 |
Asymptote (vector Graphics Language)
Asymptote is a descriptive vector graphics language — developed by Andy Hammerlindl, John C. Bowman (University of Alberta), and Tom Prince — which provides a natural coordinate-based framework for technical drawing. Asymptote runs on all major platforms (Unix, Mac OS, Microsoft Windows). It is free software, available under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is a free-software license published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). The license allows developers and companies to use and integrate a software component released under the LGPL into their own ... (LGPL). Syntax and notable features Asymptote typesets labels and equations with LaTeX, producing high-quality PostScript, Portable Document Format, PDF, Scalable Vector Graphics, SVG, or 3D PRC (file format), PRC output. It is inspired by MetaPost, but has a C++-like syntax. It provides a language for typesetting mathematical figures, just as TeX/LaTeX prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
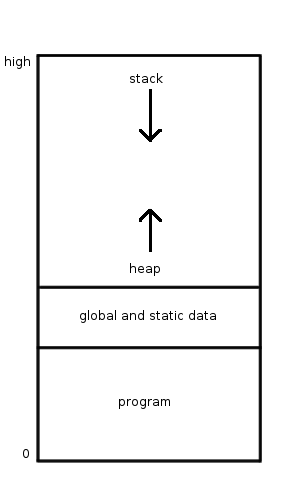 |
Imperative Programming
In computer science, imperative programming is a programming paradigm of software that uses statements that change a program's state. In much the same way that the imperative mood in natural languages expresses commands, an imperative program consists of commands for the computer to perform. Imperative programming focuses on describing ''how'' a program operates step by step, rather than on high-level descriptions of its expected results. The term is often used in contrast to declarative programming, which focuses on ''what'' the program should accomplish without specifying all the details of ''how'' the program should achieve the result. Imperative and procedural programming Procedural programming is a type of imperative programming in which the program is built from one or more procedures (also termed subroutines or functions). The terms are often used as synonyms, but the use of procedures has a dramatic effect on how imperative programs appear and how they are constructed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Simplex Method
In mathematical optimization, Dantzig's simplex algorithm (or simplex method) is a popular algorithm for linear programming. The name of the algorithm is derived from the concept of a simplex and was suggested by T. S. Motzkin. Simplices are not actually used in the method, but one interpretation of it is that it operates on simplicial '' cones'', and these become proper simplices with an additional constraint. The simplicial cones in question are the corners (i.e., the neighborhoods of the vertices) of a geometric object called a polytope. The shape of this polytope is defined by the constraints applied to the objective function. History George Dantzig worked on planning methods for the US Army Air Force during World War II using a desk calculator. During 1946 his colleague challenged him to mechanize the planning process to distract him from taking another job. Dantzig formulated the problem as linear inequalities inspired by the work of Wassily Leontief, however, at that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Free Plotting Software
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, having the ability to do something, without having to obey anyone/anything * Freethought, a position that beliefs should be formed only on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism * Emancipate, to procure political rights, as for a disenfranchised group * Free will, control exercised by rational agents over their actions and decisions * Free of charge, also known as gratis. See Gratis vs libre. Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free format, a file format which can be used without restrictions * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment * Freeware, a broader class of software available at no cost Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Free Graphics Software
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, having the ability to do something, without having to obey anyone/anything * Freethought, a position that beliefs should be formed only on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism * Emancipate, to procure political rights, as for a disenfranchised group * Free will, control exercised by rational agents over their actions and decisions * Free of charge, also known as gratis. See Gratis vs libre. Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free format, a file format which can be used without restrictions * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment * Freeware, a broader class of software available at no cost Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media personal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
PyX (vector Graphics Language)
PyX is a Python package for the creation of PostScript, PDF, and static SVG files. It combines an abstraction of the PostScript drawing model with a TeX/LaTeX interface. Complex tasks like 2d and 3d plots in publication-ready quality are built out of these primitives.https://pyx-project.org/ Its goals are similar to those of other metalanguages for PDF drawing, such as TikZ or Asymptote. PyX is licensed under the GNU GPL version 2. It was originally the graphics library for Pyxplot. Although Pyxplot no longer depends directly on Pyx, it continues to incorporate substantial pieces of the PyX codebase. See also * GeoGebra – free Dynamic Mathematics program with Asymptote export * PSTricks * TikZ * Asymptote (vector graphics language) Asymptote is a descriptive vector graphics language — developed by Andy Hammerlindl, John C. Bowman (University of Alberta), and Tom Prince — which provides a natural coordinate-based framework for technical drawing. Asymptote runs on all m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
TikZ
PGF/Ti''k''Z is a pair of languages for producing vector graphics (e.g., technical illustrations and drawings) from a geometric/algebraic description, with standard features including the drawing of points, lines, arrows, paths, circles, ellipses and polygons. PGF is a lower-level language, while Ti''k''Z is a set of higher-level macros that use PGF. The top-level PGF and Ti''k''Z commands are invoked as TeX macros, but in contrast with PSTricks, the PGF/Ti''k''Z graphics themselves are described in a language that resembles MetaPost. Till Tantau is the designer of the PGF and Ti''k''Z languages. He is also the main developer of the only known interpreter for PGF and Ti''k''Z, which is written in TeX. PGF is an acronym for "Portable Graphics Format". Ti''k''Z was introduced in version 0.95 of PGF, and it is a recursive acronym for "Ti''k''Z ist ''kein'' Zeichenprogramm" (German for "Ti''k''Z is ''not'' a drawing program"). Overview The PGF/Ti''k''Z interpreter can be used from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
GeoGebra
GeoGebra (a portmanteau of ''geometry'' and ''algebra'') is an interactive geometry, algebra, statistics and calculus application, intended for learning and teaching mathematics and science from primary school to university level. GeoGebra is available on multiple platforms, with apps for desktops (Windows, macOS and Linux), tablets (Android, iPad and Windows) and web. History GeoGebra's creator, Markus Hohenwarter, started the project in 2001 as part of his master's thesis at the University of Salzburg. After a successful Kickstarter campaign, GeoGebra expanded its offering to include an iPad, an Android and a Windows Store app version. 2013 GeoGebra incorporated Bernard Parisse's Xcas into its CAS view. The project is now freeware (with open-source portions) and multi-lingual, and Hohenwarter continues to lead its development at the University of Linz. GeoGebra includes both commercial and not-for-profit entities that work together from the head office in Linz, Austria, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Asymptote Heaviside Function
In analytic geometry, an asymptote () of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as one or both of the ''x'' or ''y'' coordinates tends to infinity. In projective geometry and related contexts, an asymptote of a curve is a line which is tangent to the curve at a point at infinity. The word asymptote is derived from the Greek ἀσύμπτωτος (''asumptōtos'') which means "not falling together", from ἀ priv. + σύν "together" + πτωτ-ός "fallen". The term was introduced by Apollonius of Perga in his work on conic sections, but in contrast to its modern meaning, he used it to mean any line that does not intersect the given curve. There are three kinds of asymptotes: ''horizontal'', ''vertical'' and ''oblique''. For curves given by the graph of a function , horizontal asymptotes are horizontal lines that the graph of the function approaches as ''x'' tends to Vertical asymptotes are vertical lines near which the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Heaviside Function
The Heaviside step function, or the unit step function, usually denoted by or (but sometimes , or ), is a step function, named after Oliver Heaviside (1850–1925), the value of which is zero for negative arguments and one for positive arguments. It is an example of the general class of step functions, all of which can be represented as linear combinations of translations of this one. The function was originally developed in operational calculus for the solution of differential equations, where it represents a signal that switches on at a specified time and stays switched on indefinitely. Oliver Heaviside, who developed the operational calculus as a tool in the analysis of telegraphic communications, represented the function as . The Heaviside function may be defined as: * a piecewise function: H(x) := \begin 1, & x > 0 \\ 0, & x \le 0 \end * using the Iverson bracket notation: H(x) := 0">>0/math> * an indicator function: H(x) := \mathbf_=\mathbf 1_(x) * the derivative of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Yacc
Yacc (Yet Another Compiler-Compiler) is a computer program for the Unix operating system developed by Stephen C. Johnson. It is a Look Ahead Left-to-Right Rightmost Derivation (LALR) parser generator, generating a LALR parser (the part of a compiler that tries to make syntactic sense of the source code) based on a formal grammar, written in a notation similar to Backus–Naur Form (BNF). Yacc is supplied as a standard utility on BSD and AT&T Unix. GNU-based Linux distributions include Bison, a forward-compatible Yacc replacement. History In the early 1970s, Stephen C. Johnson, a computer scientist at Bell Labs / AT&T, developed Yacc because he wanted to insert an exclusive or operator into a B language compiler (developed using McIlroy's TMG compiler-compiler), but it turned out to be a hard task. As a result, he was directed by his colleague at Bell Labs Al Aho to Donald Knuth's work on LR parsing, which served as the basis for Yacc. Yacc was influenced by and received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |