|
Attapady Kurumba Language
Attapady Kurumba, also called Pal Kurumba, is an unclassified Southern Dravidian language spoken by a Scheduled tribe of India. It shows only approximately 50% lexical similarity with the other South Dravidian languages named Kurumba, but up to 82% with Muduga and 52% with Kannada Kurumba; Attapady Kurumba, Muduga Muduga, also called Mudugar, is an unclassified Southern Dravidian language of India influenced by Kannada and Tulu. It is mainly spoken by Muduga tribes in the Attappady valley south of the Nilgiris in Palakkad district, Kerala. It is mutually i ..., and Irula each use their mother tongue when speaking to each other. Thudukki variety of Attapady Kurumba is reportedly most pure. References Dravidian languages {{dr-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
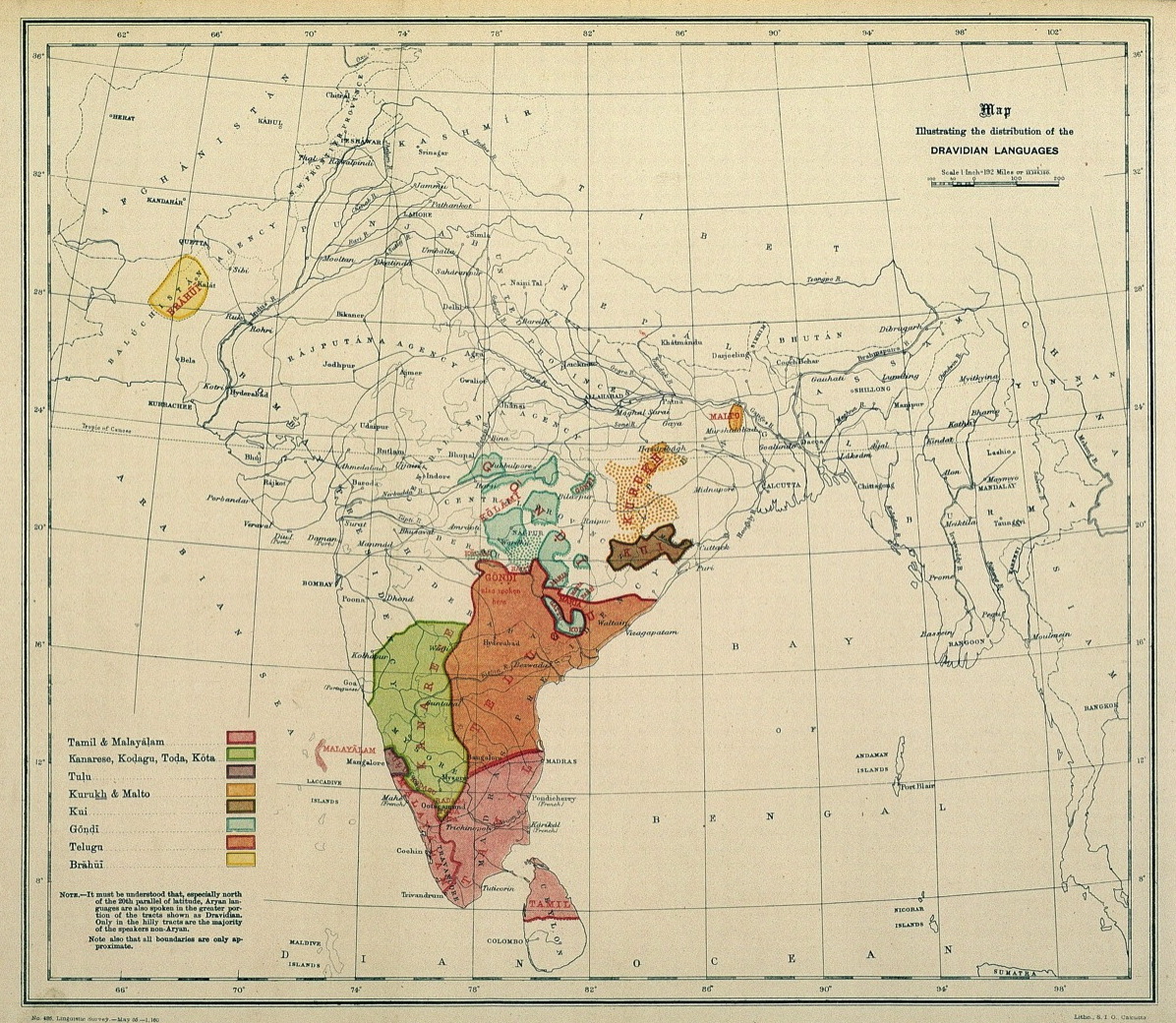
Southern Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages (or sometimes Dravidic) are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, mainly in southern India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan. Since the colonial era, there have been small but significant immigrant communities in Mauritius, Myanmar, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, United Kingdom, Australia, France, Canada, Germany, South Africa, and the United States. The Dravidian languages are first attested in the 2nd century BCE, as Tamil-Brahmi script, inscribed on the cave walls in the Madurai and Tirunelveli districts of Tamil Nadu. The Dravidian languages with the most speakers are (in descending order of number of speakers) Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam, all of which have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu and Kodava. There are also a number of Dravidian-speaking scheduled tribes, such as the Kurukh in Eastern India and Gondi in Central India. Outside of India, Brahui is mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Tribe
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India. The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designated in one or other of the categories. For much of the period of British rule in the Indian subcontinent, they were known as the Depressed Classes. In modern literature, the ''Scheduled Castes'' are sometimes referred to as Dalit, meaning "broken" or "dispersed", having been popularised by B. R. Ambedkar (1891–1956), a Dalit himself, an economist, reformer, chairman of the Constituent Assembly of India, and Dalit leader during the independence struggle. Ambedkar preferred the term Dalit to Gandhi's term, Harijan, meaning "person of Hari/Vishnu" (or Man of God). In September 2018, the government "issued an advisory to all private satellite channels asking them to 'refrain' from using the nomenclature 'Dalit'", though "rights groups a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Similarity
In linguistics, lexical similarity is a measure of the degree to which the word sets of two given languages are similar. A lexical similarity of 1 (or 100%) would mean a total overlap between vocabularies, whereas 0 means there are no common words. There are different ways to define the lexical similarity and the results vary accordingly. For example, '' Ethnologues method of calculation consists in comparing a regionally standardized wordlist (comparable to the Swadesh list) and counting those forms that show similarity in both form and meaning. Using such a method, English was evaluated to have a lexical similarity of 60% with German and 27% with French. Lexical similarity can be used to evaluate the degree of genetic relationship between two languages. Percentages higher than 85% usually indicate that the two languages being compared are likely to be related dialects. The lexical similarity is only one indication of the mutual intelligibility of the two languages, since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurumba Language
Kurumba, is a Southern Dravidian language of the Tamil–Kannada subgroup spoken by the Kurumba tribe. The Ethnologue classifies it as a separate language under Tamil-Kannada group. Geographical distribution Kurumba speakers are situated in Pudukkottai, Theni, Dindigul, Coimbatore, Dharmapuri, Krishnagiri, Vellore, and Salem districts of Tamil Nadu, in addition to areas of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to t .... References Dravidian languages Languages of Karnataka Languages of Kerala {{Dr-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muduga Language
Muduga, also called Mudugar, is an unclassified Southern Dravidian language of India influenced by Kannada and Tulu Tulu may refer to: People * Derartu Tulu (born 1972), Ethiopian long-distance runner *Walid Yacoubou (born 1997), Togolese footballer nicknamed "Tulu" India *Tulu calendar, traditional solar calendar generally used in the regions of southwest Ka .... It is mainly spoken by Muduga tribes in the Attappady valley south of the Nilgiris in Palakkad district, Kerala. It is mutually intelligible with Attapady Kurumba. References Dravidian languages {{dr-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irula Language
Irula is a Dravidian language spoken by the Irulas who inhabit the area of the Nilgiri mountains, in the states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Karnataka, India. It is closely related to Tamil. It is written in the Tamil script. Origins The language was first described and classified by indologist Kamil Zvelebil, who in 1955 showed that the Irula language is an independent Southern Dravidian language that is akin to Tamil, particularly Old Tamil, with some Kannada Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ...-like features. Before that, it was traditionally denied or put to doubt, and Irula was described as a crude or corrupt mixture of Tamil and Kannada. According to a tentative hypothesis by Kamil Zvelebil, a pre-Dravidian Melanid population that forms the bulk of the Iru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |