intended to be launched on flight 29 of a SpaceX Falcon 9 to geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) on 3 September 2016. On 1 September 2016, during the run-up to a static fire test, there was an anomaly on the launch pad, resulting in an explosion and the loss of the vehicle and AMOS-6. There were no injuries. Terminology AMOS stands for "Affordable Modular Optimized Satellite" and is also an allusion to the prophet Amos. This spacecraft is the second implementation of the AMOS-4000 satellite bus, the first was the AMOS-4. It is one of a AMOS series of satellites built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI). History Spacecom, the AMOS satellites operator, announced in June 2012 that it had signed a US$195 million contract to build AMOS-6, the newest addition to the AMOS constellation, with Isr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacDonald, Dettwiler And Associates
MDA Ltd. is a Canadian space technology company headquartered in Brampton, Ontario, Canada, that provides geointelligence, robotics & space operations, and satellite systems. History MDA (formerly MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates) was founded in 1969 by John S. MacDonald and Vern Dettwiler in the basement of MacDonald's Vancouver home. The company became a subsidiary of Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC) from the United States on 17 November 1995. MDA was primary contractor for, and took ownership of, the RADARSAT-2 Earth observation satellite. MDA bought the space robotics division of Spar Aerospace—manufacturer of the Canadarm—in March 1999, renaming it MD Robotics. The company completed the Mobile Servicing System (including the Canadarm2) for the International Space Station. OSC sold its entire stake in 2001. Nearly 70% was sold to a group of Canadian investors; the Ontario Teachers' Pension Plan (OTPP) became the largest shareholder with a 29% stake. In the 2000s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMOS-2 (satellite)
AMOS-2 is an Israeli commercial second generation communication satellite, part of the AMOS series of satellites. The satellite was positioned at 4° West longitude in the geostationary orbit. Transmission and communication services given by this satellite include: direct distribution of television and radio translations to communication centers, distribution of internet services, data transmissions to communication networks. The new satellite, like its predecessor, will be positioned 36,000 kilometers above the Earth, and it will lie close to AMOS-1, so that the two can share a single space antenna. Satellite description AMOS-2 carries 28 Ku-band transponders; twenty-two active with six as backups. With a mass of 1370 kg at launch, AMOS-2 incorporated a 400 newtons liquid apogee boost motor and fourteen 10 newtons reaction control thrusters for raising the satellite's orbit from geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) to its final geostationary orbit as well as for its a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held. Bus-derived satellites are opposed to specially produced satellites. Bus-derived satellites are usually customized to customer requirements, for example with specialized sensors or transponders, in order to achieve a specific mission. They are commonly used for geosynchronous satellites, particularly communications satellites, but are also used in spacecraft which occupy lower orbits, occasionally including low Earth orbit missions. Examples Some satellite bus examples include: * Boeing DS&S 702 * Lockheed Martin Space Systems A2100 * Alphabus * INVAP ARSAT-3K * Airbus D&S Eurostar * ISRO's I-1K, I-2K, I-3K, I-4K, I-6K, and Indian Mini Satellite bus * NASA Ames MCSB * SSL 1300 * Orbital ATK GEOStar * Mitsubishi Electric DS2000 * Spacecraft bus of the James Webb Space Telescope * SPUTNIX TabletSat * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amos (prophet)
In the Hebrew Bible and Christian Old Testament, Amos (; he, עָמוֹס – ''ʿĀmōs'') was one of the Twelve Minor Prophets. An older contemporary of Hosea and Isaiah, Amos was active c. 760–755 BCE during the rule of kings Jeroboam II of Israel and Uzziah of Judah. He was from the southern Kingdom of Judah but preached in the northern Kingdom of Israel. Amos wrote at a time of relative peace and prosperity but also of neglect of God's laws. He spoke against an increased disparity between the very wealthy and the very poor. His major themes of justice, God's omnipotence, and divine judgment became staples of prophecy. The Book of Amos is attributed to him. Life Before becoming a prophet, Amos was a sheep herder and a sycamore fig farmer.Coogan, Michael. ''A Brief Introduction to the Old Testament''. p. 257. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009. His prior professions and his claim "I am not a prophet nor a son of a prophet" () indicates that Amos was not from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Fire
Launch vehicle system tests assess the readiness of a launch system to safely reach orbit. Launch vehicles undergo system tests before they launch. A wet dress rehearsal (WDR) and a more extensive static fire tests a fully assembled launch vehicle and its associated ground support equipment (GSE) prior to launch. The spacecraft/payload may or may not be attached to the launch vehicle during the WDR or static fire, but sufficient elements of the rocket and all relevant ground support equipment are in place to help verify that the rocket is ready for flight. Propellant load tests and static fire tests may also be done on prototype rocket stages as well, in which case no fully assembled launch vehicle is involved. Wet dress rehearsal A wet dress rehearsal is called "wet" because the liquid propellant components (such as liquid oxygen, liquid hydrogen, etc.) are loaded into the rocket during the test. In a pure wet dress rehearsal the rocket engines are not ignited. Wet dress rehear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostationary Transfer Orbit
A geosynchronous transfer orbit or geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) is a type of geocentric orbit. Satellite, Satellites that are destined for geosynchronous orbit, geosynchronous (GSO) or geostationary orbit (GEO) are (almost) always put into a GTO as an intermediate step for reaching their final orbit. A GTO is highly Elliptic orbit, elliptic. Its perigee (closest point to Earth) is typically as high as low Earth orbit (LEO), while its apogee (furthest point from Earth) is as high as geostationary (or equally, a geosynchronous) orbit. That makes it a Hohmann transfer orbit between LEO and GSO. Larson, Wiley J. and James R. Wertz, eds. Space Mission Design and Analysis, 2nd Edition. Published jointly by Microcosm, Inc. (Torrance, CA) and Kluwer Academic Publishers (Dordrecht/Boston/London). 1991. While some geostationary orbit, GEO satellites are launched direct to that orbit, often the launch vehicle lacks the power to put both the rocket and the satellite into that orbit. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falcon 9 Flight 29
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene. Adult falcons have thin, tapered wings, which enable them to fly at high speed and change direction rapidly. Fledgling falcons, in their first year of flying, have longer flight feathers, which make their configuration more like that of a general-purpose bird such as a broad wing. This makes flying easier while learning the exceptional skills required to be effective hunters as adults. The falcons are the largest genus in the Falconinae subfamily of Falconidae, which itself also includes another subfamily comprising caracaras and a few other species. All these birds kill with their beaks, using a tomial "tooth" on the side of their beaks—unlike the hawks, eagles, and other birds of prey in the Accipitridae, which use their feet. The largest falcon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AsiaSat 8
AsiaSat 8 then AMOS-7 is a Hong Kong-turned-Israeli geostationary communications satellite which is operated by the Asia Satellite Telecommunications Company (Asiasat). Satellite description AsiaSat 8 was built by Space Systems/Loral, and is based on the LS-1300 satellite bus. The satellite carries twenty-four Ku-band transponders and one Ka-band payload, and was planned to be initially positioned above the equator, at a longitude of 105.5° East, providing coverage of southern and south-eastern Asia, China and the Middle East. Launch SpaceX was contracted to launch AsiaSat 8, using a Falcon 9 v1.1 launch vehicle. The launch took place from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) on 5 August 2014 at 08:00 UTC. 4 Aug 2014, accessed 5 Aug 2014 |