|
Attribute Clash
Attribute may refer to: * Attribute (philosophy), an extrinsic property of an object * Attribute (research), a characteristic of an object * Grammatical modifier, in natural languages * Attribute (computing), a specification that defines a property of an object, element, or file * Attribute (role-playing games), a type of statistic for a fictional character See also * Attribute clash, a display artefact on some home computers * Attribute hierarchy method, a cognitively based psychometric procedure * Attribution (other) Attribution may refer to: * Attribution (copyright), concept in copyright law requiring an author to be credited * Attribution (journalism), the identification of the source of reported information * Attribution (law), legal doctrines by which li ... * Property (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attribute (philosophy)
In logic and philosophy (especially metaphysics), a property is a characteristic of an object; a red object is said to have the property of redness. The property may be considered a form of object in its own right, able to possess other properties. A property, however, differs from individual objects in that it may be instantiated, and often in more than one object. It differs from the logical/mathematical concept of class by not having any concept of extensionality, and from the philosophical concept of class in that a property is considered to be distinct from the objects which possess it. Understanding how different individual entities (or particulars) can in some sense have some of the same properties is the basis of the problem of universals. Terms and usage A property is any member of a class of entities that are capable of being attributed to objects. Terms similar to ''property'' include ''predicable'', ''attribute'', ''quality'', ''feature'', ''characteristic'', ''type'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attribute (research)
In science and research, an attribute is a quality of an object (person, thing, etc.).Earl R. Babbie, ''The Practice of Social Research'', 12th edition, Wadsworth Publishing, 2009, , p. 14-18 Attributes are closely related to variables. A variable is a logical set of attributes. Variables can "vary" – for example, be high or low. How high, or how low, is determined by the value of the attribute (and in fact, an attribute could be just the word "low" or "high"). ''(For example see: Binary option)'' While an attribute is often intuitive, the variable is the operationalized way in which the attribute is represented for further data processing. In data processing data are often represented by a combination of ''items'' (objects organized in rows), and multiple variables (organized in columns). Values of each variable statistically "vary" (or are distributed) across the variable's domain. A domain is a set of all possible values that a variable is allowed to have. The values are orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Modifier
In linguistics, a modifier is an optional element in phrase structure or clause structure which ''modifies'' the meaning of another element in the structure. For instance, the adjective "red" acts as a modifier in the noun phrase "red ball", providing extra details about which particular ball is being referred to. Similarly, the adverb "quickly" acts as a modifier in the verb phrase "run quickly". Modification can be considered a high-level domain of the functions of language, on par with predication and reference. Premodifiers and postmodifiers Modifiers may come either before or after the modified element (the '' head''), depending on the type of modifier and the rules of syntax for the language in question. A modifier placed before the head is called a premodifier; one placed after the head is called a postmodifier. For example, in ''land mines'', the word ''land'' is a premodifier of ''mines'', whereas in the phrase ''mines in wartime'', the phrase ''in wartime'' is a postmodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attribute (computing)
In computing, an attribute is a specification that defines a property of an object, element, or file. It may also refer to or set the specific value for a given instance of such. For clarity, attributes should more correctly be considered metadata. An attribute is frequently and generally a property of a property. However, in actual usage, the term attribute can and is often treated as equivalent to a property depending on the technology being discussed. An attribute of an object usually consists of a name and a value; of an element, a type or class name; of a file, a name and extension. * Each named attribute has an associated set of rules called operations: one doesn't sum characters or manipulate and process an integer array as an image object—one doesn't process text as type floating point (decimal numbers). * It follows that an object definition can be extended by imposing data typing: a representation format, a default value, and legal operations (rules) and restrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
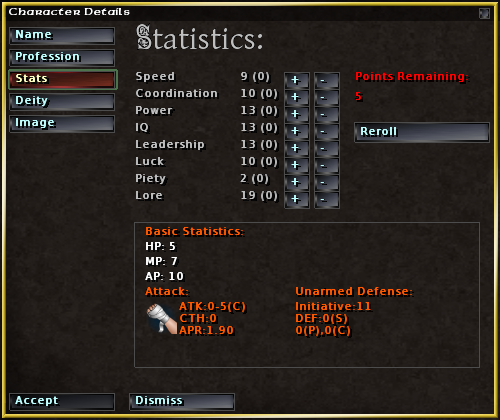
Attribute (role-playing Games)
An attribute is a piece of data (a "statistic (role-playing games), statistic") that describes to what extent a fictional character in a role-playing game possesses a specific natural, in-born Property (philosophy), characteristic common to all characters in the game. That piece of data is usually an abstract number or, in some cases, a dice pool, set of dice. Some games use different terms to refer to an attribute, such as statistic, (primary) characteristic or ability. A number of role-playing games like ''Fate (role-playing game system), Fate'' do not use attributes at all. The nature of attributes There is no uniform consensus on what ability scores are, even if many role-playing games have them, but games that use them have a common theme. According to the BBC Cult TV website "''All characters have Attributes — basic physical and mental abilities.''" and in the ''Pathfinder Roleplaying Game'' "''Each character has six ability scores that represent his character's most b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attribute Clash
Attribute may refer to: * Attribute (philosophy), an extrinsic property of an object * Attribute (research), a characteristic of an object * Grammatical modifier, in natural languages * Attribute (computing), a specification that defines a property of an object, element, or file * Attribute (role-playing games), a type of statistic for a fictional character See also * Attribute clash, a display artefact on some home computers * Attribute hierarchy method, a cognitively based psychometric procedure * Attribution (other) Attribution may refer to: * Attribution (copyright), concept in copyright law requiring an author to be credited * Attribution (journalism), the identification of the source of reported information * Attribution (law), legal doctrines by which li ... * Property (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attribute Hierarchy Method
The attribute hierarchy method (AHM), is a cognitively based psychometric procedure developed by Jacqueline Leighton, Mark Gierl, and Steve Hunka at the Centre for Research in Applied Measurement and Evaluation (CRAME) at the University of Alberta. The AHM is one form of cognitive diagnostic assessment that aims to integrate cognitive psychology with educational measurement for the purposes of enhancing instruction and student learning.Leighton, J. P., Gierl, M. J., & Hunka, S. M. (2004). The attribute hierarchy model for cognitive assessment: A variation on Tatsuoka's rule-space approach. Journal of Educational Measurement, 41, 205–237. A cognitive diagnostic assessment (CDA), is designed to measure specific knowledge states and cognitive processing skills in a given domain. The results of a CDA yield a profile of scores with detailed information about a student’s cognitive strengths and weaknesses. This cognitive diagnostic feedback has the potential to guide instructors, paren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attribution (other)
Attribution may refer to: * Attribution (copyright), concept in copyright law requiring an author to be credited * Attribution (journalism), the identification of the source of reported information * Attribution (law), legal doctrines by which liability is extended to a defendant who did not actually commit the criminal act * Attribution (marketing), concept in marketing of assigning a value to a marketing activity based on desired outcome * Attribution (psychology), concept in psychology whereby people attribute traits and causes to things they observe * Performance attribution Performance attribution, or investment performance attribution is a set of techniques that performance analysts use to explain why a portfolio's performance differed from the benchmark. This difference between the portfolio return and the benchmar ..., technique in quantitative finance for explaining the active performance of a portfolio See also * Attribute (other) * Credits {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |