|
Aviation Act Of 1917
Aviation Act of 1917 was a United States military appropriations bill authorizing a temporary increase for the United States Army Signal Corps. The Act of Congress authorized provisions for airship or dirigible operations governed by the U.S. Army Signal Corps Aeronautical Division. The legislation provided United States President Woodrow Wilson emergency authority for the maintenance, manufacture, operation, purchase, and repair of airships and associated aerial machines. Sections of the Act In an attempt to meet the progressive necessities of World War I, House bill 5326 was penned as ten sections by the United States 65th Congressional session. :Sec. 1 – Temporary Increase of Army Signal Corps and Aviation Sections :Sec. 2 – Additional Commissioned Personnel Authorized ::Qualifications ::Appointments by U.S. President ::Appointments by U.S. President and Senate :Sec. 3 – Additional Enlisted Men by Enlistment or Draft ::Age limit for men drafted ::Chauffeur grades crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States. Founded in 1828, it was predominantly built by Martin Van Buren, who assembled a wide cadre of politicians in every state behind war hero Andrew Jackson, making it the world's oldest active political party.M. Philip Lucas, "Martin Van Buren as Party Leader and at Andrew Jackson's Right Hand." in ''A Companion to the Antebellum Presidents 1837–1861'' (2014): 107–129."The Democratic Party, founded in 1828, is the world's oldest political party" states Its main political rival has been the Republican Party since the 1850s. The party is a big tent, and though it is often described as liberal, it is less ideologically uniform than the Republican Party (with major individuals within it frequently holding widely different political views) due to the broader list of unique voting blocs that compose it. The historical predecessor of the Democratic Party is considered to be th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airship Hangar
Airship hangars (also known as airship sheds) are large specialized buildings that are used for sheltering airships during construction, maintenance and storage. Rigid airships always needed to be based in airship hangars because weathering was a serious risk. History Early hangars The first real airship hangar was built as Hangar “Y” at Chalais-Meudon near Paris in 1879 where the engineers Charles Renard and Arthur Constantin Krebs constructed their first airship “ La France”. Hangar “Y” is one of the few remaining airship hangars in Europe. The construction of the first operational rigid airship LZ1 by Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin started in 1899 in a floating hangar on Lake Constance at Manzell today part of Friedrichshafen. The floating hangar turned into the direction of the wind on its own and so it was easier to move the airship into the hangar exactly against the wind. For the same reason later rotating hangars were built at Biesdorf (today part of Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
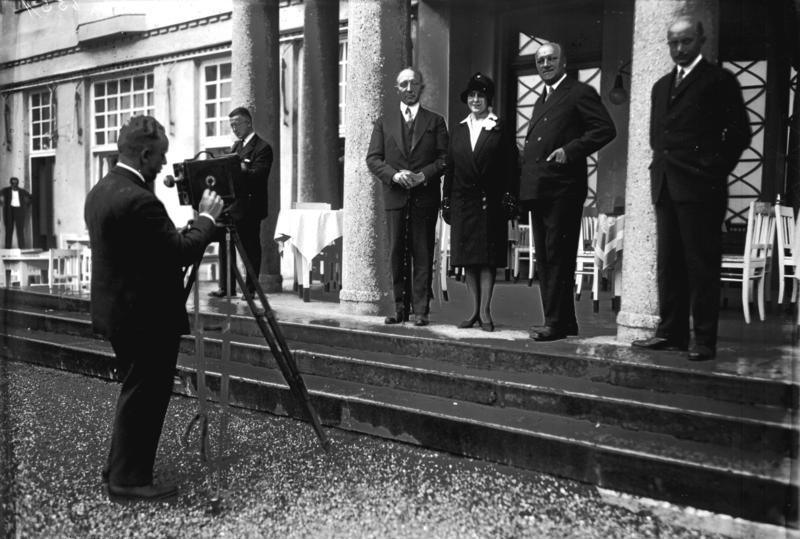
Grace Marguerite Hay Drummond-Hay
Grace Marguerite, Lady Hay Drummond-Hay (née Lethbridge, 12 September 1895 – 12 February 1946) was a British journalist, who was the first woman to travel around the world by air (in a zeppelin). Although she was not an aviator herself at first, she contributed to the glamour of aviation and general knowledge of it, by writing articles about her aerial adventures for US newspapers in the late 1920s and early 1930s. Early life Grace Lethbridge was the eldest daughter of Sidney Thomas Lethbridge and his wife Grace Emily (née Willis). Her father was the managing director of the Spratt's dog and animal food company. Her father's sister was dancer Alice Lethbridge. She was married in 1920 to Sir Robert Hay Drummond-Hay (1846–1925) at the age of 25, her husband being nearly fifty years older.Sir Robert Hay-Drummond-Hay ThePeera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-class Blimp
The E class of US Navy blimps comprised a single airship, built during World War I by Goodyear as one of a group of three small blimps offered to the US government. Two were purchased for the US Navy and one for the US Army. The Navy blimps were designated E-1, F-1, and the Army airship A-1. These airships had identical envelopes but different cars. The E-1 was delivered to Pensacola, Florida in December 1918. It was flown only at Pensacola serving as a trainer at the Airship School. A new envelope was provided in December 1920. E-1 was retired from service sometime in 1924. Operators ; *United States Navy The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ... Specifications See also References {{USN non-rigid airship classes 1910s United States military trainer aircr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of US Navy Airship Units (pre-WWII)
Unlike later blimp squadrons, which contained several airships, the large rigid airship units consisted of a single airship and, in the case of the USS ''Akron'' and USS ''Macon'', a small contingent of fixed-wing aircraft. 1910s 1919 A semi rigid airship, the O-1, is purchased from Italy October, The ZR-2 (R38) is placed under contract from Britain, where construction had been started on it as the ''R38.'' 1920s 1921 The first large US airship hangar is built at Lakehurst, New Jersey On the fourth test flight of R-38 severe control inputs at low altitude and high speed cause the structural failure of the airship with the loss of the majority of the crew. Sixteen of the men killed were USN training to fly the ship back to Cape May, NJ. The ZR-2 (R38) crashed before the US Navy could take delivery of the airship; therefore ZR-2 did not officially receive its US designation, though it was painted with its planned Navy designation. 1922 The first American-built rigid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirigible Pilot Badge
The Dirigible/Balloon Pilot Insignia was a military decoration of the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps that was issued to those service members who received training and qualification as dirigible pilots. The badge first appeared in Navy Uniform Regulations in 1922, during which time the Navy was experimenting with lighter-than-air craft, as opposed to conventional, fixed-wing aircraft.Evolution of Naval Wings , Naval History and Heritage Command, last accessed 17 January 2013Complete Guide to United States Marine Corps Medals, Badges and Insignia World War II to Present [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R38-class Airship
The ''R.38'' class (also known as the ''A'' class) of rigid airships was designed for Britain's Royal Navy during the final months of the First World War, intended for long-range patrol duties over the North Sea. Four similar airships were originally ordered by the Admiralty, but orders for three of these (''R.39'', ''R.40'' and ''R.41'') were cancelled after the armistice with Germany and ''R.38'', the lead ship of the class, was sold to the United States Navy in October 1919 before completion. On 24 August 1921, ''R.38'' (designated ZR-2 by the USN) was destroyed by a structural failure while in flight over the city of Hull. It crashed into the Humber Estuary, killing 44 out of the 49 crew aboard. At the time of its first flight it was the world's largest airship. Its destruction was the first of the great airship disasters, followed by the Italian-built US semi-rigid airship ''Roma'' in 1922 (34 dead), the French '' Dixmude'' in 1923 (52 dead), the USS ''Shenandoah'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balloon Pilot Badge
The Balloon Pilot Badge is a military badge of the United States Armed Forces which was issued during the First and Second World Wars. The badge was issued by both the United States Army and the U.S. Air Force, with the Navy equivalent known as the Dirigible Pilot Badge. Originally known as the Aeronaut Badge, the Balloon Pilot Badge was created in 1918 and awarded to pilots of military observation balloons. The badge consisted of a balloon centered on a standard Pilot's Badge and was issued in two degrees. The senior degree of the Aeronaut Badge was denoted by a star centered above the winged balloon. The Aeronaut Badge was awarded under the authority of the United States Army Air Service and the United States Army Air Corps until the mid-1930s. The badge was then redesignated the Balloon Pilot Badge and, during the Second World War (WWII), was issued by the Army Air Forces. Like its predecessor, the Balloon Pilot Badge was issued in junior and senior degrees. The Army Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observer Badge
The Observer Badge is a military badge of the United States armed forces dating from the First World War. The badge was issued to co-pilots, navigators, and flight support personnel (as air observer) who had received a variation in the training required for the standard Pilot's Badge. The Observer Badge survived through the Second World War and into the 1950s, at which time the concept of an Observer Badge was phased out in favor of the modern Aircrew Badge and Navigator-Observer Badges. In addition to wings for Naval Aviators and Naval Flight Officers, the United States Navy still maintains an "Observer Badge" which is issued to flight-qualified mission specialists, such as a select number of meteorologists and intelligence officers in both the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps. The U.S. Air Force awards its USAF Observer Badge, which is identical to the USAF Navigator Badge, to Air Force officers who have qualified as NASA Space Shuttle Mission Specialists, have flown an act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balloon Buster
Balloon busters were military pilots known for destroying enemy observation balloons. These pilots were noted for their fearlessness, as balloons were stationary targets able to receive heavy defenses, from the ground and the air. Seventy-seven flying aces in World War I were each credited with destroying five or more balloons, and thus were balloon aces. The crucial role of observation balloons An observation balloon was both a vulnerable and a valuable target: the balloon was moored in a stationary position and was lifted by flammable hydrogen gas, whose use was necessitated by the scarcity of helium reserves among European powers. The artillery observer, suspended in the wicker basket beneath, typically had a wireless transmitter, binoculars and/or a long-range camera. His job was to observe actions on the front-line and behind it, to spot enemy troop movements or unusual activity of any sort, and to call down artillery fire onto any worthwhile targets. Balloon observers we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Defense Act Of 1916
The National Defense Act of 1916, , was a United States federal law that updated the Militia Act of 1903, which related to the organization of the military, particularly the National Guard. The principal change of the act was to supersede provisions as to exemptions. The 1916 act included an expansion of the United States Army, Army and the United States National Guard, National Guard, the creation of an Officers' and an Enlisted Reserve Corps, and the creation of a Reserve Officers' Training Corps. The President of the United States, President was also given expanded authority to federalize the National Guard of the United States, National Guard, with changes to the duration and the circumstances under which he could call it up. The United States Army, Army began the creation of an United States Army Aviation Branch, Aviation arm, and the federal government took steps to ensure the immediate availability of wartime weapons and equipment by contracting in advance for producti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Service Act
The Aviation Service Act is a U.S. law passed in 1914. It created within the Signal Corps an Aviation Section to replace the Aeronautical Division. It directed the Aviation Section to operate and supervise "''all military .S. Armyaircraft, including balloons and aeroplanes, all appliances pertaining to said craft, and signaling apparatus of any kind when installed on said craft.''" The section would also train "''officers and enlisted men in matters pertaining to military aviation''," and thus embraced all facets of the Army's air organization and operation. The old Aeronautical Division continued to exist, but operated as the Washington office of the new section. See also :1914 in aviation :Aviation Act of 1917 Aviation Act of 1917 was a United States military appropriations bill authorizing a temporary increase for the United States Army Signal Corps. The Act of Congress authorized provisions for airship or dirigible operations governed by the U.S. Army ... References { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |