|
AIRPASS I
AIRPASS was a British airborne interception radar and fire-control radar system developed by Ferranti. It was the world's first airborne monopulse radar system and fed data to the world's first head-up display. The name is an acronym for "Airborne Interception Radar and Pilot's Attack Sight System". In the Royal Air Force (RAF) it was given the official name Radar, Airborne Interception, Mark 23, normally shortened to AI.23. AIRPASS was used on the English Electric Lightning throughout its lifetime. The basic AIRPASS electronics system was later adapted as the basis for a terrain following radar for navigation and targeting for air-to-ground attacks. This AIRPASS II was originally intended for the BAC TSR.2, but when that aircraft was cancelled in 1965, it was subsequently used in the Blackburn Buccaneer. Elements of the AIRPASS design were used on many subsequent radars from Ferranti, while its head-up display was licensed for use in the United States where it was quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Electric Lightning F6, UK - Air Force AN1103896
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community * En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
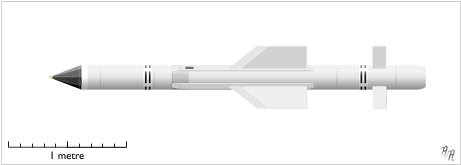
De Havilland Firestreak
The de Havilland Firestreak is a British first-generation, passive infrared homing (heat seeking) air-to-air missile. It was developed by de Havilland Propellers (later Hawker Siddeley) in the early 1950s, entering service in 1957. It was the first such weapon to enter active service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) and Fleet Air Arm, equipping the English Electric Lightning, de Havilland Sea Vixen and Gloster Javelin. It was a rear-aspect, fire and forget pursuit weapon, with a field of attack of 20 degrees either side of the target.Gibson 2007, p. 33 Developed under the rainbow code "Blue Jay", Firestreak was the third heat-seeking missile to enter service, after the US AIM-4 Falcon and AIM-9 Sidewinder, both of which entered service the previous year. In comparison to those designs, the Firestreak was larger and almost twice as heavy, carrying a much larger warhead. It had otherwise similar performance in terms of speed and range. It was also a very complex system, with an unusu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency (IF) is a frequency to which a carrier wave is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called heterodyning, resulting in a signal at the difference or beat frequency. Intermediate frequencies are used in superheterodyne radio receivers, in which an incoming signal is shifted to an IF for amplification before final detection is done. Conversion to an intermediate frequency is useful for several reasons. When several stages of filters are used, they can all be set to a fixed frequency, which makes them easier to build and to tune. Lower frequency transistors generally have higher gains so fewer stages are required. It's easier to make sharply selective filters at lower fixed frequencies. There may be several such stages of intermediate frequency in a superheterodyne receiver; t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheterodyne
A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was long believed to have been invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong, but after some controversy the earliest patent for the invention is now credited to French radio engineer and radio manufacturer Lucien Lévy. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle; except those software-defined radios using ''direct sampling''. History Heterodyne Early Morse code radio broadcasts were produced using an alternator connected to a spark gap. The output signal was at a carrier frequency defined by the physical construction of the gap, modulated by the alternating current signal from the alternator. Since the output frequency of the alternator was generally in the audible range, this produces an audible a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Oscillator
In electronics, a local oscillator (LO) is an electronic oscillator used with a mixer to change the frequency of a signal. This frequency conversion process, also called heterodyning, produces the sum and difference frequencies from the frequency of the local oscillator and frequency of the input signal. Processing a signal at a fixed frequency gives a radio receiver improved performance. In many receivers, the function of local oscillator and mixer is combined in one stage called a " converter" - this reduces the space, cost, and power consumption by combining both functions into one active device. Applications Local oscillators are used in the superheterodyne receiver, the most common type of radio receiver circuit. They are also used in many other communications circuits such as modems, cable television set top boxes, frequency division multiplexing systems used in telephone trunklines, microwave relay systems, telemetry systems, atomic clocks, radio telescopes, and milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klystron
A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian,Pond, Norman H. "The Tube Guys". Russ Cochran, 2008 p.31-40 which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from UHF up into the microwave range. Low-power klystrons are used as oscillators in terrestrial microwave relay communications links, while high-power klystrons are used as output tubes in UHF television transmitters, satellite communication, radar transmitters, and to generate the drive power for modern particle accelerators. In a klystron, an electron beam interacts with radio waves as it passes through resonant cavities, metal boxes along the length of a tube. The electron beam first passes through a cavity to which the input signal is applied. The energy of the electron beam amplifies the signal, and the amplified signal is taken from a cavity at the other end of the tube. The output signal can be coupled back into the input cavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound, with minimal loss of energy by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, wave intensities decrease according to the inverse square law as they expand into three-dimensional space. There are different types of waveguides for different types of waves. The original and most common meaningInstitute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, “The IEEE standard dictionary of electrical and electronics terms”; 6th ed. New York, N.Y., Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, c1997. IEEE Std 100-1996. d. Standards Coordinating Committee 10, Terms and Definitions; Jane Radatz, (chair)/ref> is a hollow conductive metal pipe used to carry high frequency radio waves, particularly microwaves. Dielectric waveguides are used at higher radio frequencies, and transparent dielectric waveguides and optical fibers serve as waveguides f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Control
Numerical control (also computer numerical control, and commonly called CNC) is the automated control of machining tools (such as drills, lathes, mills, grinders, routers and 3D printers) by means of a computer. A CNC machine processes a piece of material (metal, plastic, wood, ceramic, or composite) to meet specifications by following coded programmed instructions and without a manual operator directly controlling the machining operation. A CNC machine is a motorized maneuverable tool and often a motorized maneuverable platform, which are both controlled by a computer, according to specific input instructions. Instructions are delivered to a CNC machine in the form of a sequential program of machine control instructions such as G-code and M-code, and then executed. The program can be written by a person or, far more often, generated by graphical computer-aided design (CAD) or computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. In the case of 3D printers, the part to be printed is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and currently in microwave ovens and linear particle accelerators. It generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field while moving past a series of cavity resonators, which are small, open cavities in a metal block. Electrons pass by the cavities and cause microwaves to oscillate within, similar to the functioning of a whistle producing a tone when excited by an air stream blown past its opening. The resonant frequency of the arrangement is determined by the cavities' physical dimensions. Unlike other vacuum tubes, such as a klystron or a traveling-wave tube (TWT), the magnetron cannot function as an amplifier for increasing the intensity of an applied microwave signal; the magnetron serves solely as an oscillator, generating a microwave signal from direct current electricity supplied to the vacuum tube. The use of magnetic fields as a means to control the flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rainbow Codes
The Rainbow Codes were a series of code names used to disguise the nature of various British military research projects. They were mainly used by the Ministry of Supply from the end of the Second World War until 1958, when the ministry was broken up and its functions distributed among the forces. The codes were replaced by an alphanumeric code system. History During WWII, British intelligence was able to glean details of new German technologies simply by considering their code names. For instance, when they heard of a new system known as ''Wotan'', Reginald Victor Jones asked around and found that Wotan was a one-eyed god. Based on this, he guessed it was a radio navigation system using a single radio beam. This proved correct, and the Royal Air Force was able to quickly render it useless through jamming. Wishing to avoid making this sort of mistake, Ministry of Supply (MoS) initiated a system that would be entirely random and deliberately unrelated to the program in any way, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Lever
Thrust levers or throttle levers are found in the cockpit of aircraft, and are used by the pilot, copilot, or autopilot to control the thrust output of the aircraft's engines, by controlling the fuel flow to those engines. In multi-engine aircraft, each thrust lever displays the engine number of the engine it controls. Normally, there is one thrust lever for each engine. The thrust levers are normally found in the aircraft's center console, or on the dashboard of smaller aircraft. For aircraft equipped with thrust reversal, the control for each thrust reverser is usually found adjacent to the corresponding engine's thrust lever. The position of each lever can be described by the current angle indicated. This is referred to as the ''Throttle Lever Angle'' or ''TLA''. The greater the TLA, the greater the engine thrust. The throttle lever assembly is often designed to incorporate high-pressure (HP) cock switches so that the pilot has instinctive control of the fuel supply to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoke (aeronautics)
A yoke, alternatively known as a control wheel or a control column, is a device used for piloting some fixed-wing aircraft.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 563. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. . The pilot uses the yoke to control the attitude of the plane, usually in both pitch and roll. Rotating the control wheel controls the ailerons and the roll axis. Fore and aft movement of the control column controls the elevator and the pitch axis. When the yoke is pulled back, the nose of the aircraft rises. When the yoke is pushed forward, the nose is lowered. When the yoke is turned left, the plane rolls to the left, and when it is turned to the right, the plane rolls to the right. Small to medium-size aircraft, usually limited to propeller-driven, feature a mechanical system whereby the yoke is connected directly to the control surfaces with cables and rods. Human muscle power alone is not enough for larger and more powerful aircraft, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |