|
Atmosphere Of Venus
The atmosphere of Venus is the very dense layer of gases surrounding the planet Venus. Venus's atmosphere is composed of 96.5% carbon dioxide and 3.5% nitrogen, with other chemical compounds present only in trace amounts. It is much denser and hotter than atmosphere of Earth, that of Earth; the temperature at the surface is 740 Kelvin, K (467 °C, 872 °F), and the pressure is , roughly the pressure found under water on Earth. The atmosphere of Venus supports decks of opaque clouds of sulfuric acid that cover the entire planet, preventing optics, optical Earth-based and orbital observation of the surface. Information about surface topography has been obtained exclusively by radar imaging. Aside from the very surface layers, the atmosphere is in a state of vigorous circulation. The upper layer of troposphere exhibits a phenomenon of Atmospheric super-rotation, super-rotation, in which the atmosphere circles the planet in just four Earth days, much faster than the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar Fraction
In chemistry, the Mole (unit), mole fraction or molar fraction, also called mole proportion or molar proportion, is a quantity (science), quantity defined as the ratio between the amount of substance, amount of a constituent substance, ''ni'' (expressed in unit of measurement, unit of mole (unit), moles, symbol mol), and the total amount of all constituents in a mixture, ''n''tot (also expressed in moles): :x_i = \frac It is mathematical symbol, denoted ''xi'' (lowercase Latin alphabet, Roman letter ''x''), sometimes (lowercase Greek alphabet, Greek letter Chi (letter), chi). (For mixtures of gases, the letter ''y'' is recommended.) It is a dimensionless quantity with dimension (physics), dimension of \mathsf/\mathsf and dimensionless unit of moles per mole (mol/mol or molmol−1) or simply 1; metric prefixes may also be used (e.g., nmol/mol for nano-, 10−9). When expressed in percent, it is known as the mole percent or molar percentage (unit symbol %, sometimes "mol%", equival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By definition, the Celsius scale (symbol °C) and the Kelvin scale have the exact same magnitude; that is, a rise of 1 K is equal to a rise of 1 °C and vice versa, and any temperature in degrees Celsius can be converted to kelvin by adding 273.15. The 19th century British scientist Lord Kelvin first developed and proposed the scale. It was often called the "absolute Celsius" scale in the early 20th century. The kelvin was formally added to the International System of Units in 1954, defining 273.16 K to be the triple point of water. The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Rankine scales were redefined in terms of the Kelvin scale using this definition. The 2019 revision of the SI now defines the kelvin in terms of energy by setting the Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically perceived by humans as warmth) and ultraviolet (which can have physiological effects such as sunburn) lights. However, according to the American Meteorological Society, there are "conflicting conventions as to whether all three [...] are referred to as light, or whether that term should only be applied to the visible portion of the spectrum." Upon reaching the Earth, sunlight is light scattering by particles, scattered and attenuation, filtered through the atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon. When direct solar radiation is not blocked by clouds, it is experienced as sunshine, a combination of bright light and radiant heat (atmospheric). When cloud cover, blocked by clouds or dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionization
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive Electric charge, charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule is called an ion. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with subatomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules, electrons, positrons, protons, antiprotons, and ions, or through the interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected. Uses Everyday examples of gas ionization occur within a fluorescent lamp or other electrical discharge lamps. It is also used in radiation detectors such as the Geiger- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermosphere
The thermosphere is the layer in the Earth's atmosphere directly above the mesosphere and below the exosphere. Within this layer of the atmosphere, ultraviolet radiation causes photoionization/photodissociation of molecules, creating ions; the bulk of the ionosphere thus exists within the thermosphere. Taking its name from the Greek θερμός (pronounced ''thermos'') meaning heat, the thermosphere begins at about 80 km (50 mi) above sea level. At these high altitudes, the residual atmospheric gases sort into strata according to molecular mass (see turbosphere). Thermospheric temperatures increase with altitude due to absorption of highly energetic solar radiation. Temperatures are highly dependent on solar activity, and can rise to or more. Radiation causes the atmospheric particles in this layer to become electrically charged, enabling radio waves to be refracted and thus be received beyond the horizon. In the exosphere, beginning at about 600 km (375 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesosphere
The mesosphere (; ) is the third layer of the atmosphere, directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere, temperature decreases as altitude increases. This characteristic is used to define limits: it begins at the top of the stratosphere (sometimes called the stratopause), and ends at the mesopause, which is the coldest part of Earth's atmosphere, with temperatures below . The exact upper and lower boundaries of the mesosphere vary with latitude and with season (higher in winter and at the tropics, lower in summer and at the poles), but the lower boundary is usually located at altitudes from above sea level, and the upper boundary (the mesopause) is usually from . The stratosphere and mesosphere are sometimes collectively referred to as the "middle atmosphere", which spans altitudes approximately between above Earth's surface. The mesopause, at an altitude of , separates the mesosphere from the thermosphere—the second-outermost la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
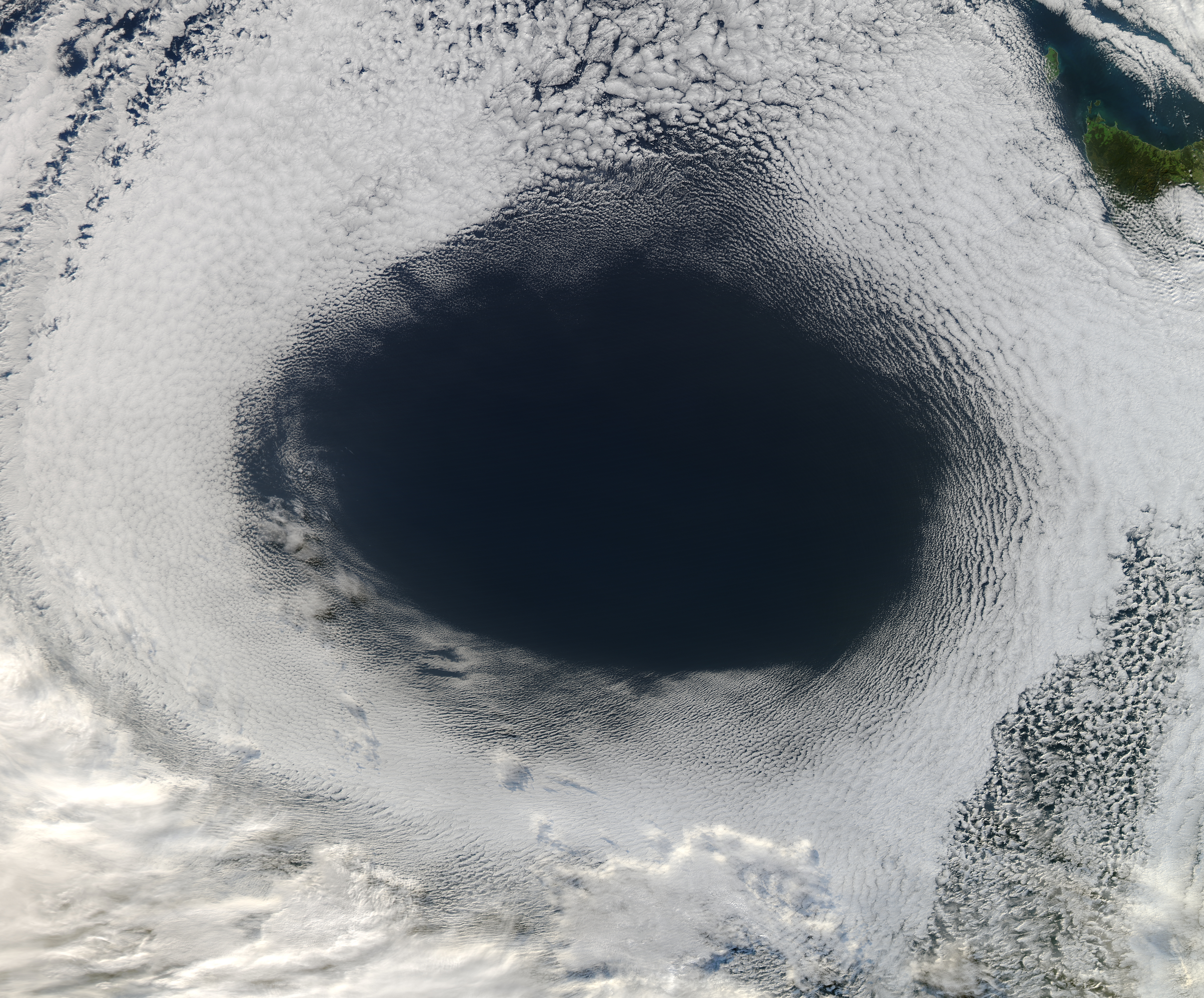
Vortex
In fluid dynamics, a vortex (: vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil. Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis. In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex carries s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclonic
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation. The strongest high-pressure areas result from masses of cold air which spread out from polar regions into cool neighboring regions. These highs weaken once they extend out over warmer bodies of water. Weaker—but more frequently occurring—are high-pressure areas caused by atmospheric subsidence: Air becomes cool enough to precipitate out its water vapor, and large masses of cooler, drier air descend from above. Within high-pressure areas, winds flow from where the pressure is highest, at the center of the area, towards the periphery where the pressure is lower. However, the direction is not straight from the center outwards, but curved du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidereal Day
Sidereal time ("sidereal" pronounced ) is a system of timekeeping used especially by astronomers. Using sidereal time and the celestial coordinate system, it is easy to locate the positions of celestial objects in the night sky. Sidereal time is a "time scale that is based on Earth's rate of rotation measured relative to the fixed stars". A sidereal day (also known as the sidereal rotation period) represents the time for one rotation about the planet axis relative to the stars. Viewed from the same location, a star seen at one position in the sky will be seen at the same position on another night at the same time of day (or night), if the day is defined as a sidereal day. This is similar to how the time kept by a sundial (Solar time) can be used to find the location of the Sun. Just as the Sun and Moon appear to rise in the east and set in the west due to the rotation of Earth, so do the stars. Both solar time and sidereal time make use of the regularity of Earth's rot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Super-rotation
Atmospheric super-rotation is a phenomenon where a planet's atmosphere rotates faster than the planet itself. This behavior is observed in the atmospheres of Venus, Titan, Jupiter, and Saturn. Venus exhibits the most extreme super-rotation, with its atmosphere circling the planet in four Earth days, much faster than the planet's own rotation of 243 Earth days. The phenomenon of atmospheric super-rotation can influence a planet's climate and atmospheric dynamics. Dynamics of super-rotation In understanding super-rotation, the role of atmospheric waves and instabilities is crucial. These dynamics, including Rossby waves and Kelvin waves, are integral in transferring momentum and energy within atmospheres, contributing to the maintenance of super-rotation. For instance, on Venus, the interaction of thermal tides with planetary-scale Rossby waves is thought to contribute significantly to its rapid super-rotational winds. Similarly, in Earth's atmosphere, Kelvin waves generate eastwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and ''sphere, sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Imaging
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), direction (geometry), direction (azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, Marine radar, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map Weather radar, weather formations, and terrain-following radar, terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym and initialism, acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an wikt:anacronym, anacronym, a common noun, Acronym#All-caps style, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio spectrum, radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna (radio), antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a radio receiver, receiver an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |