|
Ataxic Respiration
Ataxic respiration is an abnormal pattern of breathing characterized by complete irregularity of breathing, with irregular pauses and increasing periods of apnea. As the breathing pattern deteriorates, it merges with agonal respiration. Cause It is caused by damage to the medulla oblongata due to strokes or trauma. It generally indicates a poor prognosis, and usually progresses to complete apnea. The term is sometimes used interchangeably with Biot's respiration. Treatment It is believed that intensive care technology may be masking the presence of Biot’s Respirations. This could be related to the fact that treatment for Biot’s Respirations typically results with intubation immediately upon diagnosis, with mechanical ventilation Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apnea
Apnea, BrE: apnoea, is the temporal cessation of breathing. During apnea, there is no movement of the muscles of inhalation, and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged. Depending on how blocked the airways are ( patency), there may or may not be a flow of gas between the lungs and the environment, but if there's sufficient flow, gas exchange within the lungs and cellular respiration wouldn't be severely affected. Voluntarily doing this is called holding one's breath. Apnea may first be diagnosed in childhood, and it is recommended to consult an ENT specialist, allergist or sleep physician to discuss symptoms when noticed; malformation and/or malfunctioning of the upper airways may be observed by an orthodontist. Cause Apnea can be involuntary—for example, drug-induced (such as by opiate toxicity), mechanically / physiologically induced (for example, by strangulation or choking), or a consequence of neurological disease or trauma. During sleep, people with sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonal Respiration
Agonal respiration, gasping respiration or agonal breathing is a distinct abnormal pattern of breathing and brainstem reflex characterized by gasping, labored breathing, accompanied by strange vocalizations and myoclonus. Possible causes include cerebral ischemia, extreme hypoxia (inadequate oxygen supply to tissue), or even anoxia (total depletion of oxygen). Agonal breathing is an extremely serious medical sign requiring immediate medical attention, as the condition generally progresses to complete apnea and heralds death. The duration of agonal respiration can be as brief as two breaths or last up to several hours. The term is sometimes (inaccurately) used to refer to labored, gasping breathing patterns accompanying organ failure (e.g. liver failure and kidney failure), SIRS, septic shock, and metabolic acidosis (see Kussmaul breathing, or in general any labored breathing, including Biot's respirations and ataxic respirations). Correct usage would restrict the term t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is retained for terms that relate to the medulla oblongata, particularly in reference to medical conditions. The word bulbar can refer to the nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
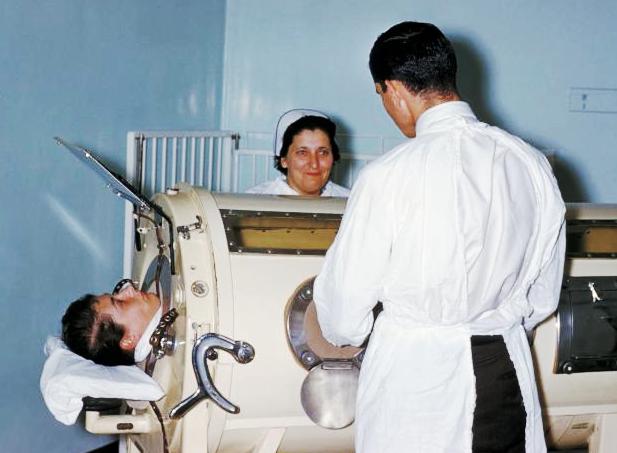
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |