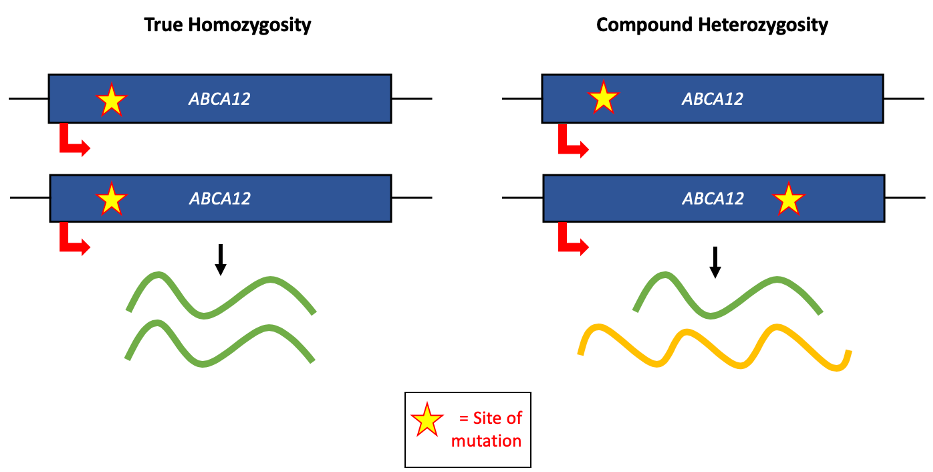
|
ABCA12
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 12 also known as ATP-binding cassette transporter 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABCA12'' gene. ABCA12 belongs to a group of genes called the ATP-binding cassette family, which makes proteins that transport molecules across cell membranes. The ABCA12 gene is active in some types of skin cells and in several other tissues, such as testis, placenta, lung, stomach, and fetal brain and liver. This protein appears to be essential for normal development of the skin, which provides a barrier between the body and its surrounding environment. It transports epidermoside, a glucosylceramide, out of the keratinocytes of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. The ABCA12 gene is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 2 between positions 34 and 35, from base pair 215,621,772 to base pair 215,828,656. Clinical significance Harlequin-type ichthyosis Several mutations in the ABCA12 gene are known to cause harlequin-type ichthyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harlequin-type Ichthyosis
Harlequin-type ichthyosis is a genetic disorder that results in thickened skin over nearly the entire body at birth. The skin forms large, diamond/trapezoid/rectangle-shaped plates that are separated by deep cracks. These affect the shape of the eyelids, nose, mouth, and ears and limit movement of the arms and legs. Restricted movement of the chest can lead to breathing difficulties. These plates fall off over several weeks. Other complications can include premature birth, infection, problems with body temperature, and dehydration. The condition is the most severe form of ichthyosis, a group of genetic disorders characterised by scaly skin. Harlequin-type ichthyosis is caused by mutations in the ''ABCA12'' gene. This gene codes for a protein necessary for transporting lipids out of cells in the outermost layer of skin. The disorder is autosomal recessive and inherited from parents who are carriers. Diagnosis is often based on appearance at birth and confirmed by genetic testin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATP-binding Cassette Family
The ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC transporters) are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters belong to translocases. ABC transporters often consist of multiple subunits, one or two of which are transmembrane proteins and one or two of which are membrane-associated AAA ATPases. The ATPase subunits utilize the energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding and hydrolysis to provide the energy needed for the translocation of substrates across membranes, either for uptake or for export of the substrate. Most of the uptake systems also have an extracytoplasmic receptor, a solute binding protein. Some homologous ATPases function in non-transport-related processes such as translation of RNA and DNA repair. ABC transporters are considered to be an ABC superfamily based on the similarities of the sequence and organization of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellar Ichthyosis
Lamellar ichthyosis, also known as ichthyosis lamellaris and nonbullous congenital ichthyosis, is a rare inherited skin disorder, affecting around 1 in 600,000 people. Presentation Affected babies are born in a collodion membrane, a shiny, waxy-appearing outer layer to the skin. This is shed 10–14 days after birth, revealing the main symptom of the disease, extensive scaling of the skin caused by hyperkeratosis. With increasing age, the scaling tends to be concentrated around joints in areas such as the groin, the armpits, the inside of the elbow and the neck. The scales often tile the skin and may resemble fish scales. Collodion baby In medicine, the term collodion baby applies to newborns who appear to have an extra layer of skin (known as a ''collodion membrane'') that has a collodion-like quality. It is a descriptive term, not a specific diagnosis or disorder (as such, it is a syndrome). Appearance and treatment at birth The appearance is often described as a shiny fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 2 (human)
Chromosome 2 is one of the twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 2 is the second-largest human chromosome, spanning more than 242 million base pairs and representing almost eight percent of the total DNA in human cells. Chromosome 2 contains the HOXD homeobox gene cluster. Chromosomes Humans have only twenty-three pairs of chromosomes, while all other extant members of Hominidae have twenty-four pairs. It is believed that Neanderthals and Denisovans had twenty-three pairs. Human chromosome 2 is a result of an end-to-end fusion of two ancestral chromosomes.It has been hypothesized that Human Chromosome 2 is a fusion of two ancestral chromosomes by Alec MacAndrew; accessed 18 May 2006. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratum Corneum
The stratum corneum (Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis. The human stratum corneum comprises several levels of flattened corneocytes that are divided into two layers: the ''stratum disjunctum'' and ''stratum compactum''. The skin's protective acid mantle and lipid barrier sit on top of the stratum disjunctum. The stratum disjunctum is the uppermost and loosest layer of skin. The stratum compactum is the comparatively deeper, more compacted and more cohesive part of the stratum corneum. The corneocytes of the stratum disjunctum are larger, more rigid and more hydrophobic than that of the stratum compactum. The stratum corneum is the dead tissue that performs protective and adaptive physiological functions including mechanical shear, impact resistance, water flux and hydration regulation, microbial proliferation and invasion regulation, initiation of inflammation through cytokine activation and dendritic cell activity, and selective permeability to exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis (skin)
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucosylceramide
Glucocerebroside (also called glucosylceramide) is any of the cerebrosides in which the monosaccharide head group is glucose. Clinical significance In Gaucher disease, the enzyme glucocerebrosidase is nonfunctional and cannot break down glucocerebroside into glucose and ceramide in the lysosome. Affected macrophages Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ..., called Gaucher cells, have a distinct appearance similar to "wrinkled tissue paper" under light microscopy, because the substrates build-up within the lysosome. See also * Glucosylceramide synthase * Gauchers disease * Glucocerebrosidase References External links * * Glycolipids Carbohydrates {{biochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |