|
Aysén Region
The Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region ( es, Región de Aysén, , '), often shortened to Aysén Region or Aisén,Examples of name usage1, official regional government site refers to the region as "Región de Aysén"., Chile's official meteorological agency refers to the region as "Región de Aisén".3 Chilean government official website refers of Pilar Cuevas Mardones as intendant of "Región de Aysén" .4 Chile's Ministry of Public Works calls the region "Región de Aysén" in the title of their 2011 report on that region.5, Corporación Nacional Forestal, a government agency refers to the region as "Región de Aysén" in their homepage. Here is some evidence of the short name use in English:I ''The Guardian'' reports on the 2012 Aysén protest.II ''Santiago Times'', a local English language newspaper use "Aysén Region" in a note referring to the same protest.III''Santiago Times'' again. *Vscientific paper in ''Journal of Hospital Infection'' referring to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
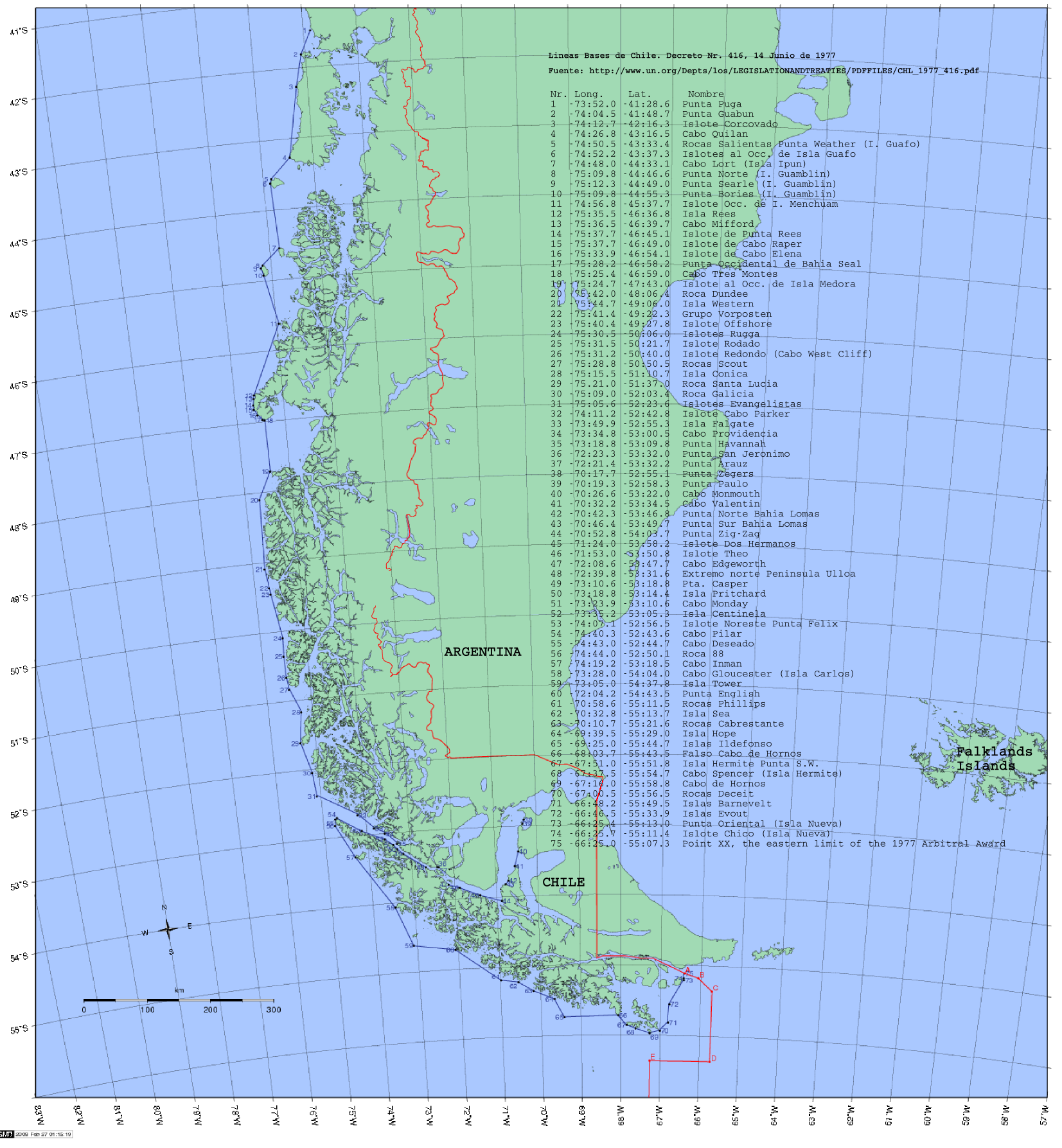
Regions Of Chile
Chile is divided into 16 regions (in Spanish, ''regiones''; singular ''región''), which are the country's first-level administrative division. Each region is headed by an intendant (''intendente)'', appointed by the President of Chile, and a directly elected regional board (''consejo regional''). The regions are divided into provinces (the second-level administrative division), each headed by a governor (''gobernador'') appointed by the President. There are 56 provinces in total. Provinces are divided into communes (the third and lowest level administrative division), which are governed by municipal councils. Naming Each region was given a Roman numeral, followed by a name (e.g. ''IV Región de Coquimbo'', read as "fourth region of Coquimbo" in Spanish). When the regional structure was created, Roman numerals were assigned in ascending order from north to south, with the northernmost region designated as I (first) and the southernmost region as XII (twelfth). The Santiago Metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Hospital Infection
The ''Journal of Hospital Infection'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal published by Elsevier on behalf of the Healthcare Infection Society. The journal publishes articles describing original research on epidemiology, healthcare, and antimicrobial resistance. According to the 2018 ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor of 3.354. The journal was established in 1980 and the editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ... is J. Gray. References External links * Microbiology journals Publications established in 1980 Monthly journals English-language journals Elsevier academic journals {{med-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catedral De Mármol
General Carrera Lake (Chilean part, officially renamed in 1959) or Lake Buenos Aires (Argentine part) is a lake located in Patagonia and shared by Argentina and Chile. Both names are internationally accepted, while the autochthonous name of the lake is Chelenko, which means "stormy waters" in Aonikenk. Another historical name is Coluguape from Mapuche, a derivative of this name is applied to Colhué Huapí Lake after Argentine explorer Francisco Moreno reached this lake in 1876 conflating it with Coluguape (General Carrera Lake). The lake is of glacial origin and is surrounded by the Andes mountain range. The lake drains to the Pacific Ocean on the west through the Baker River. During the last glaciation the lake drained to the Atlantic through Deseado River. The weather in this area of Chile and Argentina is generally cold and humid. But the lake itself has a sunny microclimate, a weather pattern enjoyed by the few settlements along the lake, such as Puerto Guadal, Fachina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lago Gral
__NOTOC__ Lago, which means "lake" in Italian, Portuguese, Spanish and Galician, may refer to: Places *Lago, Calabria, a ''comune'' in the Province of Cosenza, Italy *Lago, Mexico, a municipality zone in the State of Mexico *Lago District, a ''distrito'' in Niassa Province, Mozambique * Lago, Portugal, a ''freguesia'' in the District of Braga * Lago, Asturias, a ''parroquia'' in the ''municipio'' of Allande, Spain *Lago, Texas, a census-designated place *Lagos, Nigeria, the largest city in Nigeria People *Anders Lago, Swedish politician *Ângela Lago (1945–2017), Brazilian children's writer and illustrator *Antonio Lago, Venice-born French motor vehicle manufacturer *Fábio Lago, Brazilian actor *Nais Lago, Italian actress *Virginia Lago (born 1946), Argentine actress Other uses *Lago (Madrid Metro), a station on Line 5 *Talbot-Lago, a type of car *''Lago'', a fictional western town depicted in the film, ''High Plains Drifter'' See also * Lagos (other) Lagos is the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Foliage In The Aisén Region
Autumn, also known as fall in American English and Canadian English, is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September ( Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Southern Hemisphere). Autumn is the season when the duration of daylight becomes noticeably shorter and the temperature cools considerably. Day length decreases and night length increases as the season progresses until the Winter Solstice in December (Northern Hemisphere) and June (Southern Hemisphere). One of its main features in temperate climates is the striking change in colour for the leaves of deciduous trees as they prepare to shed. Date definitions Some cultures regard the autumnal equinox as "mid-autumn", while others with a longer temperature lag treat the equinox as the start of autumn. In the English-speaking world of high latitude countries, autumn traditionally began with Lammas Day and ended around Hallowe'en, the approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carretera Austral
The Carretera Austral (CH-7, ''in English: Southern Way'') is the name given to Chile's Route 7. The highway runs south for about from Puerto Montt to Villa O'Higgins, passing through rural Patagonia. Carretera Austral provides road access to Chile's Aysén Region and southern parts of Los Lagos Region. These areas are sparsely populated and despite its length, Carretera Austral provides access to only about 100,000 people. The largest city along the entire road is Coyhaique with a population of 44,850 in 2002. History Construction of the highway was commenced in 1976 under the dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet in order to connect a number of remote communities. Before that, in the 1950s and 1970s, there had been unsuccessful attempts to build access roads in the region. It is among the most ambitious infrastructure projects developed in Chile during the 20th century. As it was constructed during the military dictatorship, the Carretera Austral bears the unofficial name of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Volcanic Zone
The Andean Volcanic Belt is a major volcanic belt along the Andean cordillera in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. It is formed as a result of subduction of the Nazca Plate and Antarctic Plate underneath the South American Plate. The belt is subdivided into four main volcanic zones which are separated by volcanic gaps. The volcanoes of the belt are diverse in terms of activity style, products, and morphology. While some differences can be explained by which volcanic zone a volcano belongs to, there are significant differences within volcanic zones and even between neighboring volcanoes. Despite being a type location for calc-alkalic and subduction volcanism, the Andean Volcanic Belt has a broad range of volcano-tectonic settings, as it has rift systems and extensional zones, transpressional faults, subduction of mid-ocean ridges and seamount chains as well as a large range of crustal thicknesses and magma ascent paths and different amounts of crustal assimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Patagonian Ice Field
The Southern Patagonian Ice Field ( es, Hielo Continental or '), located at the Southern Patagonic Andes between Chile and Argentina, is the world's second largest contiguous extrapolar ice field. It is the bigger of two remnant parts of the Patagonian Ice Sheet, which covered all of southern Chile during the last glacial period, locally called the Llanquihue glaciation. Geography The Southern Patagonia Ice Field extends from parallels 48° 15′ S to 51° 30′ S for approximately , and has an approximate area of , of which 14,200 km2 belong to Chile and 2,600 km2 belong to Argentina. The ice mass feeds dozens of glaciers in the area, among which are the Upsala (765 km2), Viedma (978 km2) and Perito Moreno (258 km2) in the Los Glaciares National Park in Argentina, and the Pío XI Glacier or Bruggen Glacier (1,265 km2, the largest in area and longest in the southern hemisphere outside of Antarctica), O'Higgins (820 km2), Grey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Patagonian Ice Field
The Northern Patagonian Ice Field, located in southern Chile, is the smaller of two remnant parts in which the Patagonian Ice Sheet in the Andes Mountains of southern South America can be divided. It is completely contained within the boundaries of Laguna San Rafael National Park. Description The Northern Patagonian Ice Field is a vestige of the Patagonian Ice Sheet, an extensive ice sheet that covered all of Chilean Patagonia and the westernmost parts of Argentine Patagonia during the Quaternary glaciations. Today, with its glaciers largely in retreat and only an area of , it is still the second largest continuous mass of ice outside of the polar regions. Its survival depends on its elevation (), favorable terrain and a cool, moist, oceanic climate. The ice field has 28 exit glaciers, the largest two — San Quintin and San Rafael — nearly reach sea level to the west at the Pacific Ocean. Smaller exit glaciers, like San Valentín and Nef, feed numerous rivers and glacially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fjords And Channels Of Chile
The southern coast of Chile presents a large number of fjords and fjord-like channels from the latitudes of Cape Horn (55° S) to Reloncaví Estuary (42° S). Some fjords and channels are important navigable channels providing access to ports like Punta Arenas, Puerto Chacabuco and Puerto Natales. History Indigenous peoples The earliest known inhabitants of the fjords and channels were, from north to south, the Chono, Alacalufe and Yaghan, all of whom shared a life style as canoe-faring hunter-gatherers. They also shared physical traits such as being of low stature, long-headed (''Dolichocephalic''), and having a "low face".Trivero Rivera 2005, p. 42. Despite similarities their languages were completely different.Trivero Rivera 2005, p. 33. The Chono moved around in the area from Chiloé Archipelago to 50° S and the Alacalufe from 46° S to the Strait of Magellan. Thus both groups overlapped in Gulf of Penas, Guayaneco Archipelago and other islands. Yaghans inhabited a reduced a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a greenhouse climate state. Quaternary Period Within the Quaternary, which started about 2.6 million years before present, there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone. Penultimate Glacial Period The Penultimate Glacial Period (PGP) is the glacial period that occurred before the Last Glacial Period. It began about 194,000 years ago and ended 135,000 years ago, with the beginning of the Eemian interglacial. Last Glacial Period The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |