|
AKNA
AKNA is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AKNA'' gene. The protein is an AT-hook transcription factor which contains an AT-hook binding motif. The protein is expressed as different isoforms. AKNA is known to upregulate expression of the receptor CD40 and its ligand CD40L/CD154. AKNA is an essential part in the construction, organization, and proliferation of the centrosomal microtubules in order to maintain the neural stem cells during the process of neurogenesis. Due to these functions AKNA plays in the centrosomal microtubules it also has an active role in delamination during the formation of the subventricular zone, and the regulation of the amount of access provided to cells in this zone. Furthermore, because of AKNA's role in the centrosomal microtubules it also plays a part in the management of the modification of epithelial cells losing their polarity and attachment, and transforming into the mobile mesenchymal stem cells, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD40 (protein)
Cluster of differentiation 40, CD40 is a costimulatory protein found on antigen-presenting cells and is required for their activation. The binding of CD154 (CD40L) on TH cells to CD40 activates antigen presenting cells and induces a variety of downstream effects. Deficiency can cause Hyper-IgM syndrome type 3. Function The protein receptor encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor has been found to be essential in mediating a broad variety of immune and inflammatory responses including T cell-dependent immunoglobulin class switching, memory B cell development, and germinal center formation. AT-hook transcription factor AKNA is reported to coordinately regulate the expression of this receptor and its ligand, which may be important for homotypic cell interactions. The interaction of this receptor and its ligand is found to be necessary for amyloid-beta-induced microglial activation, and thus is thought to be an early event in Alzheimer disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subventricular Zone
The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a region situated on the outside wall of each lateral ventricle of the vertebrate brain. It is present in both the embryonic and adult brain. In embryonic life, the SVZ refers to a secondary proliferative zone containing neural progenitor cells, which divide to produce neurons in the process of neurogenesis. The primary neural stem cells of the brain and spinal cord, termed radial glial cells, instead reside in the ventricular zone (VZ) (so-called because the VZ lines the inside of the developing ventricles). In the developing cerebral cortex, which resides in the dorsal telencephalon, the SVZ and VZ are transient tissues that do not exist in the adult. However, the SVZ of the ventral telencephalon persists throughout life. The adult SVZ is composed of four distinct layers of variable thickness and cell density as well as cellular composition. Along with the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the SVZ is one of two places where neurogenesis has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse. While bleeding after sex may not be serious, it may also indicate the presence of cervical cancer. Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) causes more than 90% of cases; most women who have had HPV infections, however, do not develop cervical cancer. HPV 16 and 18 strains are responsible for nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers. Other risk factors include smoking, a weak immune system, birth control pills, starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners, but these are less important. Genetic factors also contribute to cervical cancer risk. Cervical cancer typically develops from precancerous changes over 10 to 20 years. About 90% of cervical cancer cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akna (Inuit Mythology)
In Inuit mythology, Akna ("mother") is a goddess of fertility and childbirth. Akna. First People.com References Fertility goddesses Inuit goddesses Creator goddesses Childhood goddesses {{NorthAm-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adherens Junction
Adherens junctions (or zonula adherens, intermediate junction, or "belt desmosome") are protein complexes that occur at cell–cell junctions, cell–matrix junctions in epithelial and endothelial tissues, usually more basal than tight junctions. An adherens junction is defined as a cell junction whose cytoplasmic face is linked to the actin cytoskeleton. They can appear as bands encircling the cell (zonula adherens) or as spots of attachment to the extracellular matrix (focal adhesion). Adherens junctions uniquely disassemble in uterine epithelial cells to allow the blastocyst to penetrate between epithelial cells. A similar cell junction in non-epithelial, non-endothelial cells is the fascia adherens. It is structurally the same, but appears in ribbonlike patterns that do not completely encircle the cells. One example is in cardiomyocytes. Proteins Adherens junctions are composed of the following proteins: * cadherins. The cadherins are a family of transmembrane proteins tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
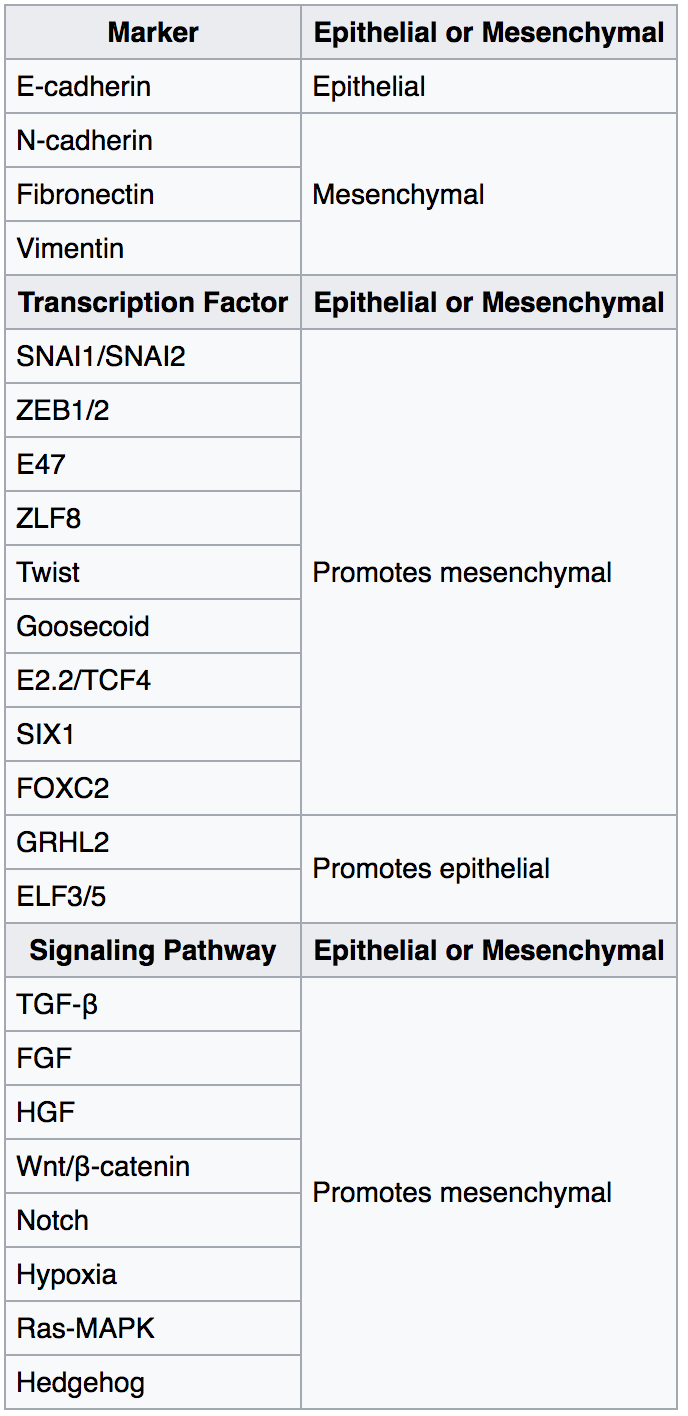
Epithelial–mesenchymal Transition
The epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process by which epithelial cells lose their cell polarity and cell–cell adhesion, and gain migratory and invasive properties to become mesenchymal stem cells; these are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types. EMT is essential for numerous developmental processes including mesoderm formation and neural tube formation. EMT has also been shown to occur in wound healing, in organ fibrosis and in the initiation of metastasis in cancer progression. Introduction Epithelial–mesenchymal transition was first recognized as a feature of embryogenesis by Betty Hay in the 1980s. EMT, and its reverse process, MET ( mesenchymal-epithelial transition) are critical for development of many tissues and organs in the developing embryo, and numerous embryonic events such as gastrulation, neural crest formation, heart valve formation, secondary palate development, and myogenesis. Epithelial and mesenchyma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Stem Cell
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are self-renewing, multipotent cells that firstly generate the radial glial progenitor cells that generate the neurons and glia of the nervous system of all animals during embryonic development. Some neural progenitor stem cells persist in highly restricted regions in the adult vertebrate brain and continue to produce neurons throughout life. Differences in the size of the central nervous system are among the most important distinctions between the species and thus mutations in the genes that regulate the size of the neural stem cell compartment are among the most important drivers of vertebrate evolution. Stem cells are characterized by their capacity to differentiate into multiple cell types. They undergo symmetric or asymmetric cell division into two daughter cells. In symmetric cell division, both daughter cells are also stem cells. In asymmetric division, a stem cell produces one stem cell and one specialized cell. NSCs primarily differentiate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs), radial glial cells (RGCs), basal progenitors (BPs), intermediate neuronal precursors (INPs), subventricular zone astrocytes, and subgranular zone radial astrocytes, among others. Neurogenesis is most active during embryonic development and is responsible for producing all the various types of neurons of the organism, but it continues throughout adult life in a variety of organisms. Once born, neurons do not divide (see mitosis), and many will live the lifespan of the animal. Neurogenesis in mammals Developmental neurogenesis During embryonic development, the mammalian central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) is derived from the neural tube, which contains NSCs that will later generate neurons. However, neurogenesis does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD154
CD154, also called CD40 ligand or CD40L, is a protein that is primarily expressed on activated T cells and is a member of the Tumor necrosis factors, TNF superfamily of molecules. It binds to CD40 (protein), CD40 on antigen-presenting cells (APC), which leads to many effects depending on the target cell type. In total CD40L has three binding partners: CD40, Alpha-5 beta-1, α5β1 integrin and αIIbβ3. CD154 acts as a costimulatory molecule and is particularly important on a subset of T cells called Follicular B helper T cells, T follicular helper cells (TFH cells). On TFH cells, CD154 promotes B cell maturation and function by engaging CD40 on the B cell surface and therefore facilitating cell-cell communication. A defect in this gene results in an inability to undergo immunoglobulin class switching and is associated with hyper IgM syndrome. Absence of CD154 also stops the formation of germinal centers and therefore prohibiting antibody affinity maturation, an important process in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |